* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Agents of Disease
Survey
Document related concepts
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Social history of viruses wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to viruses wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
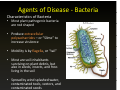
Agents of Disease ‐ g Bacteria Characteristics of Bacteria • Most plant pathogenic bacteria are rod shaped • Produce Produce extracellular extracellular polysacharrides – or “Slime” to increase virulence • Mobility is by flagella, or “tail” • Most are soil inhabitants surviving on plant debris, but also in seeds, insects, and free‐ , , living in the soil • Spread Spread by wind splashed water, by wind splashed water contaminated tools, vectors, and contaminated seeds Agents of Disease ‐ g Bacteria Agents of Disease ‐ g Bacteria Disease Cycle of Fireblight of Pome Fruits (Erwinia amylovora) Agents of Disease ‐ g Bacteria Disease Cycle of Fireblight of Pome Fruits (Erwinia amylovora) Agents of Disease ‐ g Bacteria Bacterial Diseases– Vegetables and Trees Olive Knot Halo Blight of Cucumber Crown Gall Bacterial Spot of Melon Agents of Disease ‐ Bacteria g Bacterial Diseases– Tomatoes Speck Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato Agents of Disease ‐ g Bacteria Bacterial Diseases– Tomatoes Bacterial Spot Xanthomonas campestris Agents of Disease ‐ g Bacteria Bacterial Diseases– Tomatoes Bacterial Canker Cl ib t michiganensis Clavibacter i hi i Agents of Disease Viruses Agents of Disease ‐ Characteristics of Viruses: • N Nucleoprotein l t i (is it really (i it ll living?) • Shortens the life of the plant – A true vampire! • Multiplies on in the host – needs cell “machinery” to reproduce d – Replicates by inserting DNA into plant’s DNA • Vary by size, but very, very, b b very small – Not visible by light microscopy • Not much is known about viruses that do not cause disease Agents of Disease ‐ g Viruses Characteristics of Viruses • Viruses are detected by symptoms on the plant th l t – Mottling, mosaics, spots, dwarfing, striping, leaf rolling, ring spots, and other weird stuff • Need a lab to “officially” diagnose a virus • Viruses “go with the flow,” usually causing systemic infections causing systemic infections • Survive in infected plant material, vectors and on surfaces vectors, and on surfaces • Transmitted by insect – fungi – h human – parasitic plant vectors, iti l t t root‐grafts, vegetative propagation, seeds, pollen. ELISA Diagnostic tool for Viruses ELISA Diagnostic tool for Viruses Agents of Disease ‐ g Viruses Agents of Disease ‐ Viruses Agents of Disease ‐ Viruses Tomato spotted wilt virus on Pepper Curly top on tomato Tomato spotted wilt virus Tomato spotted wilt virus Rose Mosaic Virus