Chapter 6: The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... The modern periodic table is shown in Figure 6-4 and on the inside back cover of your textbook. A larger, two-page version of the table appears in Figure 6-7 on pages 156-157. The table consists of boxes, each containing an element name, symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass. A typical box from the ...
... The modern periodic table is shown in Figure 6-4 and on the inside back cover of your textbook. A larger, two-page version of the table appears in Figure 6-7 on pages 156-157. The table consists of boxes, each containing an element name, symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass. A typical box from the ...
General and Inorganic Chemistry I.
... X-ray wavelength and its atomic number (Z), and therefore resequenced the table by nuclear charge rather than atomic weight. Thus Moseley placed argon (Z=18) before potassium (Z=19) based on their X-ray wavelengths, despite the fact that argon has a greater atomic weight (39.9) than potassium (39.1) ...
... X-ray wavelength and its atomic number (Z), and therefore resequenced the table by nuclear charge rather than atomic weight. Thus Moseley placed argon (Z=18) before potassium (Z=19) based on their X-ray wavelengths, despite the fact that argon has a greater atomic weight (39.9) than potassium (39.1) ...
Periodic Table Jeopardy
... THESE ELEMENTS HAVE TRANSITIONAL OXIDATION STATES AND ARE GOOD CONDUCTORS What are Transition Metals? ANSWER RETURN ...
... THESE ELEMENTS HAVE TRANSITIONAL OXIDATION STATES AND ARE GOOD CONDUCTORS What are Transition Metals? ANSWER RETURN ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... and properties of undiscovered elements that were later found. Mendeleev left blank spaces in the table where he thought the undiscovered elements should go. By noting trends in the properties of known elements, he was able to predict the properties of the yet-to-be-discovered elements scandium, gal ...
... and properties of undiscovered elements that were later found. Mendeleev left blank spaces in the table where he thought the undiscovered elements should go. By noting trends in the properties of known elements, he was able to predict the properties of the yet-to-be-discovered elements scandium, gal ...
classification of elements and periodicity in properties
... predicted not only the existence of gallium and germanium, but also described some of their general physical properties. These elements were discovered later. Some of the properties predicted by Mendeleev for these elements and those found experimentally are listed in Table 3.3. ...
... predicted not only the existence of gallium and germanium, but also described some of their general physical properties. These elements were discovered later. Some of the properties predicted by Mendeleev for these elements and those found experimentally are listed in Table 3.3. ...
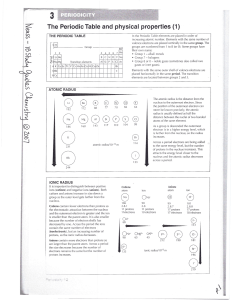
The Periodic Table and physical properties (1)
... Isoelectronic species are atoms and ions that have the same number of electrons. For a specific number of electrons, the higher the nuclear charge, the greater the forces of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons. Hence, the smaller the atomic or ionic radius. Ions of sodium, magnesium and ...
... Isoelectronic species are atoms and ions that have the same number of electrons. For a specific number of electrons, the higher the nuclear charge, the greater the forces of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons. Hence, the smaller the atomic or ionic radius. Ions of sodium, magnesium and ...
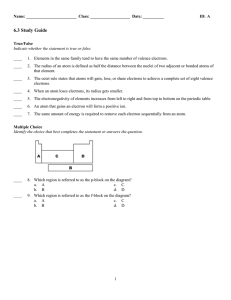
6.3 Study Guide
... 19. Explain the significance of the stair-step line located near the right-hand side of the periodic table 20. Do the figures in this partial periodic table demonstrate the trend in atomic radius, ionic radius, or neither of these? Relate your answer to the structure of atoms across the periodic tab ...
... 19. Explain the significance of the stair-step line located near the right-hand side of the periodic table 20. Do the figures in this partial periodic table demonstrate the trend in atomic radius, ionic radius, or neither of these? Relate your answer to the structure of atoms across the periodic tab ...
The Modern Periodic Table
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
Chapter 6: The Periodic Table
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
2000 - SolPass
... Instruction: Provide students an opportunity to describe a molecular shape and bond type based on the Lewis electron dot diagram, to analyze a Lewis diagram, to write the chemical equation for a given reaction, to determine the number of elements in a chemical formula, to identify a compound given i ...
... Instruction: Provide students an opportunity to describe a molecular shape and bond type based on the Lewis electron dot diagram, to analyze a Lewis diagram, to write the chemical equation for a given reaction, to determine the number of elements in a chemical formula, to identify a compound given i ...
GRADE 12A: Chemistry 1
... Allow students to add silver nitrate solution to aqueous solutions of potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium iodide, and tell them to record the colours of the precipitates formed. Then tell them to add aqueous ammonia solution to each precipitate and record their observations. Students ...
... Allow students to add silver nitrate solution to aqueous solutions of potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium iodide, and tell them to record the colours of the precipitates formed. Then tell them to add aqueous ammonia solution to each precipitate and record their observations. Students ...
Lecture Notes
... type of distinguishing electron! (_________ electrons) • The last electron added to the electron configuration for an element when electron subshells are filled in order of increasing energy • It is also the one that causes an element’s electron configuration to differ from that of the element immed ...
... type of distinguishing electron! (_________ electrons) • The last electron added to the electron configuration for an element when electron subshells are filled in order of increasing energy • It is also the one that causes an element’s electron configuration to differ from that of the element immed ...
CHAPTER 1. ATOMS: THE QUANTUM WORLD
... ♦ Atomic Number, Z : Number of protons in the nucleus ♦ Total charge on an atomic nucleus of atomic number Z : +Ze Æ There must be Z electrons around it to ensure total atomic neutrality The Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation Spectroscopy (分光法) : analysis of the light emitted or absorbed b ...
... ♦ Atomic Number, Z : Number of protons in the nucleus ♦ Total charge on an atomic nucleus of atomic number Z : +Ze Æ There must be Z electrons around it to ensure total atomic neutrality The Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation Spectroscopy (分光法) : analysis of the light emitted or absorbed b ...
Unit Description and Student Understandings
... Can students differentiate between atomic fission and fusion? ...
... Can students differentiate between atomic fission and fusion? ...
Chapter_6_Notes_Periodic
... showed no chemical reactivity. They are also known as NOBLE GASES to convey the nonreactivity nature of these gases. Similarly, copper, silver and gold are referred to as Noble metals because of their resistance to chemical reaction. THE PERIODIC LAW CONCEPT Mosley, by studying the X-rays emitted fr ...
... showed no chemical reactivity. They are also known as NOBLE GASES to convey the nonreactivity nature of these gases. Similarly, copper, silver and gold are referred to as Noble metals because of their resistance to chemical reaction. THE PERIODIC LAW CONCEPT Mosley, by studying the X-rays emitted fr ...
Unit 1 Safety and Science
... to start out with a simpler version of the whole story. We will go back about 100 years and use the German physicist Niels Bohr’s model of the atom as a simple way to understand what an atom is. It is not completely accurate, but its faults will not prevent you from gaining a basic understanding abo ...
... to start out with a simpler version of the whole story. We will go back about 100 years and use the German physicist Niels Bohr’s model of the atom as a simple way to understand what an atom is. It is not completely accurate, but its faults will not prevent you from gaining a basic understanding abo ...
Ch 14 power point
... oxygen, with 8 protons, gains/steals two eand then has 10 e-. The superscript is telling you that it has two too many electrons relative to its neutral form. ...
... oxygen, with 8 protons, gains/steals two eand then has 10 e-. The superscript is telling you that it has two too many electrons relative to its neutral form. ...
ppt - northcampus.net
... In a multi-electron atom, electrons are simultaneously attracted to the nucleus and repelled by one another. This results in shielding, where an electron is partially shielded from the positive charge of the nucleus by the other electrons. Although all electrons shield one another to some extent ...
... In a multi-electron atom, electrons are simultaneously attracted to the nucleus and repelled by one another. This results in shielding, where an electron is partially shielded from the positive charge of the nucleus by the other electrons. Although all electrons shield one another to some extent ...
File atoms1
... All of the above examples are considered matter because they have mass and take up space. Can you think of anything that would not be considered matter? ...
... All of the above examples are considered matter because they have mass and take up space. Can you think of anything that would not be considered matter? ...
C H A P T E R
... principal energy levels, including the 2s and 2p orbitals. Elements in Period 5 have outer electrons that fill the 5s, 5d, and 5p orbitals. This correlation between period number and the number of occupied energy levels holds for all seven periods. So a periodic table is not needed to tell to which ...
... principal energy levels, including the 2s and 2p orbitals. Elements in Period 5 have outer electrons that fill the 5s, 5d, and 5p orbitals. This correlation between period number and the number of occupied energy levels holds for all seven periods. So a periodic table is not needed to tell to which ...
Chapter 3
... "law of octaves", about 55 elements: pattern of reactivity follows after 8 elements. However, no one had found a clear "order" in their properties until Mendeleev, Dmitri (18341907) arranged 63 then known elements in the order of increasing atomic mass in a periodic table and showed some chemical pr ...
... "law of octaves", about 55 elements: pattern of reactivity follows after 8 elements. However, no one had found a clear "order" in their properties until Mendeleev, Dmitri (18341907) arranged 63 then known elements in the order of increasing atomic mass in a periodic table and showed some chemical pr ...
Chapter3
... Br) and (S Se Te).1865: Newlands – "law of octaves", about 55 elements: pattern of reactivity follows after 8 elements. However, no one had found a clear "order" in their properties until Mendeleev, Dmitri (1834-1907) arranged 63 then known elements in the order of increasing atomic mass in a period ...
... Br) and (S Se Te).1865: Newlands – "law of octaves", about 55 elements: pattern of reactivity follows after 8 elements. However, no one had found a clear "order" in their properties until Mendeleev, Dmitri (1834-1907) arranged 63 then known elements in the order of increasing atomic mass in a period ...
Chapter 3. Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
... Br) and (S Se Te).1865: Newlands – "law of octaves", about 55 elements: pattern of reactivity follows after 8 elements. However, no one had found a clear "order" in their properties until Mendeleev, Dmitri (1834-1907) arranged 63 then known elements in the order of increasing atomic mass in a period ...
... Br) and (S Se Te).1865: Newlands – "law of octaves", about 55 elements: pattern of reactivity follows after 8 elements. However, no one had found a clear "order" in their properties until Mendeleev, Dmitri (1834-1907) arranged 63 then known elements in the order of increasing atomic mass in a period ...