Unit 6: Periodic Table and Bonding
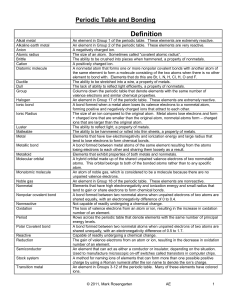
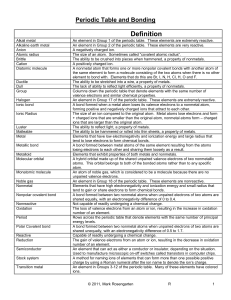
... A bond formed when a metal atom loses its valence electrons to a nonmetal atom, forming positive and negatively charged ions that attract to each other. The size of an ion compared to the original atom. Metal atoms lose electrons and form + charged ions that are smaller than the original atom, nonme ...
... A bond formed when a metal atom loses its valence electrons to a nonmetal atom, forming positive and negatively charged ions that attract to each other. The size of an ion compared to the original atom. Metal atoms lose electrons and form + charged ions that are smaller than the original atom, nonme ...
Unit 6: Periodic Table and Bonding
... A bond formed when a metal atom loses its valence electrons to a nonmetal atom, forming positive and negatively charged ions that attract to each other. The size of an ion compared to the original atom. Metal atoms lose electrons and form + charged ions that are smaller than the original atom, nonme ...
... A bond formed when a metal atom loses its valence electrons to a nonmetal atom, forming positive and negatively charged ions that attract to each other. The size of an ion compared to the original atom. Metal atoms lose electrons and form + charged ions that are smaller than the original atom, nonme ...
Chapter 6 Section 3 Periodic Trends
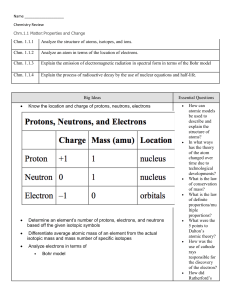
... Some compounds are composed of particles called ions. An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge. An atom is electrically neutral because it has equal numbers of protons and electrons. For example, an atom of sodium (Na) has 11 positively charged protons and 11 negati ...
... Some compounds are composed of particles called ions. An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge. An atom is electrically neutral because it has equal numbers of protons and electrons. For example, an atom of sodium (Na) has 11 positively charged protons and 11 negati ...
These are the periodic trends we need to know
... number is just a placement tool, and has no real meaning or attachment to any physical characteristic of atoms or elements. Its use is to order the elements on the developing periodic table so that the elements line up correctly based upon similarities in chemical behavior (the use of the number ali ...
... number is just a placement tool, and has no real meaning or attachment to any physical characteristic of atoms or elements. Its use is to order the elements on the developing periodic table so that the elements line up correctly based upon similarities in chemical behavior (the use of the number ali ...
class xi chemistry holiday homework
... Law of conservation of mass : ‘Mass can neither be created nor destroyed.’ In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of reactants is equal to that of products. Law of constant composition : A chemical compound is always found to be made of same elements combined together in the same fixed ...
... Law of conservation of mass : ‘Mass can neither be created nor destroyed.’ In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of reactants is equal to that of products. Law of constant composition : A chemical compound is always found to be made of same elements combined together in the same fixed ...
The Periodic Table
... Recall that the four different sublevels (s, p, d, and f) each consist of a different number of orbitals. The s sublevel has one orbital, the p sublevel has three orbitals, the d sublevel has five orbitals, and the f sublevel has seven orbitals. In the first period, only the 1s sublevel is being fil ...
... Recall that the four different sublevels (s, p, d, and f) each consist of a different number of orbitals. The s sublevel has one orbital, the p sublevel has three orbitals, the d sublevel has five orbitals, and the f sublevel has seven orbitals. In the first period, only the 1s sublevel is being fil ...
Periodic Trends
... Using your periodic table and the atomic radius chart, determine which of the elements in each pair has a larger atomic radius: 1. Cesium (Cs) and Potassium (K) 2. Calcium (Ca) and Gold (Au) 3. Rubidium (Rb) and Strontium (Sr) 4. Oxygen (O) and Sulfur (S) 5. Xenon (Xe) and Neon (Ne) 6. Aluminum (Al) ...
... Using your periodic table and the atomic radius chart, determine which of the elements in each pair has a larger atomic radius: 1. Cesium (Cs) and Potassium (K) 2. Calcium (Ca) and Gold (Au) 3. Rubidium (Rb) and Strontium (Sr) 4. Oxygen (O) and Sulfur (S) 5. Xenon (Xe) and Neon (Ne) 6. Aluminum (Al) ...
Chapter 1 - WebAssign
... If a test supports a hypothesis, another experiment is devised to further test the hypothesis. If a test does not support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis is changed or even discarded depending upon how badly it fails the test. After a hypothesis has been supported by many independent observers, it ...
... If a test supports a hypothesis, another experiment is devised to further test the hypothesis. If a test does not support a hypothesis, then the hypothesis is changed or even discarded depending upon how badly it fails the test. After a hypothesis has been supported by many independent observers, it ...
Review Atomic Structure
... The columns are called groups or families. Groups have similar physical and chemical properties and the same number of valence electrons ...
... The columns are called groups or families. Groups have similar physical and chemical properties and the same number of valence electrons ...
chapter 17 - keishabrady
... __Teaching Transparency 30A, Melting Points and Boiling Points of Period 6 Elements __Visual Strategy, Figure 12, TE Point out why there is no firm agreement on exact values for atomic radii. (GENERAL) __Using the Handbook, TE Summaries of group trends for groups 1 through 17 can be found in the Ele ...
... __Teaching Transparency 30A, Melting Points and Boiling Points of Period 6 Elements __Visual Strategy, Figure 12, TE Point out why there is no firm agreement on exact values for atomic radii. (GENERAL) __Using the Handbook, TE Summaries of group trends for groups 1 through 17 can be found in the Ele ...
Families and Periods of the Periodic Table - CK
... being the energy level involved. Each larger member of the family has its single s electron in the next larger principal energy level. As the atomic sizes in this family increase, the valence electrons are located further from the nucleus and are therefore easier to lose. Lithium reacts readily with ...
... being the energy level involved. Each larger member of the family has its single s electron in the next larger principal energy level. As the atomic sizes in this family increase, the valence electrons are located further from the nucleus and are therefore easier to lose. Lithium reacts readily with ...
Chapter 5
... radium • Group 2 metals are less reactive than the alkali metals, but are still too reactive to be found in nature in pure form. ...
... radium • Group 2 metals are less reactive than the alkali metals, but are still too reactive to be found in nature in pure form. ...
Unit 3 - Youngstown City Schools
... through each element they identify. The first group to correctly complete a vertical, horizontal, or diagonal row is the winner.} [IIIA] 2. Teacher discusses properties and characteristics of the families on the periodic table. This is an introduction to using properties to identify elements. Teache ...
... through each element they identify. The first group to correctly complete a vertical, horizontal, or diagonal row is the winner.} [IIIA] 2. Teacher discusses properties and characteristics of the families on the periodic table. This is an introduction to using properties to identify elements. Teache ...
Periods and Blocks of the Periodic Table
... radium • Group 2 metals are less reactive than the alkali metals, but are still too reactive to be found in nature in pure form. ...
... radium • Group 2 metals are less reactive than the alkali metals, but are still too reactive to be found in nature in pure form. ...
Lorna Merklinger
... 2. How do elements affect our everyday lives? 3. How does an element’s position on the periodic table affect the periodic properties? Learning Goal: 1. Students will be able to utilize the periodic table and understand how it is organized. Objectives: 1. Describe the atomic structure of an element u ...
... 2. How do elements affect our everyday lives? 3. How does an element’s position on the periodic table affect the periodic properties? Learning Goal: 1. Students will be able to utilize the periodic table and understand how it is organized. Objectives: 1. Describe the atomic structure of an element u ...
05-Notes - HCC Learning Web
... showed no chemical reactivity. They are also known as NOBLE GASES to convey the nonreactivity nature of these gases. Similarly, copper, silver and gold are referred to as Noble metals because of their resistance to chemical reaction. THE PERIODIC LAW CONCEPT Mosley, by studying the X-rays emitted fr ...
... showed no chemical reactivity. They are also known as NOBLE GASES to convey the nonreactivity nature of these gases. Similarly, copper, silver and gold are referred to as Noble metals because of their resistance to chemical reaction. THE PERIODIC LAW CONCEPT Mosley, by studying the X-rays emitted fr ...
Ionization Energy
... In a multi-electron atom, electrons are simultaneously attracted to the nucleus and repelled by one another. This results in shielding, where an electron is partially shielded from the positive charge of the nucleus by the other electrons. Although all electrons shield one another to some extent ...
... In a multi-electron atom, electrons are simultaneously attracted to the nucleus and repelled by one another. This results in shielding, where an electron is partially shielded from the positive charge of the nucleus by the other electrons. Although all electrons shield one another to some extent ...
Chm. 1.1.1 Analyze the structure of atoms, isotopes, and ions. Chm
... Infer the atomic size, reactivity, electronegativity, and ionization energy of an element from its position on the Periodic Table. ...
... Infer the atomic size, reactivity, electronegativity, and ionization energy of an element from its position on the Periodic Table. ...
Chapter_5_Notes_Periodic
... showed no chemical reactivity. They are also known as NOBLE GASES to convey the nonreactivity nature of these gases. Similarly, copper, silver and gold are referred to as Noble metals because of their resistance to chemical reaction. THE PERIODIC LAW CONCEPT Mosley, by studying the X-rays emitted fr ...
... showed no chemical reactivity. They are also known as NOBLE GASES to convey the nonreactivity nature of these gases. Similarly, copper, silver and gold are referred to as Noble metals because of their resistance to chemical reaction. THE PERIODIC LAW CONCEPT Mosley, by studying the X-rays emitted fr ...
Chapter 4
... them in order of increasing radius: K+, Ne, Ar, Kr, P3-, S2-, and Cl-. Strategy Isoelectronic series are species with identical electron configurations but different nuclear charges. Determine the number of electrons in each species. The radii of isoelectronic series members decreases with increasin ...
... them in order of increasing radius: K+, Ne, Ar, Kr, P3-, S2-, and Cl-. Strategy Isoelectronic series are species with identical electron configurations but different nuclear charges. Determine the number of electrons in each species. The radii of isoelectronic series members decreases with increasin ...
chapter 6 - HCC Learning Web
... showed no chemical reactivity. They are also known as NOBLE GASES to convey the nonreactivity nature of these gases. Similarly, copper, silver and gold are referred to as Noble metals because of their resistance to chemical reaction. THE PERIODIC LAW CONCEPT Mosley, by studying the X-rays emitted fr ...
... showed no chemical reactivity. They are also known as NOBLE GASES to convey the nonreactivity nature of these gases. Similarly, copper, silver and gold are referred to as Noble metals because of their resistance to chemical reaction. THE PERIODIC LAW CONCEPT Mosley, by studying the X-rays emitted fr ...
Document
... In a multi-electron atom, electrons are simultaneously attracted to the nucleus and repelled by one another. This results in shielding, where an electron is partially shielded from the positive charge of the nucleus by the other electrons. Although all electrons shield one another to some extent, ...
... In a multi-electron atom, electrons are simultaneously attracted to the nucleus and repelled by one another. This results in shielding, where an electron is partially shielded from the positive charge of the nucleus by the other electrons. Although all electrons shield one another to some extent, ...
Slide 1
... radius increases as well. These trends hold for both positive and negative ions. Metals tend to lose one or more electrons and form a positive ion. As you move across a period, the ionic radii of metal cations tend to decrease because of the increasing nuclear charge. As you come to the nonmetal ele ...
... radius increases as well. These trends hold for both positive and negative ions. Metals tend to lose one or more electrons and form a positive ion. As you move across a period, the ionic radii of metal cations tend to decrease because of the increasing nuclear charge. As you come to the nonmetal ele ...
Chapter 6: The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... properties. For this reason, they are often referred to as the main group, or representative elements. The elements in groups 3 to 12 are referred to as the transition elements. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. ...
... properties. For this reason, they are often referred to as the main group, or representative elements. The elements in groups 3 to 12 are referred to as the transition elements. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. ...