CPO Science Link Teacher`s Guide
... On the far right on the periodic table is Group 18, the noble gases, including the elements helium (He), neon (Ne), and argon (Ar). These elements do not naturally form chemical bonds with other atoms. They are almost always found in their pure state, not as part of compounds. Elements in Groups 3 t ...
... On the far right on the periodic table is Group 18, the noble gases, including the elements helium (He), neon (Ne), and argon (Ar). These elements do not naturally form chemical bonds with other atoms. They are almost always found in their pure state, not as part of compounds. Elements in Groups 3 t ...
Chem Periodicity, Reactivity, Redox 2009 Yingxin
... Down the group, the reactivity of Group II metals increases Reacts with acids to form salt and hydrogen gas Displacement Reaction: When a more reactive metal reacts with the compound of another less reactive metal, the metal will be displaced from the compound. ...
... Down the group, the reactivity of Group II metals increases Reacts with acids to form salt and hydrogen gas Displacement Reaction: When a more reactive metal reacts with the compound of another less reactive metal, the metal will be displaced from the compound. ...
Student Exploration: Electron Configuration
... 9. Apply: Atoms are most stable when their outermost level is full. If their outermost level is not full, atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons until the level fills up. While doing this, atoms react and form chemical bonds with other atoms. Based on this, what can you infer about the reactiv ...
... 9. Apply: Atoms are most stable when their outermost level is full. If their outermost level is not full, atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons until the level fills up. While doing this, atoms react and form chemical bonds with other atoms. Based on this, what can you infer about the reactiv ...
Trends of the Periodic
... Reactivity refers to how likely or vigorously an atom is to react with other substances. This is usually determined by how easily electrons can be removed (ionization energy) and how badly they want to take other atom's electrons (electronegativity) because it is the transfer/interaction of electro ...
... Reactivity refers to how likely or vigorously an atom is to react with other substances. This is usually determined by how easily electrons can be removed (ionization energy) and how badly they want to take other atom's electrons (electronegativity) because it is the transfer/interaction of electro ...
Bonding 1 - Deans Community High School
... negative electron will decrease and consequently the ionisation energy will decrease. This explains the fall in ionisation energy as we descend a group. As the nuclear charge increases, its attraction for the outermost electron/s increases and consequently ionisation energy increases. This explains ...
... negative electron will decrease and consequently the ionisation energy will decrease. This explains the fall in ionisation energy as we descend a group. As the nuclear charge increases, its attraction for the outermost electron/s increases and consequently ionisation energy increases. This explains ...
Study guide for periodic table trends. A. By referring to electron
... Define the term first ionization energy and state what is meant by the term periodicity? The minimum energy to remove one electron from a gaseous atom. Or the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms and periodicity is the repeating pattern of physical and chemi ...
... Define the term first ionization energy and state what is meant by the term periodicity? The minimum energy to remove one electron from a gaseous atom. Or the energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms and periodicity is the repeating pattern of physical and chemi ...
120CH03 - Louisiana Tech University
... What to do with all this info? • Rules for writing electron configuration: • 1. The no. of electrons in neutral atom = atomic no. (no. of protons) • 2. Fill the lowest energy sublevel completely, then the next lowest, etc. • 3. No more than two electrons can be placed in a single orbital. The elect ...
... What to do with all this info? • Rules for writing electron configuration: • 1. The no. of electrons in neutral atom = atomic no. (no. of protons) • 2. Fill the lowest energy sublevel completely, then the next lowest, etc. • 3. No more than two electrons can be placed in a single orbital. The elect ...
ElectronConfigurationSE
... the filling of the d subshells. Now locate the purple lanthanides and actinides on the bottom rows of the periodic table. A. How many elements are in the in the lanthanides series? _____________________ B. Which subshell is represented by the lanthanides family? _____________________ C. Which subshe ...
... the filling of the d subshells. Now locate the purple lanthanides and actinides on the bottom rows of the periodic table. A. How many elements are in the in the lanthanides series? _____________________ B. Which subshell is represented by the lanthanides family? _____________________ C. Which subshe ...
Course Content
... 3. AVOID MISSING CLASS, BUT IF YOU ARE ABSENT: Bring a written excuse Catch up the work you missed There are no make-ups for laboratories missed, but you must do the lab report. The maximum grade you can obtain is 95% 4. FOLLOW ALL ISP RULES ...
... 3. AVOID MISSING CLASS, BUT IF YOU ARE ABSENT: Bring a written excuse Catch up the work you missed There are no make-ups for laboratories missed, but you must do the lab report. The maximum grade you can obtain is 95% 4. FOLLOW ALL ISP RULES ...
Periodic Trends.notebook
... charges and the fusion of carbon nuclei is not reached. Thus, the carbon core contracts to an extremely dense white dwarf which radiates its last energy and becomes a black dwarf (which is really a giant diamond in space). In very massive stars (greater than 4 solar masses), the heat generated fr ...
... charges and the fusion of carbon nuclei is not reached. Thus, the carbon core contracts to an extremely dense white dwarf which radiates its last energy and becomes a black dwarf (which is really a giant diamond in space). In very massive stars (greater than 4 solar masses), the heat generated fr ...
Are There Property Patterns? Introduction
... Introduction Chemists often look for patterns in the properties of different tested materials in order to predict the properties of untested samples. For example, it seems plausible to imagine that substances containing “lighter” molecules or atoms will melt at lower temperatures than substances mad ...
... Introduction Chemists often look for patterns in the properties of different tested materials in order to predict the properties of untested samples. For example, it seems plausible to imagine that substances containing “lighter” molecules or atoms will melt at lower temperatures than substances mad ...
How can atomic theory explain patterns in the periodic table?
... properties of that element. For example, an atom of carbon is represented in Figure 2.15. Each atom has a tiny, dense nucleus containing neutrons and protons. (A hydrogen nucleus has a single proton only.) The nucleus is surrounded by electrons, which exist in specific electron energy shells. Most o ...
... properties of that element. For example, an atom of carbon is represented in Figure 2.15. Each atom has a tiny, dense nucleus containing neutrons and protons. (A hydrogen nucleus has a single proton only.) The nucleus is surrounded by electrons, which exist in specific electron energy shells. Most o ...
Document
... Toward the close of the nineteenth century, chemists had two invaluable conceptual tools to aid them in their understanding of matter. The first was John Dalton’s atomic theory, which you have studied intensively in previous chemistry courses. Dalton’s atomic theory, first published in 1809, provide ...
... Toward the close of the nineteenth century, chemists had two invaluable conceptual tools to aid them in their understanding of matter. The first was John Dalton’s atomic theory, which you have studied intensively in previous chemistry courses. Dalton’s atomic theory, first published in 1809, provide ...
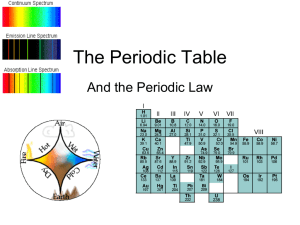
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table The how and why
... elements in columns by similar properties in order of increasing atomic mass Found some inconsistencies - felt that the properties were more important than the mass, so switched order. Found some gaps Must be undiscovered elements Predicted their properties before they were found ...
... elements in columns by similar properties in order of increasing atomic mass Found some inconsistencies - felt that the properties were more important than the mass, so switched order. Found some gaps Must be undiscovered elements Predicted their properties before they were found ...
COLLEGE ENTRANCE TEST REVIEW CHEMISTRY
... properties of metals (shiny or lustrous, malleable and ductile, oxides form basic ionic solids, and tend to form cations in ...
... properties of metals (shiny or lustrous, malleable and ductile, oxides form basic ionic solids, and tend to form cations in ...
Chapt6
... elements in columns by similar properties in order of increasing atomic mass Found some inconsistencies - felt that the properties were more important than the mass, so switched order. Found some gaps Must be undiscovered elements Predicted their properties before they were found ...
... elements in columns by similar properties in order of increasing atomic mass Found some inconsistencies - felt that the properties were more important than the mass, so switched order. Found some gaps Must be undiscovered elements Predicted their properties before they were found ...
CHM 101 Name___________________ Interactive Periodic Trends
... Nitrogen can occur in a variety of oxidation states. Rank these ions in different oxidation states from highest to lowest radius and explain your answer: N+3 ...
... Nitrogen can occur in a variety of oxidation states. Rank these ions in different oxidation states from highest to lowest radius and explain your answer: N+3 ...
The Structure of the Atom
... search for methods of separating metals from ores. E. Raison bun or plum pudding model. F. Earliest suggestion that matter was composed of atoms. G. Particles that have the same electronic configuration. H. Subatomic particle not found in the nucleus of the atom. I. The number of protons found in th ...
... search for methods of separating metals from ores. E. Raison bun or plum pudding model. F. Earliest suggestion that matter was composed of atoms. G. Particles that have the same electronic configuration. H. Subatomic particle not found in the nucleus of the atom. I. The number of protons found in th ...
Compounds have different properties from the elements that make
... clear that they cannot all be elements. In fact, while there are just over 100 elements, there are millions of different substances. Most substances are compounds. A compound is a substance made of atoms of two or more different elements. Just as the 26 letters in the alphabet can form thousands of ...
... clear that they cannot all be elements. In fact, while there are just over 100 elements, there are millions of different substances. Most substances are compounds. A compound is a substance made of atoms of two or more different elements. Just as the 26 letters in the alphabet can form thousands of ...
Valence Electrons - Warren County Public Schools
... Noble Gases, Transitional, Alkali, Halogens, Alkaline Earth 3. Circle the elements below that are representative: , ...
... Noble Gases, Transitional, Alkali, Halogens, Alkaline Earth 3. Circle the elements below that are representative: , ...
Chapter 6 the Periodic Table
... • First ionization energies generally decrease as you move down a group. • With the valence electrons farther away from the nucleus, less energy is required to remove them. ...
... • First ionization energies generally decrease as you move down a group. • With the valence electrons farther away from the nucleus, less energy is required to remove them. ...
NC SCS Chemistry
... the element cards with similar patterns in the same group. To make this task simpler and less time consuming, have students use just the properties of combines with # of oxygens and combines with # of chlorines to group the elements. Groups do not contain the same number of elements – a group ma ...
... the element cards with similar patterns in the same group. To make this task simpler and less time consuming, have students use just the properties of combines with # of oxygens and combines with # of chlorines to group the elements. Groups do not contain the same number of elements – a group ma ...
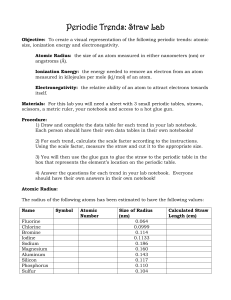
Periodic Trends: Straw Lab
... 1) In a sentence, describe the relationship between atomic number and the size of the atom’s radius going down a group on the periodic table. 2) Why does this relationship make sense in relation to what you know about elements on the periodic table? 3) In a sentence, describe the relationship betwee ...
... 1) In a sentence, describe the relationship between atomic number and the size of the atom’s radius going down a group on the periodic table. 2) Why does this relationship make sense in relation to what you know about elements on the periodic table? 3) In a sentence, describe the relationship betwee ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... Linus Pauling, an American chemist (and winner of two Nobel prizes!) came up with the concept of electronegativity in 1932 to help explain the nature of chemical bonds. Today we still measure electronegativities of elements using the Pauling scale. Since fluorine is the most electronegative element ...
... Linus Pauling, an American chemist (and winner of two Nobel prizes!) came up with the concept of electronegativity in 1932 to help explain the nature of chemical bonds. Today we still measure electronegativities of elements using the Pauling scale. Since fluorine is the most electronegative element ...
1.1 elements and the periodic table
... (b) Alkali metals and alkaline earth metals show a periodic recurrence of decreasing melting points as you move down a group, whereas nonmetals show a periodic recurrence of increasing melting points as you move down a group. Thus, based on the periodic recurrence of decreasing melting points Li, Na ...
... (b) Alkali metals and alkaline earth metals show a periodic recurrence of decreasing melting points as you move down a group, whereas nonmetals show a periodic recurrence of increasing melting points as you move down a group. Thus, based on the periodic recurrence of decreasing melting points Li, Na ...