Periodic Trends: Straw Lab
... 3) In a sentence, describe the relationship between atomic number and the size of each atom’s radius when going across a period on the periodic table. ...
... 3) In a sentence, describe the relationship between atomic number and the size of each atom’s radius when going across a period on the periodic table. ...
periodic-trends_atomic-and-ionic-radii
... A group is a vertical column of the periodic table. Elements with similar physical and chemical properties belong in a group. The group number gives the number of valence electrons in an element. For example, the Alkali Metals are in Group 1 (one valence electron), and the Halogens are in Group 7 (7 ...
... A group is a vertical column of the periodic table. Elements with similar physical and chemical properties belong in a group. The group number gives the number of valence electrons in an element. For example, the Alkali Metals are in Group 1 (one valence electron), and the Halogens are in Group 7 (7 ...
chapter 6 - TAMU Chemistry
... The minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from an isolated gaseous atom to form a 1+ ion. ...
... The minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from an isolated gaseous atom to form a 1+ ion. ...
CHAPTER 6
... The minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from an isolated gaseous atom to form a 1+ ion. ...
... The minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from an isolated gaseous atom to form a 1+ ion. ...
Periodic Table - Red Deer Public
... • Elements were arranged in order of increasing mass. • Elements with similar properties were placed in the same row. ...
... • Elements were arranged in order of increasing mass. • Elements with similar properties were placed in the same row. ...
Chapter 8 Electron Configurations and Periodicity
... Mendeleev’s periodic table generally organized elements by increasing atomic mass and with similar properties in columns. In some places, there were missing elements whose properties he predicted. When gallium, scandium, and germanium were isolated and characterized, their properties were almost id ...
... Mendeleev’s periodic table generally organized elements by increasing atomic mass and with similar properties in columns. In some places, there were missing elements whose properties he predicted. When gallium, scandium, and germanium were isolated and characterized, their properties were almost id ...
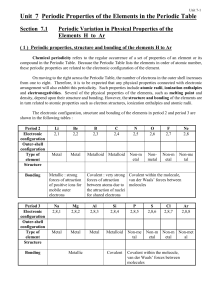
Unit 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements in the Periodic Table
... The ionic oxides contain O2- ions in the crystal lattice. Thus, the oxides of Group I metals react vigorously with water to form alkaline solutions. O2-(s) + H2O(l) → 2 OH-(aq) Li2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2 Li+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2 Na+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) These oxides would react even more vigoro ...
... The ionic oxides contain O2- ions in the crystal lattice. Thus, the oxides of Group I metals react vigorously with water to form alkaline solutions. O2-(s) + H2O(l) → 2 OH-(aq) Li2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2 Li+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2 Na+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) These oxides would react even more vigoro ...
periodic tabel - IIT
... In 1869 the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev and the German chemist Lothar Meyer independently proposed a much more extensive classification of elements. Both these classifications emphasized the periodicity of the properties of the elements with their atomic masses. While Mendeleev’s classification ...
... In 1869 the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev and the German chemist Lothar Meyer independently proposed a much more extensive classification of elements. Both these classifications emphasized the periodicity of the properties of the elements with their atomic masses. While Mendeleev’s classification ...
Periodic Trends
... • By 1860 about 60 elements were known and a method was needed for organization. ...
... • By 1860 about 60 elements were known and a method was needed for organization. ...
The d-and f-Block Elements
... tendency of (n-1)d as well as ns electrons to take part in bond formation. f. Magnetic properties: Most of transition metals are paramagnetic in nature due to presence of unpaired electrons. It increase s from Sc to Cr and then decreases because number of unpaired and then decrease because number of ...
... tendency of (n-1)d as well as ns electrons to take part in bond formation. f. Magnetic properties: Most of transition metals are paramagnetic in nature due to presence of unpaired electrons. It increase s from Sc to Cr and then decreases because number of unpaired and then decrease because number of ...
Chapter 6: Section 1 Searching for an Organizing Principle
... -can be used to predict the type of bond that will form during a reaction (covalent or ionic) -scientists use ionization energy to calculate values for electronegativity -High electronegativity = strong tendency to attract electrons -tend to gain electrons and form anions -Low electronegativity = we ...
... -can be used to predict the type of bond that will form during a reaction (covalent or ionic) -scientists use ionization energy to calculate values for electronegativity -High electronegativity = strong tendency to attract electrons -tend to gain electrons and form anions -Low electronegativity = we ...
The physical characteristics of the atom of an element are called
... 14. Variation in Atomic Radius in Group: Within a family or vertical column of the periodic table, the atomic radius increases regularly with atomic number as). as we descend the groups, the principal quantum number (n) increases and the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. This happens b ...
... 14. Variation in Atomic Radius in Group: Within a family or vertical column of the periodic table, the atomic radius increases regularly with atomic number as). as we descend the groups, the principal quantum number (n) increases and the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. This happens b ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends
... • If a small amount of boron is mixed with silicon, the mixture is a good conductor of electric current. Silicon can be cut into wafers, and used to make computer chips. ...
... • If a small amount of boron is mixed with silicon, the mixture is a good conductor of electric current. Silicon can be cut into wafers, and used to make computer chips. ...
1.9 Electronegativity
... Atomic radius – half the internuclear distance between neighboring atoms of the same element in a metal (metallic radius) or in a molecule (covalent radius). Ionic radius – typically determined by assigning the radius of O2- (in an Oh hole of a solid oxide crystal) as 1.40 Å and subsequently determi ...
... Atomic radius – half the internuclear distance between neighboring atoms of the same element in a metal (metallic radius) or in a molecule (covalent radius). Ionic radius – typically determined by assigning the radius of O2- (in an Oh hole of a solid oxide crystal) as 1.40 Å and subsequently determi ...
Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... each element, it identi es the chemical symbol, the atomic number, and the mass number, while organizing elements according to their propensity to react with other elements. The number of protons and electrons in an element are equal. The number of protons and neutrons may be equal for some elements ...
... each element, it identi es the chemical symbol, the atomic number, and the mass number, while organizing elements according to their propensity to react with other elements. The number of protons and electrons in an element are equal. The number of protons and neutrons may be equal for some elements ...
2. Classification of Elements and periodicity in properties
... ¾ They are chemically inactive. ¾ They are placed at the extreme right of the periodic table. REPRESENTATIVE ELEMENTS: ¾ s-block or p-block elements except '0' group are called representative elements. ¾ They have only one incomplete outer shell. ¾ These elements attain the nearest inert gas configu ...
... ¾ They are chemically inactive. ¾ They are placed at the extreme right of the periodic table. REPRESENTATIVE ELEMENTS: ¾ s-block or p-block elements except '0' group are called representative elements. ¾ They have only one incomplete outer shell. ¾ These elements attain the nearest inert gas configu ...
TREND
... 11. What property do the noble gases share? How does this property relate to the electron configuration of the noble gases? 12. How do the electron configurations of the transition metals differ form the electron configurations of the metals in groups 1 and 2? 13. What group numbers make up the main ...
... 11. What property do the noble gases share? How does this property relate to the electron configuration of the noble gases? 12. How do the electron configurations of the transition metals differ form the electron configurations of the metals in groups 1 and 2? 13. What group numbers make up the main ...
AR IE Graphing - GuerinChemistry
... The last section considered neutral atoms in their ground state. Chemists have found that, by supplying sufficient energy, they can remove the most loosely held electron in the atom. The atom is thereby made into a positive ion. Such ion is called a cation. The energy required for this process is re ...
... The last section considered neutral atoms in their ground state. Chemists have found that, by supplying sufficient energy, they can remove the most loosely held electron in the atom. The atom is thereby made into a positive ion. Such ion is called a cation. The energy required for this process is re ...
Periodic Trends_CP_2016_Notes
... • ______ on the periodic table • Represent the ________ that the valence electrons occupy. • Valence Electrons – ____________ electrons in an atom. – The electrons that are lost, gained, or shared in chemical reactions. – The _________ ________ ________ in an element's outer shell determines the che ...
... • ______ on the periodic table • Represent the ________ that the valence electrons occupy. • Valence Electrons – ____________ electrons in an atom. – The electrons that are lost, gained, or shared in chemical reactions. – The _________ ________ ________ in an element's outer shell determines the che ...
Chapter 2 - Department of Chemistry and Physics
... Nonmetals, and Metalloids Groups or families Vertical group of elements on periodic table Similar chemical and physical properties ...
... Nonmetals, and Metalloids Groups or families Vertical group of elements on periodic table Similar chemical and physical properties ...
Unit 3.pmd
... Each question has one correct option. Choose the correct option. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers which is related to the electronic configuration. Depending upon the type of orbitals receiving the last electron, the elements in the periodic t ...
... Each question has one correct option. Choose the correct option. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers which is related to the electronic configuration. Depending upon the type of orbitals receiving the last electron, the elements in the periodic t ...
Chp4Sec1and2
... the pattern that led to the periodic table? Mendeleev noticed that a pattern of properties appeared when he arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. ...
... the pattern that led to the periodic table? Mendeleev noticed that a pattern of properties appeared when he arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. ...
Review of Electronegativity
... Atomic radius – half the internuclear distance between neighboring atoms of the same element in a metal (metallic radius) or in a molecule (covalent radius). Ionic radius – typically determined by assigning the radius of O2- (in an Oh hole of a solid oxide crystal) as 1.40 Å and subsequently determi ...
... Atomic radius – half the internuclear distance between neighboring atoms of the same element in a metal (metallic radius) or in a molecule (covalent radius). Ionic radius – typically determined by assigning the radius of O2- (in an Oh hole of a solid oxide crystal) as 1.40 Å and subsequently determi ...