Physical Science
... History of the Periodic Table The periodic table was discovered by Dmitri Mendeleev in the late 1800s. He arranged the elements in order by their atomic masses. The first periodic table was written on paper!! p.554 In 1913, Henry Moseley rearranged the periodic table by their atomic numbers instead ...
... History of the Periodic Table The periodic table was discovered by Dmitri Mendeleev in the late 1800s. He arranged the elements in order by their atomic masses. The first periodic table was written on paper!! p.554 In 1913, Henry Moseley rearranged the periodic table by their atomic numbers instead ...
Unit One Periodicity of Elements and their Properties
... 2. They are covalent compounds in which the difference in electronegativity between elements forming their molecules is relatively high 3. There is a direct relationship between the atomic size of the atom of an element and its electronegativity. 4. Fluorine has the least electronegativity which equ ...
... 2. They are covalent compounds in which the difference in electronegativity between elements forming their molecules is relatively high 3. There is a direct relationship between the atomic size of the atom of an element and its electronegativity. 4. Fluorine has the least electronegativity which equ ...
Periodic Table
... ____ 16. Which of the following is true about the electron configurations of the noble gases? a. The highest occupied s and p sublevels are completely filled. b. The highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially filled. c. The electrons with the highest energy are in a d sublevel. d. The electron ...
... ____ 16. Which of the following is true about the electron configurations of the noble gases? a. The highest occupied s and p sublevels are completely filled. b. The highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially filled. c. The electrons with the highest energy are in a d sublevel. d. The electron ...
File
... Henry Moseley (Rutherford’s assistant) • Discovered a method for counting each element’s protons with x-rays •Found that if elements were organized by atomic number, and not mass, the problems disappeared. (1912) Periodic law – Properties vary with their atomic numbers in a periodic way. (Current ba ...
... Henry Moseley (Rutherford’s assistant) • Discovered a method for counting each element’s protons with x-rays •Found that if elements were organized by atomic number, and not mass, the problems disappeared. (1912) Periodic law – Properties vary with their atomic numbers in a periodic way. (Current ba ...
Ch 5 Notes
... (shiny), conductive (heat and electricity), malleable (bendable), ductile (stretchable), high density, high melting point • Chemical Properties: Most will react with oxygen ...
... (shiny), conductive (heat and electricity), malleable (bendable), ductile (stretchable), high density, high melting point • Chemical Properties: Most will react with oxygen ...
Activity 16 Elements and the Periodic Table
... Do you see another of the patterns that Mendeleev and other scientists recognized? ___________ Neutral atoms contain equal numbers of protons (+) and electrons (-). Because of this, you know that neutral atoms of lithium, beryllium, boron and carbon also have 3, 4, 5, and 6 electrons respectively. W ...
... Do you see another of the patterns that Mendeleev and other scientists recognized? ___________ Neutral atoms contain equal numbers of protons (+) and electrons (-). Because of this, you know that neutral atoms of lithium, beryllium, boron and carbon also have 3, 4, 5, and 6 electrons respectively. W ...
Periodic Table Notes 2
... showed similar patterns of chemical behavior were placed into groups. His chart was incomplete at the time, but Mendeleev predicted that new elements were yet to be discovered, so he left blank spaces in his first version of the periodic table. Over the years, modified versions of the original perio ...
... showed similar patterns of chemical behavior were placed into groups. His chart was incomplete at the time, but Mendeleev predicted that new elements were yet to be discovered, so he left blank spaces in his first version of the periodic table. Over the years, modified versions of the original perio ...
The Periodic Table
... Carbon is found in three different forms and can form many compounds. Nonmetals and their compounds are plentiful on Earth. Halogens, such as chlorine, are located in Group 17 of the periodic table. Noble gases, such as neon, make up Group 18 of the periodic table. They are unreactive. ...
... Carbon is found in three different forms and can form many compounds. Nonmetals and their compounds are plentiful on Earth. Halogens, such as chlorine, are located in Group 17 of the periodic table. Noble gases, such as neon, make up Group 18 of the periodic table. They are unreactive. ...
Year 11 Chemistry: Chapter 3 ~ The Periodic Table
... Nobel gases have been known to form compounds with fluoride ions. QUESTIONS: ...
... Nobel gases have been known to form compounds with fluoride ions. QUESTIONS: ...
Example
... • Atomic mass: the average of all the isotopes’ mass • What type of element it is (metal, nonmetal, etc) • What elements can bond together (valence #) • In what ratio elements bond (oxidation #) ...
... • Atomic mass: the average of all the isotopes’ mass • What type of element it is (metal, nonmetal, etc) • What elements can bond together (valence #) • In what ratio elements bond (oxidation #) ...
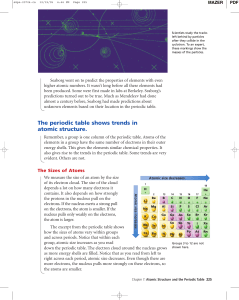
The periodic table shows trends in atomic structure.
... Seaborg went on to predict the properties of elements with even higher atomic numbers. It wasn’t long before all these elements had been produced. Some were first made in labs at Berkeley. Seaborg’s predictions turned out to be true. Much as Mendeleev had done almost a century before, Seaborg had ma ...
... Seaborg went on to predict the properties of elements with even higher atomic numbers. It wasn’t long before all these elements had been produced. Some were first made in labs at Berkeley. Seaborg’s predictions turned out to be true. Much as Mendeleev had done almost a century before, Seaborg had ma ...
Periodic Table and Trends
... Defined by an atoms tendency to attract electrons in a chemical bond. In a chemical bond, atoms have to share electrons The atom with a higher electronegativity will keep the electrons closer to it. ...
... Defined by an atoms tendency to attract electrons in a chemical bond. In a chemical bond, atoms have to share electrons The atom with a higher electronegativity will keep the electrons closer to it. ...
Trends on the Periodic Table
... alkaline, or basic, solution, hence their name. Alkaline earth metals (2)—These also are reactive metals, but they don’t explode in water; pastes of these are used in batteries. Halogens (17)—Known as the “salt formers,” they are used in modern lighting and always exist as diatomic molecules in thei ...
... alkaline, or basic, solution, hence their name. Alkaline earth metals (2)—These also are reactive metals, but they don’t explode in water; pastes of these are used in batteries. Halogens (17)—Known as the “salt formers,” they are used in modern lighting and always exist as diatomic molecules in thei ...
The History and Arrangement of the Periodic Table
... that are to the right of the zigzag on the periodic table ► Not shiny, dull in appearance ► Do not conduct heat or electricity ► Are brittle and break easily ► Cannot be drawn into wire or hammered ...
... that are to the right of the zigzag on the periodic table ► Not shiny, dull in appearance ► Do not conduct heat or electricity ► Are brittle and break easily ► Cannot be drawn into wire or hammered ...
Arrangement of the Periodic Table
... that are to the right of the zigzag on the periodic table ► Not shiny, dull in appearance ► Do not conduct heat or electricity ► Are brittle and break easily ► Cannot be drawn into wire or hammered ...
... that are to the right of the zigzag on the periodic table ► Not shiny, dull in appearance ► Do not conduct heat or electricity ► Are brittle and break easily ► Cannot be drawn into wire or hammered ...
Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table PLO`s
... Identify the major divisions within the periodic table including the names and locations of each family of elements. ...
... Identify the major divisions within the periodic table including the names and locations of each family of elements. ...
The periodic table
... Problems with the octaves • Newlands' table showed a repeating or periodic pattern of properties, but it had problems. For example, he put iron in the same group as oxygen and sulphur, which are two non-metals. As a result, his table was not accepted by other scientists • Newland’s did not realise ...
... Problems with the octaves • Newlands' table showed a repeating or periodic pattern of properties, but it had problems. For example, he put iron in the same group as oxygen and sulphur, which are two non-metals. As a result, his table was not accepted by other scientists • Newland’s did not realise ...
Periodic Table and Trends
... The top, right-area of the periodic table has the smallest atomic radius (helium) Which would you assume to have the largest atomic radius: Al, Al+, or AlWhich would you assume to have the smallest atomic radius: C2+, C+, C, C-, C2- ...
... The top, right-area of the periodic table has the smallest atomic radius (helium) Which would you assume to have the largest atomic radius: Al, Al+, or AlWhich would you assume to have the smallest atomic radius: C2+, C+, C, C-, C2- ...
structure of atoms
... Some nuclei are unstable and emit one or more of the following an alpha particle (group of 2 protons + 2 neutrons) a beta particle (electrons) positron (short-lived, positively-charged particle with the same mass as an electron) electromagnetic radiation (gamma rays) Approximately 200 radioisot ...
... Some nuclei are unstable and emit one or more of the following an alpha particle (group of 2 protons + 2 neutrons) a beta particle (electrons) positron (short-lived, positively-charged particle with the same mass as an electron) electromagnetic radiation (gamma rays) Approximately 200 radioisot ...
The Periodic Table
... Each group has characteristic properties that are directly related to electron configuration & especially the number of valence electrons ...
... Each group has characteristic properties that are directly related to electron configuration & especially the number of valence electrons ...
Periodic Table Notes
... that are to the right of the zigzag on the periodic table ► Not shiny, dull in appearance ► Do not conduct heat or electricity ► Are brittle and break easily ► Cannot be drawn into wire or hammered ...
... that are to the right of the zigzag on the periodic table ► Not shiny, dull in appearance ► Do not conduct heat or electricity ► Are brittle and break easily ► Cannot be drawn into wire or hammered ...
lab19
... 1. Properties such as atomic radius and energy required to remove the easiest electron are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. 2. As the atomic number increases, electrons increase, which causes there to be more valence electrons, and results in a larger atom (larger atomic radius value). 3. ...
... 1. Properties such as atomic radius and energy required to remove the easiest electron are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. 2. As the atomic number increases, electrons increase, which causes there to be more valence electrons, and results in a larger atom (larger atomic radius value). 3. ...
Perioidicty Slide Show 2011
... Highly reactive (only have 1 outer electron to lose)-therefore not found in nature in elemental state; reacts with O2, to form oxide coating and H2O to form basic (alkali) solutions. Increase in reactivity down the group (Fr is most reactive metal). Softest of all metals (can be cut with a knife) an ...
... Highly reactive (only have 1 outer electron to lose)-therefore not found in nature in elemental state; reacts with O2, to form oxide coating and H2O to form basic (alkali) solutions. Increase in reactivity down the group (Fr is most reactive metal). Softest of all metals (can be cut with a knife) an ...
Chapter 7
... the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle • discuss what is meant by the s, p, d, and f blocks of elements in the periodic table • use orbital diagrams to predict the number of unpaired electrons in an atom and whether the atom is diamagnetic or paramagnetic 2. Explain the ...
... the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle • discuss what is meant by the s, p, d, and f blocks of elements in the periodic table • use orbital diagrams to predict the number of unpaired electrons in an atom and whether the atom is diamagnetic or paramagnetic 2. Explain the ...