Periodic Trends Activity (EChem)
... 2. Make a line graph of the values in group 1. Does Zeff increase, decrease, or remain the same as you move down a group? ______________________________ Knowing the pattern of Zeff is very important! The values of Zeff explain a lot of the other trends you are about to discover. ...
... 2. Make a line graph of the values in group 1. Does Zeff increase, decrease, or remain the same as you move down a group? ______________________________ Knowing the pattern of Zeff is very important! The values of Zeff explain a lot of the other trends you are about to discover. ...
Effective Nuclear Charge
... 2. Make a line graph of the values in group 1. Does Zeff increase, decrease, or remain the same as you move down a group? ______________________________ Knowing the pattern of Zeff is very important! The values of Zeff explain a lot of the other trends you are about to discover. ...
... 2. Make a line graph of the values in group 1. Does Zeff increase, decrease, or remain the same as you move down a group? ______________________________ Knowing the pattern of Zeff is very important! The values of Zeff explain a lot of the other trends you are about to discover. ...
Chemistry SOL Review Packet
... 2.5 The Lewis dot diagram for a covalent compound shows that each of the atoms in the molecule has a filled valence level. Each shared pair of electrons in a Lewis diagram represents a covalent bond. A covalent molecule can also be represented by a structural formula in which each covalent bond is s ...
... 2.5 The Lewis dot diagram for a covalent compound shows that each of the atoms in the molecule has a filled valence level. Each shared pair of electrons in a Lewis diagram represents a covalent bond. A covalent molecule can also be represented by a structural formula in which each covalent bond is s ...
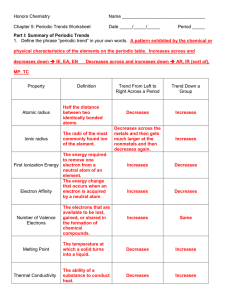
Honors Chemistry
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
CHAPTER SEVEN Periodic Properties of the Elements Effective
... NONMETALS Because of their relatively large, negative electron affinities, nonmetals tend to gain electrons when they react with metals. A nonmetal will gain enough electrons to fill its outermost occupied p subshell, giving a noble-gas electron configuration. For example, the bromine atom gains one ...
... NONMETALS Because of their relatively large, negative electron affinities, nonmetals tend to gain electrons when they react with metals. A nonmetal will gain enough electrons to fill its outermost occupied p subshell, giving a noble-gas electron configuration. For example, the bromine atom gains one ...
AP CHEMISTRY Periodic Trends Worksheet
... a. How would this account for the trend you discovered in atomic radius? Electrons are held more tightly and are pulled in closer by the nucleus as the number of protons increases within a level. b. How would this account for the trend you discovered in the first ionization energy? Because of the ad ...
... a. How would this account for the trend you discovered in atomic radius? Electrons are held more tightly and are pulled in closer by the nucleus as the number of protons increases within a level. b. How would this account for the trend you discovered in the first ionization energy? Because of the ad ...
Unit 06: Periodic Trends - Lincoln Park High School
... in order based on mass, and noticed a periodic reoccurrence of chemical and physical properties. He arranged the elements in columns. Elements in each column have similar properties. Occasionally, he would find a hole in the table. He could use the surrounding information to predict the properties o ...
... in order based on mass, and noticed a periodic reoccurrence of chemical and physical properties. He arranged the elements in columns. Elements in each column have similar properties. Occasionally, he would find a hole in the table. He could use the surrounding information to predict the properties o ...
HyperChem Lite Periodic Table Trends
... The Periodic Table is an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column. The elements are grouped in the Periodic Table according to their physical and chemical properties and their electron configurations. The electron c ...
... The Periodic Table is an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column. The elements are grouped in the Periodic Table according to their physical and chemical properties and their electron configurations. The electron c ...
Periodic Groups and Trends
... – The atomic radius gets bigger because electrons are added to energy levels farther away from the nucleus. – Plus, the inner electrons shield the outer electrons from the positive charge (“pull”) of the nucleus; known as the SHIELDING ...
... – The atomic radius gets bigger because electrons are added to energy levels farther away from the nucleus. – Plus, the inner electrons shield the outer electrons from the positive charge (“pull”) of the nucleus; known as the SHIELDING ...
Physical Science Comprehensive Fall 2010 SAMPLE QUESTIONS
... 1. Most of the elements in the periodic table can be described as: A. metals. B. nonmetals. C. metalloids. D. halogens. 2. The vertical columns of the periodic table are called: A. periods. B. groups. C. halogens. D. isotopes. 3. Horizontal rows on the periodic table are called: A. periods. B. group ...
... 1. Most of the elements in the periodic table can be described as: A. metals. B. nonmetals. C. metalloids. D. halogens. 2. The vertical columns of the periodic table are called: A. periods. B. groups. C. halogens. D. isotopes. 3. Horizontal rows on the periodic table are called: A. periods. B. group ...
Topic 1-10 KEY - Ms. Mogck`s Classroom
... Periods travel left to right, horizontally across a periodic table. Each period on the periodic table represents a different layer of electrons or a different “electron shell”. The 1st shell has 2 electrons (therefore the 1st period has 2 elements) the 2nd and 3rd shells have 8 electrons (therefore ...
... Periods travel left to right, horizontally across a periodic table. Each period on the periodic table represents a different layer of electrons or a different “electron shell”. The 1st shell has 2 electrons (therefore the 1st period has 2 elements) the 2nd and 3rd shells have 8 electrons (therefore ...
Unit 27: Chemical Periodicity and Its Applications - Edexcel
... The assessment of P1 should be done in a very straightforward way. Learners must write the electronic arrangement of at least the first 36 elements, using SPD notation and relate this notation to the position of the elements in the periodic table. It should be clear that the elements in the s block ...
... The assessment of P1 should be done in a very straightforward way. Learners must write the electronic arrangement of at least the first 36 elements, using SPD notation and relate this notation to the position of the elements in the periodic table. It should be clear that the elements in the s block ...
It gets harder to take them from the atoms towards the right
... A. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers 1. In Other Words - “Elements that are in the same up and down columns, called groups or families, have the same kinds of properties, they behave the same way ( all p 6 behave the same etc…) B. Ele ...
... A. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers 1. In Other Words - “Elements that are in the same up and down columns, called groups or families, have the same kinds of properties, they behave the same way ( all p 6 behave the same etc…) B. Ele ...
School of Elements 1. - mt
... 3. The nuclear charge also increases but increase in number of shells dominates over increase in nuclear charge. So, atomic size increases down the group. Valency varies gradually across a period. 1. In the modern periodic table, the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number (Z). 2. ...
... 3. The nuclear charge also increases but increase in number of shells dominates over increase in nuclear charge. So, atomic size increases down the group. Valency varies gradually across a period. 1. In the modern periodic table, the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number (Z). 2. ...
Lesson Plan
... direct result of the periodic nature of elemental properties, which is very important for chemistry students to understand. Elements in the same column have the same number of valance electrons; they often have the same charge and are in the same state of matter. Elements in the same column often ar ...
... direct result of the periodic nature of elemental properties, which is very important for chemistry students to understand. Elements in the same column have the same number of valance electrons; they often have the same charge and are in the same state of matter. Elements in the same column often ar ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Introduction: Electrons are arranged in orbitals, subshells, and shells. These levels of organization are shown by the boxes of the Gizmo. Each box represents an orbital. The subshells are labeled with letters (s, p, d, and f) and the shells are labeled with numbers. Question: How are electrons arra ...
... Introduction: Electrons are arranged in orbitals, subshells, and shells. These levels of organization are shown by the boxes of the Gizmo. Each box represents an orbital. The subshells are labeled with letters (s, p, d, and f) and the shells are labeled with numbers. Question: How are electrons arra ...
Periodic Trends ATOMIC RADIUS 1. Does atomic radius increase or
... F-1, there are more electrons, so the positive nucleus has a harder time pulling in all the outer electrons 10. How does the ionic radius of a nonmetal compare with its atomic radius? Not on test IONIZATION ENERGY ...
... F-1, there are more electrons, so the positive nucleus has a harder time pulling in all the outer electrons 10. How does the ionic radius of a nonmetal compare with its atomic radius? Not on test IONIZATION ENERGY ...
Atomic Size
... We have seen that there are trends in a physical property, IE1, related to the position of the elements in the periodic table. Many other physical and chemical properties of the elements in a particular group, such as the alkali metals or the halogens, are relatively similar. This suggests that many ...
... We have seen that there are trends in a physical property, IE1, related to the position of the elements in the periodic table. Many other physical and chemical properties of the elements in a particular group, such as the alkali metals or the halogens, are relatively similar. This suggests that many ...
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION
... It may be (i)electrovalency or (ii)covalency . When the proper sign is associated with valency it becomes oxidation number(ON). It is mostly a theoretical concept particularly for covalent compounds and ions. Definition: It is the theoetical charge which an atom will possess when all the atoms in a ...
... It may be (i)electrovalency or (ii)covalency . When the proper sign is associated with valency it becomes oxidation number(ON). It is mostly a theoretical concept particularly for covalent compounds and ions. Definition: It is the theoetical charge which an atom will possess when all the atoms in a ...
Periodic Trends - Mrs Molchany`s Webpage
... • Going from the left to the right across a period, the atom’s outer electrons are increasingly attracted to the nucleus because they stay within the same principal energy level. ...
... • Going from the left to the right across a period, the atom’s outer electrons are increasingly attracted to the nucleus because they stay within the same principal energy level. ...
The Periodic Table Test Review (3a-3b)
... 16. Identify the representative elements from the list given below. Na, Ca, Sc, Co, Ni, Si, N, Se, Cl, Ge 17. Why is argon placed before potassium in the modern periodic table? 18. Why do elements in the same group have similar properties? 19. Why is the size of a sodium ion (Na+) less than that of ...
... 16. Identify the representative elements from the list given below. Na, Ca, Sc, Co, Ni, Si, N, Se, Cl, Ge 17. Why is argon placed before potassium in the modern periodic table? 18. Why do elements in the same group have similar properties? 19. Why is the size of a sodium ion (Na+) less than that of ...
Electrons - TCS Moodle 2
... • They are ductile (can be drawn into wires) • They are malleable (can be hammered down) ...
... • They are ductile (can be drawn into wires) • They are malleable (can be hammered down) ...
effective nuclear charge
... • Metals tend to have low ionization energies and therefore form cations relatively easily. – Metals are easily oxidized when they undergo chemical reactions. – Cf) Nonmetals tend to form anions. ...
... • Metals tend to have low ionization energies and therefore form cations relatively easily. – Metals are easily oxidized when they undergo chemical reactions. – Cf) Nonmetals tend to form anions. ...
Honors Chemistry
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
... The easier it is to lose an electron the smaller the amount of energy needed to remove it (smaller ionization energy). 2. What happens to the amount of positive charge in the nucleus as you go from left to right across a period? The amount of positive charge increases as the number of protons increa ...
periodic table
... – An element is identified by its chemical symbol. – The number above the symbol is the atomic number – The number below the symbol is the rounded, weighted atomic mass of the element. – A row is called a period – A column is called a group or family ...
... – An element is identified by its chemical symbol. – The number above the symbol is the atomic number – The number below the symbol is the rounded, weighted atomic mass of the element. – A row is called a period – A column is called a group or family ...