Section 2: Exploring the Periodic Table The Periodic Table Section 2
... – metal: an element that is shiny and that conducts heat and electricity well – nonmetal: an element that conducts heat and electricity poorly – semiconductor (or metalloid): an element or compound that conducts electric current better than an insulator does but not as well as a conductor does ...
... – metal: an element that is shiny and that conducts heat and electricity well – nonmetal: an element that conducts heat and electricity poorly – semiconductor (or metalloid): an element or compound that conducts electric current better than an insulator does but not as well as a conductor does ...
Unit Bohr Model and Electromagnetic Radiation - Jones
... 1. Gaining energy results in the electron moving from its ground state to a higher energy level. 2. When the electron moves to a lower energy level, it releases the energy difference in the two levels as electromagnetic radiation (emissions spectrum). Chm.1.3 Understand the physical and chemical pro ...
... 1. Gaining energy results in the electron moving from its ground state to a higher energy level. 2. When the electron moves to a lower energy level, it releases the energy difference in the two levels as electromagnetic radiation (emissions spectrum). Chm.1.3 Understand the physical and chemical pro ...
Chapter 5 Chem classnotes
... What is the above periodic trend called? Which element has the highest electronegativity? ...
... What is the above periodic trend called? Which element has the highest electronegativity? ...
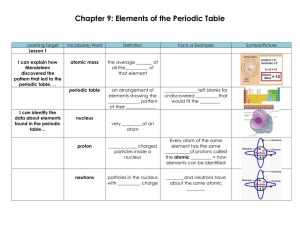
Chapter 9: Elements of the Periodic Table
... I can describe how metals are classified in the periodic table… Metals are classified as ____________metals, _____________________ metals, ______________ metals, metals in mixed groups, __________________, and ___________________. Lesson 3 I can summarize the properties of nonmetals… In general, mos ...
... I can describe how metals are classified in the periodic table… Metals are classified as ____________metals, _____________________ metals, ______________ metals, metals in mixed groups, __________________, and ___________________. Lesson 3 I can summarize the properties of nonmetals… In general, mos ...
S8P1-study-guide
... particles that carry a positive charge. Neutrons are particles that carry no electric charge. The nucleus is the center of the atom that is made up of both protons and neutrons. Electrons are particles that carry a negative charge and surround the nucleus in what is know as the electron cloud on ene ...
... particles that carry a positive charge. Neutrons are particles that carry no electric charge. The nucleus is the center of the atom that is made up of both protons and neutrons. Electrons are particles that carry a negative charge and surround the nucleus in what is know as the electron cloud on ene ...
YEAR 9 REVISION LIST November Exam 2013
... In an atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. Atoms therefore have no overall electrical charge. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. The number of protons in an atom ...
... In an atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. Atoms therefore have no overall electrical charge. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. The number of protons in an atom ...
Unit 2 Exam Review: Matter and its Properties This review does not
... CHEM 5B use the Periodic Table to identify and explain the properties of chemical families, including alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, and transition metals 21. Which elements are designated as noble gases? What is the most significant property of these elements? 22. Thi ...
... CHEM 5B use the Periodic Table to identify and explain the properties of chemical families, including alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, and transition metals 21. Which elements are designated as noble gases? What is the most significant property of these elements? 22. Thi ...
The Periodic Table
... at regular intervals —like the appearance of Haley’s comet every 76 years ...
... at regular intervals —like the appearance of Haley’s comet every 76 years ...
module-21 (worksheet-1)
... (b) The metal which is an important constituent of limestone_________________________. (c) The metal which exists in liquid state at room temperature________________________. Increasing order of reactivity :_________________________________________________________________________. 9) Properties of t ...
... (b) The metal which is an important constituent of limestone_________________________. (c) The metal which exists in liquid state at room temperature________________________. Increasing order of reactivity :_________________________________________________________________________. 9) Properties of t ...
Chapter 6 Review Name Period _____ Know the history
... 27. How are neutral atoms made into cations? They lose electrons in their outter shell 28. What is the charge of an anion? Negative, increases across a period and reamin the same going down 29. How are neutral atoms made into anions? They gain electrons to fill their valence shell 30. Metals usually ...
... 27. How are neutral atoms made into cations? They lose electrons in their outter shell 28. What is the charge of an anion? Negative, increases across a period and reamin the same going down 29. How are neutral atoms made into anions? They gain electrons to fill their valence shell 30. Metals usually ...
Metals
... • Most are silver in color • Somewhat reactive • These are most metals you are familiar with • iron, gold, copper, zinc and nickel • Since they are not that reactive they have more everyday uses. ...
... • Most are silver in color • Somewhat reactive • These are most metals you are familiar with • iron, gold, copper, zinc and nickel • Since they are not that reactive they have more everyday uses. ...
Develo ment of the Atomic Theo John Dalton - (English 1766
... elements. He noticed that when the elements were rearranged in order of increasing atomic numbers instead of their atomic masses all of the elements fell into place correctly. This is the modem periodic table that we use today. Vertical columns - groups or families, similar but not identical propert ...
... elements. He noticed that when the elements were rearranged in order of increasing atomic numbers instead of their atomic masses all of the elements fell into place correctly. This is the modem periodic table that we use today. Vertical columns - groups or families, similar but not identical propert ...
Periodic Table
... While it was the first periodic table, Mendeleev had very different elements, such as the very reactive potassium and the very stable copper, in the same family. Forty years later Moseley rearranged the elements by their atomic number which gave the table better periodicity. Mendeleev ...
... While it was the first periodic table, Mendeleev had very different elements, such as the very reactive potassium and the very stable copper, in the same family. Forty years later Moseley rearranged the elements by their atomic number which gave the table better periodicity. Mendeleev ...
Periodicity
... • is arranged in rows (across) in order of increasing energy levels of valence electrons (called periods). The period number represents the energy level for that row. • is arranged in columns (down) in order of similar orbitals for the valence electrons (called groups). • The elements are represente ...
... • is arranged in rows (across) in order of increasing energy levels of valence electrons (called periods). The period number represents the energy level for that row. • is arranged in columns (down) in order of similar orbitals for the valence electrons (called groups). • The elements are represente ...
Chapter Twelve: Atoms and the Periodic Table
... • Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. • Mendeleev used the properties of existing elements to predict properties of undiscovered elements. • The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual prope ...
... • Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. • Mendeleev used the properties of existing elements to predict properties of undiscovered elements. • The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual prope ...
Students should be able to describe
... Compounds are formed from elements by chemical reactions. Chemical reactions always involve the formation of one or more new substances, and often involve a detectable energy change. Compounds contain two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions and can be represented by formulae us ...
... Compounds are formed from elements by chemical reactions. Chemical reactions always involve the formation of one or more new substances, and often involve a detectable energy change. Compounds contain two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions and can be represented by formulae us ...
Periodic Table Development
... electrons start to be located in f orbitals f orbitals can hold 14 electrons start filling 4f orbitals on 6 period with La (atomic # 57) f – block elements called inner transition metals Periodic Table shape is due to the way electrons fill s,p,d, f orbitals of different energy levels ...
... electrons start to be located in f orbitals f orbitals can hold 14 electrons start filling 4f orbitals on 6 period with La (atomic # 57) f – block elements called inner transition metals Periodic Table shape is due to the way electrons fill s,p,d, f orbitals of different energy levels ...
periodic trends 14 - Reeths
... 16. The outermost electron should be more _____________ ____________, and the element should have a ______________ ionization energy. ...
... 16. The outermost electron should be more _____________ ____________, and the element should have a ______________ ionization energy. ...
Study Guide
... particles that carry a positive charge. Neutrons are particles that carry no electric charge. The nucleus is the center of the atom that is made up of both protons and neutrons. Electrons are particles that carry a negative charge and surround the nucleus in what is know as the electron cloud on ene ...
... particles that carry a positive charge. Neutrons are particles that carry no electric charge. The nucleus is the center of the atom that is made up of both protons and neutrons. Electrons are particles that carry a negative charge and surround the nucleus in what is know as the electron cloud on ene ...
Procedure
... Periodic Trends Graph 3 - For elements 3-20, make a graph of the energy required to remove the easiest electron (first ionization energy) as a function of atomic number. Plot atomic number on the X axis and energy required on the Y axis. After creating the graph, use a colored pen or pencil to draw ...
... Periodic Trends Graph 3 - For elements 3-20, make a graph of the energy required to remove the easiest electron (first ionization energy) as a function of atomic number. Plot atomic number on the X axis and energy required on the Y axis. After creating the graph, use a colored pen or pencil to draw ...
Chapter 6 Review
... 23. List the electron configurations for the highest occupied energy level of the elements in period 3 from left to right. ...
... 23. List the electron configurations for the highest occupied energy level of the elements in period 3 from left to right. ...
02 The structure of the periodic table II
... Mendeleev’s periodic table It made sense for iodine (I) to come after tellurium (Te) ...
... Mendeleev’s periodic table It made sense for iodine (I) to come after tellurium (Te) ...
Atoms in the Periodic Table
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely un-reactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. ...
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely un-reactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. ...
The History of the Modern Periodic Table
... Periodic Table • Periodic Table: arrangement of elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column. ...
... Periodic Table • Periodic Table: arrangement of elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column. ...
Questions on Chapter 7
... B) Rb C) Ca D) Be E) Fr 70) Which one of the following is not true about the alkali metals? A) They are low density solids at room temperature. B) They all readily form ions with a +1 charge. C) They all have 2 electrons in their valence shells. D) They are very reactive elements. E) They have the l ...
... B) Rb C) Ca D) Be E) Fr 70) Which one of the following is not true about the alkali metals? A) They are low density solids at room temperature. B) They all readily form ions with a +1 charge. C) They all have 2 electrons in their valence shells. D) They are very reactive elements. E) They have the l ...