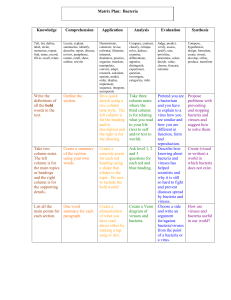
Agents of Disease
... • Mobility is by flagella, or “tail” • Most are soil inhabitants surviving on plant debris, but also in seeds, insects, and free‐ ...
... • Mobility is by flagella, or “tail” • Most are soil inhabitants surviving on plant debris, but also in seeds, insects, and free‐ ...
5echap10n16guidedreading
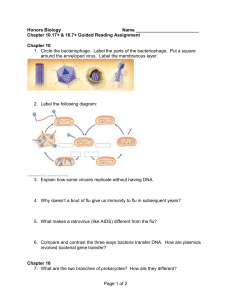
... Chapter 10.17+ & 16.7+ Guided Reading Assignment Chapter 10 1. Circle the bacteriophage. Label the parts of the bacteriophage. Put a square around the enveloped virus. Label the membranous layer. ...
... Chapter 10.17+ & 16.7+ Guided Reading Assignment Chapter 10 1. Circle the bacteriophage. Label the parts of the bacteriophage. Put a square around the enveloped virus. Label the membranous layer. ...
UNIT 5: Introduction to Virology
... UNIT 5: Introduction to Virology Virology and viruses Virology is the study of viruses and the diseases caused. Viruses are the minute entities that carry genetic information in one type of nucleic acid and require living cells for multiplication. Viral structure A virus consists of a nucleic acid g ...
... UNIT 5: Introduction to Virology Virology and viruses Virology is the study of viruses and the diseases caused. Viruses are the minute entities that carry genetic information in one type of nucleic acid and require living cells for multiplication. Viral structure A virus consists of a nucleic acid g ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... 8. Be familiar with the families of the viruses mentioned in class and the general characteristics of the virus (type of nucleic acid, whether or not it has an envelope, and the disease it causes). Use your notes and different chapters in the book to review information on the following viruses: Hepa ...
... 8. Be familiar with the families of the viruses mentioned in class and the general characteristics of the virus (type of nucleic acid, whether or not it has an envelope, and the disease it causes). Use your notes and different chapters in the book to review information on the following viruses: Hepa ...
Negative Sense RNA Viruses
... • Cleavage of sialic acid from cell membrane thus preventing binding by HA ...
... • Cleavage of sialic acid from cell membrane thus preventing binding by HA ...
Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus
... vomiting, backache, headache, sore eyes and photophobia. There may be nausea, vomiting and sore throat earlier on which may lead to diarrhea and generalized abdominal pain. ...
... vomiting, backache, headache, sore eyes and photophobia. There may be nausea, vomiting and sore throat earlier on which may lead to diarrhea and generalized abdominal pain. ...
QE GenKnowl Topics
... Name three viruses that cause diseases in man that do not fulfill Koch’s postulates. How was viral causality demonstrated in these cases? What is the difference between lysogeny and latency? What is the Hershey-Chase experiment? How did the study of lysogenic bacteriophages influence the concept of ...
... Name three viruses that cause diseases in man that do not fulfill Koch’s postulates. How was viral causality demonstrated in these cases? What is the difference between lysogeny and latency? What is the Hershey-Chase experiment? How did the study of lysogenic bacteriophages influence the concept of ...
Enter Topic Title in each section above
... A. Non-cellular; One nucleic acid; Polio; ‘Flu; Common cold; Leaf Obligate parasite; No metabolism; mosaic; AIDS or HIV; Mumps; Do not possess organelles Rubella; Rabies Q. What is meant by the term Q. Give a role of memory T-cells. immunity? A. The ability of the body to resist infection ...
... A. Non-cellular; One nucleic acid; Polio; ‘Flu; Common cold; Leaf Obligate parasite; No metabolism; mosaic; AIDS or HIV; Mumps; Do not possess organelles Rubella; Rabies Q. What is meant by the term Q. Give a role of memory T-cells. immunity? A. The ability of the body to resist infection ...
BACTERIA & VIRUSES - Bishop Shanahan High School
... becomes embedded into DNA of host and replicates with host DNA. Cell is ...
... becomes embedded into DNA of host and replicates with host DNA. Cell is ...
Viruses - OneDrive
... -Viruses are extremely small in size and measured in nanometers[nm] ,therefore, most viruses seen with electron microscope -Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites -Viruses are small and pass from the pores of bacterial filters that retain bacteria -Viruses have few enzymes, they depend on the ...
... -Viruses are extremely small in size and measured in nanometers[nm] ,therefore, most viruses seen with electron microscope -Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites -Viruses are small and pass from the pores of bacterial filters that retain bacteria -Viruses have few enzymes, they depend on the ...
Microbial Metabolism and Genetics Energy Production
... Cut/paste human and viral genes on plasmids Express “recombinant” plasmids in microbes ...
... Cut/paste human and viral genes on plasmids Express “recombinant” plasmids in microbes ...
Viruses
... Virulence is used to describe the ability of the virus to cause disease No antibiotic medications to cure viruses. Can be prevented by vaccines. Vaccines made from damaged virus (pathogen) that can no longer cause disease. ...
... Virulence is used to describe the ability of the virus to cause disease No antibiotic medications to cure viruses. Can be prevented by vaccines. Vaccines made from damaged virus (pathogen) that can no longer cause disease. ...
HOW HIV INFECTS CELLS
... There are typically 1 million T-cells per milliliter of blood. HIV slowly reduces the number of T-cells until the infected person develops the disease AIDS. Step 1 - HIV enters the host by attaching to specific host receptors. It is as if the virus has a specific key that only works on the host cell ...
... There are typically 1 million T-cells per milliliter of blood. HIV slowly reduces the number of T-cells until the infected person develops the disease AIDS. Step 1 - HIV enters the host by attaching to specific host receptors. It is as if the virus has a specific key that only works on the host cell ...
Morphology_and_physiology_of_viruses
... Acid type: RNA or DNA; single-stranded or double-stranded; strategy of replication. Size and morphology, including type of symmetry, number of capsomeres, and presence of membranes. Presence of specific enzymes, particularly RNA and DNA polymerases, and ...
... Acid type: RNA or DNA; single-stranded or double-stranded; strategy of replication. Size and morphology, including type of symmetry, number of capsomeres, and presence of membranes. Presence of specific enzymes, particularly RNA and DNA polymerases, and ...
African Horse Sickness
... African horse sickness (AHS) is a peracute, acute, subacute or mild infectious but non-contagious disease of equids caused by African horse sickness virus (AHSV). The virus is classified in the genus Orbivirus of the family Reoviridae, of which there are nine serotypes, all transmitted by Culicoides ...
... African horse sickness (AHS) is a peracute, acute, subacute or mild infectious but non-contagious disease of equids caused by African horse sickness virus (AHSV). The virus is classified in the genus Orbivirus of the family Reoviridae, of which there are nine serotypes, all transmitted by Culicoides ...
Teacher
... double-stranded DNA ( dsDNA ) : --- the commonest type of nucleic acid in viruses of human. 2) RNA: double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) : single-stranded RNA (ssRNA): --- the commonest type of nucleic acid in viruses of human.. +ssRNA : is the same as the viral mRNA ,can direct as viral mRNA -ssRNA: as a te ...
... double-stranded DNA ( dsDNA ) : --- the commonest type of nucleic acid in viruses of human. 2) RNA: double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) : single-stranded RNA (ssRNA): --- the commonest type of nucleic acid in viruses of human.. +ssRNA : is the same as the viral mRNA ,can direct as viral mRNA -ssRNA: as a te ...
Virus Structure Lecture PowerPoint
... science-related PowerPoints, articles and images. The site is designed to be a helpful resource for students, educators, and anyone interested in learning about science. • The SPO Virtual Classrooms offer many educational resources, including practice test questions, review questions, lecture PowerP ...
... science-related PowerPoints, articles and images. The site is designed to be a helpful resource for students, educators, and anyone interested in learning about science. • The SPO Virtual Classrooms offer many educational resources, including practice test questions, review questions, lecture PowerP ...
HOW HIV INFECTS CELLS
... HIV replicating cell. There are typically 1 million T-cells per milliliter of blood. HIV slowly reduces the number of T-cells until the infected person develops the disease AIDS. Step 1 - HIV enters the host by attaching to specific host receptors. It is as if the virus has a specific key that only ...
... HIV replicating cell. There are typically 1 million T-cells per milliliter of blood. HIV slowly reduces the number of T-cells until the infected person develops the disease AIDS. Step 1 - HIV enters the host by attaching to specific host receptors. It is as if the virus has a specific key that only ...
Odds for Controls
... insect vector. • When an insect vector is involved, the disease is also known as an arboviral disease. • However, not all arboviral diseases are zoonosis: where the transmission cycle takes place exclusively between insect vector and human e.g. dengue and urban yellow fever. • Examples of viral zoon ...
... insect vector. • When an insect vector is involved, the disease is also known as an arboviral disease. • However, not all arboviral diseases are zoonosis: where the transmission cycle takes place exclusively between insect vector and human e.g. dengue and urban yellow fever. • Examples of viral zoon ...
Health 3rd Quarterly Review Sheet
... Physical, Mental, Social Health and examples of each Stress, Eustress, Distress, Flight or Fight Self Esteem Communication Stimulant Depressant OTC Prescription Side Effect Addiction Withdrawal Mental Illness (Depression, Schizophrenia, Bi-polar, Concussion) Non-communicable diseases (heart disease, ...
... Physical, Mental, Social Health and examples of each Stress, Eustress, Distress, Flight or Fight Self Esteem Communication Stimulant Depressant OTC Prescription Side Effect Addiction Withdrawal Mental Illness (Depression, Schizophrenia, Bi-polar, Concussion) Non-communicable diseases (heart disease, ...
viruses
... Transcriptase to make DNA (will be covered later) Latent phase – inserts in host genome – 2 wks. - 20 years? – can’t see virus particles in bloodstream Infects cells – CD4+ T-cells (lymphocytes), macrophages Destroys immune system AIDS person frequently dies from 2ndary infection and/or cancer H ...
... Transcriptase to make DNA (will be covered later) Latent phase – inserts in host genome – 2 wks. - 20 years? – can’t see virus particles in bloodstream Infects cells – CD4+ T-cells (lymphocytes), macrophages Destroys immune system AIDS person frequently dies from 2ndary infection and/or cancer H ...
Microbes and Protists
... genetic material and protein and is unable to reproduce outside a living cell? A) virus B) fungus C) protist D) bacteria ...
... genetic material and protein and is unable to reproduce outside a living cell? A) virus B) fungus C) protist D) bacteria ...
Virus 1+2-summary+quiz2017-03-04 06:551.4 MB
... 3- what is the most common complication that could arise in children duo to influenza? ANS: Reyes syndrome ...
... 3- what is the most common complication that could arise in children duo to influenza? ANS: Reyes syndrome ...