Ch 6.1 and 6.2 Review
... table according to row and column 12 How are the terms “energy level” and “principal quantum number” related? 13 Distinguish a metal from a nonmetal according to their respective properties. 14 In order to be chemically stable, how many electrons mush an element have in its outermost energy level? 1 ...
... table according to row and column 12 How are the terms “energy level” and “principal quantum number” related? 13 Distinguish a metal from a nonmetal according to their respective properties. 14 In order to be chemically stable, how many electrons mush an element have in its outermost energy level? 1 ...
Periodic Table Notes
... that are to the right of the zigzag on the periodic table ► Not shiny, dull in appearance ► Do not conduct heat or electricity ► Are brittle and break easily ► Cannot be drawn into wire or hammered ...
... that are to the right of the zigzag on the periodic table ► Not shiny, dull in appearance ► Do not conduct heat or electricity ► Are brittle and break easily ► Cannot be drawn into wire or hammered ...
1. discuss the contributions of early scie
... this family are phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Oxygen Family has 6 valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. Halogen Fami ...
... this family are phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Oxygen Family has 6 valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. Halogen Fami ...
S block
... nonmetals: upper right side of table semimetals: “stairstep” between metals & nonmetals ...
... nonmetals: upper right side of table semimetals: “stairstep” between metals & nonmetals ...
U1 Periodic Trends - Alliance Ouchi-O`Donovan 6
... attract electrons towards itself. Units: none, scale of 0-4 with Fluorine at 4 (highest). Here, Cl is more Atoms that want to gain electrons have ...
... attract electrons towards itself. Units: none, scale of 0-4 with Fluorine at 4 (highest). Here, Cl is more Atoms that want to gain electrons have ...
Periodic Table - MunterChemistry
... acquiring an electron will give them a full outer shell which increases the stability of the atom. • Half filled orbitals also give increased stability, so that the electron affinity of carbon is greater than the electron affinity of nitrogen. ...
... acquiring an electron will give them a full outer shell which increases the stability of the atom. • Half filled orbitals also give increased stability, so that the electron affinity of carbon is greater than the electron affinity of nitrogen. ...
structure of atoms
... o They can “jump” from one orbit to another though. o Jumping down from one orbit to a lower-energy orbit happens spontaneously and results in light of a particular energy or wavelength being emitted; explains why only particular wavelength are observed (spectral lines) o Jumping up requires being “ ...
... o They can “jump” from one orbit to another though. o Jumping down from one orbit to a lower-energy orbit happens spontaneously and results in light of a particular energy or wavelength being emitted; explains why only particular wavelength are observed (spectral lines) o Jumping up requires being “ ...
CHAPTER 5 - THE PERIODIC LAW
... compounds known as __________________________________ - Fluorine - gas at room temp - Chlorine - gas at room temp - Bromine - reddish liquid - Iodine - dark purple solid - Astatine - synthetic element (mostly known to be a solid) 4) “f” block - LANTHANIDES and ACTINIDES - Lanthanides are shiny metal ...
... compounds known as __________________________________ - Fluorine - gas at room temp - Chlorine - gas at room temp - Bromine - reddish liquid - Iodine - dark purple solid - Astatine - synthetic element (mostly known to be a solid) 4) “f” block - LANTHANIDES and ACTINIDES - Lanthanides are shiny metal ...
Unit 2 Exam Review: Matter and its Properties This review does not
... CHEM 5B use the Periodic Table to identify and explain the properties of chemical families, including alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, and transition metals 21. Which elements are designated as noble gases? What is the most significant property of these elements? 22. Thi ...
... CHEM 5B use the Periodic Table to identify and explain the properties of chemical families, including alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, and transition metals 21. Which elements are designated as noble gases? What is the most significant property of these elements? 22. Thi ...
AP Chemistry-Chapter 6 MC Questions
... ____ 22. A property that measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond is a. binding energy. b. mass defect. c. electron affinity. d. ionization energy. e. electronegativity. ____ 23. Which element has the highest electronegativity? a. N b. Si c. As d. P e. C ____ 24. Which ...
... ____ 22. A property that measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond is a. binding energy. b. mass defect. c. electron affinity. d. ionization energy. e. electronegativity. ____ 23. Which element has the highest electronegativity? a. N b. Si c. As d. P e. C ____ 24. Which ...
ATOMIC THEORY OF MATTER
... – Element: smallest entity which retains all properties of element, made up of atoms of one type (@116 with 90 occurring naturally) • May be an atom (Na, Si) or a molecule (S6, N2) ...
... – Element: smallest entity which retains all properties of element, made up of atoms of one type (@116 with 90 occurring naturally) • May be an atom (Na, Si) or a molecule (S6, N2) ...
C1a 1.1 Atoms, Elements and Compounds
... • Almost all of the substances around us are not pure elements. Most substances are made up of different atoms joined together to form compounds. Some compounds are made from just two types of atom joined together (e.g. water, made from hydrogen and oxygen). Other compounds consist of many different ...
... • Almost all of the substances around us are not pure elements. Most substances are made up of different atoms joined together to form compounds. Some compounds are made from just two types of atom joined together (e.g. water, made from hydrogen and oxygen). Other compounds consist of many different ...
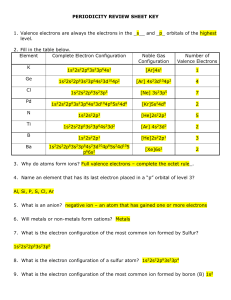
periodicity review sheet key
... 36. How many electrons does the above element contain? ___33___ 37. How many valence electrons does the above element contain? ___5______ 38. How many electrons are in the highest energy level of the above element? ___5 39. What element is it? ...
... 36. How many electrons does the above element contain? ___33___ 37. How many valence electrons does the above element contain? ___5______ 38. How many electrons are in the highest energy level of the above element? ___5 39. What element is it? ...
Next > Mendeleev and Meyer
... particular way. A great deal of information about an element can be gathered from its position in the period table. For example, you can predict with reasonably good accuracy the physical and chemical properties of the element. You can also predict what other elements a particular element will react ...
... particular way. A great deal of information about an element can be gathered from its position in the period table. For example, you can predict with reasonably good accuracy the physical and chemical properties of the element. You can also predict what other elements a particular element will react ...
Worksheet 3 - contentextra
... Neutral solution An aqueous solution that has a pH of 7. It contains the same concentrations of H + (aq) and OH– (aq) ions. Noble gases A group of very unreactive gases found in Group 0 of the Periodic Table. They exist as single atoms and have a stable s2p6 electron configuration. (Helium is an exc ...
... Neutral solution An aqueous solution that has a pH of 7. It contains the same concentrations of H + (aq) and OH– (aq) ions. Noble gases A group of very unreactive gases found in Group 0 of the Periodic Table. They exist as single atoms and have a stable s2p6 electron configuration. (Helium is an exc ...
Periodic table intro
... A group is a vertical column on the periodic table. It is also called a chemical family, because the elements in it have similar characteristics. ...
... A group is a vertical column on the periodic table. It is also called a chemical family, because the elements in it have similar characteristics. ...
Chapter 7.1 Notes
... What part of an atom determines what element it is? • The Atomic Number tells us what element the atom is. • The Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus. – EX: Hydrogen is atomic number 1. • That means there is exactly 1 proton in the nucleus of hydrogen. • Gold is atomic number 79. G ...
... What part of an atom determines what element it is? • The Atomic Number tells us what element the atom is. • The Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus. – EX: Hydrogen is atomic number 1. • That means there is exactly 1 proton in the nucleus of hydrogen. • Gold is atomic number 79. G ...
the periodic table
... “I began to look about and write down the elements with their atomic weights and typical properties, analogous elements and like atomic weights on separate cards, and this soon convinced me that the properties of elements are in periodic dependence upon their atomic weights.” --Mendeleev, Principle ...
... “I began to look about and write down the elements with their atomic weights and typical properties, analogous elements and like atomic weights on separate cards, and this soon convinced me that the properties of elements are in periodic dependence upon their atomic weights.” --Mendeleev, Principle ...
The Periodic Table
... • Not shiny (dull) • Not malleable (brittle) • Not ductile • Poor conductors of electricity. ...
... • Not shiny (dull) • Not malleable (brittle) • Not ductile • Poor conductors of electricity. ...
The Periodic Table PP
... Main Group Elements • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 are known as main group elements • Electron configurations of each element are regular and consistent • Main group elements include: ...
... Main Group Elements • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 are known as main group elements • Electron configurations of each element are regular and consistent • Main group elements include: ...
The periodic table
... Periods correspond to energy levels. Increase as the period number increases. 18 groups Elements within each group share similar ...
... Periods correspond to energy levels. Increase as the period number increases. 18 groups Elements within each group share similar ...
modern chemistry section 4-1 review hapter 4 review
... (c) according to increasing atomic number (d) based on when they were discovered 2. Mendeleev noticed that properties of elements appeared at regular intervals when the elements were arranged in order of increasing . (a) density (c) atomic number (b) reactivity (d) atomic mass 3. The modern periodic ...
... (c) according to increasing atomic number (d) based on when they were discovered 2. Mendeleev noticed that properties of elements appeared at regular intervals when the elements were arranged in order of increasing . (a) density (c) atomic number (b) reactivity (d) atomic mass 3. The modern periodic ...
6-1-Periodic Law
... It was found that if Mendeleev's table was ordered by atomic number instead of atomic mass the inconsistencies in the table were eliminated. This is the blueprint for the modern periodic table. ...
... It was found that if Mendeleev's table was ordered by atomic number instead of atomic mass the inconsistencies in the table were eliminated. This is the blueprint for the modern periodic table. ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.