1. discuss the contributions of early scie
... this family are phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Oxygen Family has 6 valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. Halogen Fami ...
... this family are phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Oxygen Family has 6 valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. Halogen Fami ...
Atoms & Elements
... Properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids Metals • are shiny and ductile. • are good conductors of heat and electricity. Nonmetals • are dull, brittle, and poor conductors. • are good insulators. Metalloids • are better conductors than nonmetals, but not as good as metals. • are used as semic ...
... Properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids Metals • are shiny and ductile. • are good conductors of heat and electricity. Nonmetals • are dull, brittle, and poor conductors. • are good insulators. Metalloids • are better conductors than nonmetals, but not as good as metals. • are used as semic ...
The placement of an element on the periodic table gives clues about
... The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. It provides a powerful tool for studying the elements and how they combine. There are over 100 known elements, so it is necessary to use a systematic method to organize them. The periodic table indicates each element's atomic symbol, atom ...
... The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. It provides a powerful tool for studying the elements and how they combine. There are over 100 known elements, so it is necessary to use a systematic method to organize them. The periodic table indicates each element's atomic symbol, atom ...
Review Packet - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... The scientist who observed a pattern of properties that repeated every eight elements was ...
... The scientist who observed a pattern of properties that repeated every eight elements was ...
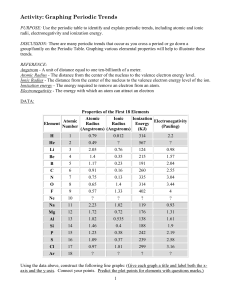
LSHS Graphing Periodic Trends Lab
... atom and [ increasing, decreasing ] the atomic radii. Because of this increase in electromagnetic, strong force atoms tend to [ gain, lose] electrons as you go across the periodic table. 9. Going down a metallic family: The number of [ p+ N e- ] energy levels increases by one, making the atomic radi ...
... atom and [ increasing, decreasing ] the atomic radii. Because of this increase in electromagnetic, strong force atoms tend to [ gain, lose] electrons as you go across the periodic table. 9. Going down a metallic family: The number of [ p+ N e- ] energy levels increases by one, making the atomic radi ...
Unit 3.2 Periodic Table Test
... An electron has the same mass as a proton. An electron has much more mass than a neutron. An electron has about the same mass as a neutron. An electron has much less mass than a proton. An electron has much less mass than a neutron. A proton has more mass than an electron. A proton has less mass tha ...
... An electron has the same mass as a proton. An electron has much more mass than a neutron. An electron has about the same mass as a neutron. An electron has much less mass than a proton. An electron has much less mass than a neutron. A proton has more mass than an electron. A proton has less mass tha ...
1 February 04, 2016
... 1. Groups - the vertical columns on the periodic table - also called chemical families - new IUPAC labelling/numbering system: Groups 1 - 18 (from left to right across the table) - old labelling system: Roman numerals followed by the letter A or B - includes elements with similar chemical properties ...
... 1. Groups - the vertical columns on the periodic table - also called chemical families - new IUPAC labelling/numbering system: Groups 1 - 18 (from left to right across the table) - old labelling system: Roman numerals followed by the letter A or B - includes elements with similar chemical properties ...
File - Unit #1-0
... 18. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Elements? 19. Elements within a group have a similar number of 20. Elements across a series have the same number of 21. A colored ion generally indicates a 22. As you go down a group, the elements generally become ( more / less) metallic. 23. The ...
... 18. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Elements? 19. Elements within a group have a similar number of 20. Elements across a series have the same number of 21. A colored ion generally indicates a 22. As you go down a group, the elements generally become ( more / less) metallic. 23. The ...
Unit 5 Notes
... 3. As you move down a group of elements AR will increase. This occurs because for every period that you move down, you are adding another principle energy level(ring of Bohr Model). 4. As you move across a period of elements AR will decrease. This is because of the stronger attraction between the op ...
... 3. As you move down a group of elements AR will increase. This occurs because for every period that you move down, you are adding another principle energy level(ring of Bohr Model). 4. As you move across a period of elements AR will decrease. This is because of the stronger attraction between the op ...
Unit 3: The Periodic Table
... 3. Identify and state the properties, including physical state, of metals, metalloids, and non-metals. 4. Distinguish between the terms groups or families and periods. 5. Relate the position of any main group element in the periodic table to its number of valence electrons and ...
... 3. Identify and state the properties, including physical state, of metals, metalloids, and non-metals. 4. Distinguish between the terms groups or families and periods. 5. Relate the position of any main group element in the periodic table to its number of valence electrons and ...
Addrienne`s Element Lesson Plan
... 2.) Make enough copies of these cards so that small groups of students will each have one set. Also make sure that all classroom periodic tables are put away or covered up…not cheating! 3.) Committing to an Outcome and Exposing Beliefs: Inform the students what they are going to be doing today and a ...
... 2.) Make enough copies of these cards so that small groups of students will each have one set. Also make sure that all classroom periodic tables are put away or covered up…not cheating! 3.) Committing to an Outcome and Exposing Beliefs: Inform the students what they are going to be doing today and a ...
Periodic Table Quiz
... The pictures below show the position of di erent elements on the periodic table. Which picture has an X in the locations of the three elements that would be most similar in the way they react? A. ...
... The pictures below show the position of di erent elements on the periodic table. Which picture has an X in the locations of the three elements that would be most similar in the way they react? A. ...
Periodic Table HW Unit
... Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These forms differ in their molecular or crystal structure, and hence in their properties. For Groups 1, 2, and 13-‐18 on the Perio ...
... Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These forms differ in their molecular or crystal structure, and hence in their properties. For Groups 1, 2, and 13-‐18 on the Perio ...
Exam # 2 Review - HCC Learning Web
... Classify the following compounds : TiO2, H2O, NH3, HCl What is the chemical formula for the binary compound composed of Li+ and O2- ions? What is the chemical formula for the binary compound composed of Al3+ and O2- ions? What is the chemical formula for the binary compound composed of Sr2+ and Br- ...
... Classify the following compounds : TiO2, H2O, NH3, HCl What is the chemical formula for the binary compound composed of Li+ and O2- ions? What is the chemical formula for the binary compound composed of Al3+ and O2- ions? What is the chemical formula for the binary compound composed of Sr2+ and Br- ...
Chapter 5—The Periodic Law
... 74. The most characteristic property of the noble gases is that they a. have low boiling points. c. are gases at ordinary temperatures. b. are radioactive. d. are largely unreactive. 76. When determining the size of an atom by measuring the distance between identical adjacent nuclei, the radius of ...
... 74. The most characteristic property of the noble gases is that they a. have low boiling points. c. are gases at ordinary temperatures. b. are radioactive. d. are largely unreactive. 76. When determining the size of an atom by measuring the distance between identical adjacent nuclei, the radius of ...
Notes - Chemistry
... – 6 valence e– Forms 2- ions. It prefers to _________ 2 e- rather than give away 6) – O and S are reactive and found in many compounds ...
... – 6 valence e– Forms 2- ions. It prefers to _________ 2 e- rather than give away 6) – O and S are reactive and found in many compounds ...
PT trends
... Developed concept of arranging PT by atomic number Periodic law – there is a periodic repetition of properties when elements are arranged by atomic # ...
... Developed concept of arranging PT by atomic number Periodic law – there is a periodic repetition of properties when elements are arranged by atomic # ...
Cations (positive ions) are smaller than their respective atoms.
... 1) Metals- high luster, good conductors, ductile, malleable, most are solid at room temp (except Hg is liquid) 2)Nonmetals- low luster, poor conductors, very brittle, various states of matter at room temperature (ex: S is solid, O is gas, Br is liquid) 3) Semi-Conductors - sit on stair-step line met ...
... 1) Metals- high luster, good conductors, ductile, malleable, most are solid at room temp (except Hg is liquid) 2)Nonmetals- low luster, poor conductors, very brittle, various states of matter at room temperature (ex: S is solid, O is gas, Br is liquid) 3) Semi-Conductors - sit on stair-step line met ...
Periodic Table History & Organization
... In small atoms, e- are close to the nucleus where the attraction is stronger Why small jumps within each group? Stable e- configurations don’t want to lose e- ...
... In small atoms, e- are close to the nucleus where the attraction is stronger Why small jumps within each group? Stable e- configurations don’t want to lose e- ...
The Periodic Table of Elements
... Never form hydrogen gas from acids dilute acids Always form position ions (cations) Always form negative ions (anions) ...
... Never form hydrogen gas from acids dilute acids Always form position ions (cations) Always form negative ions (anions) ...
File - the prayas tutorial
... discovered later but the properties were similar to eka-boron, eka-aluminium and ekasilicon. Noble gases like Helium, Neon, and Argon have been mentioned in his context though they are highly inert and low concentration in our atmosphere. When these gases were discovered they placed a new group with ...
... discovered later but the properties were similar to eka-boron, eka-aluminium and ekasilicon. Noble gases like Helium, Neon, and Argon have been mentioned in his context though they are highly inert and low concentration in our atmosphere. When these gases were discovered they placed a new group with ...
Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table Understanding Main Ideas
... 3. _____________ In the periodic table, the number of valence electrons in each element decreases from left to right across each period. 4. _____________ The reactivity of a metal depends on how easily it loses its valence electrons. 5. _____________ Within each period in the periodic table, element ...
... 3. _____________ In the periodic table, the number of valence electrons in each element decreases from left to right across each period. 4. _____________ The reactivity of a metal depends on how easily it loses its valence electrons. 5. _____________ Within each period in the periodic table, element ...
Chemistry Midterm Exam Review Sheet
... 35. Why do elements lose or gain electrons? 36. Why do ions have a + or – charge? 37. How many electrons are lost or gained if an ion has the following charge: a. +1 ...
... 35. Why do elements lose or gain electrons? 36. Why do ions have a + or – charge? 37. How many electrons are lost or gained if an ion has the following charge: a. +1 ...