Viruses - Hudson City School District
... form of brain damage that leads to a rapid decrease of mental function and movement. • You Tube The BSE Prion and Variant ...
... form of brain damage that leads to a rapid decrease of mental function and movement. • You Tube The BSE Prion and Variant ...
Virology study guide for mid
... 3. c. Direct introduction or translocation of viral genomes into the cytoplasm through channels in the plasma membrane e.g. non-enveloped viruses(Picornavirus). 4. Uncoating means:- the process where by the viral genome is released in a form suitable for transcription. Examples: 5. replication of DN ...
... 3. c. Direct introduction or translocation of viral genomes into the cytoplasm through channels in the plasma membrane e.g. non-enveloped viruses(Picornavirus). 4. Uncoating means:- the process where by the viral genome is released in a form suitable for transcription. Examples: 5. replication of DN ...
Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
... (Virus is always in a person, never goes away so always susceptible to cold sores) ...
... (Virus is always in a person, never goes away so always susceptible to cold sores) ...
Viruses
... 2. Viruses require a host organism, or living cell, to reproduce. 3. Viruses are parasites because they harm living cells. A virus has two basic parts: 1. a core of hereditary material 2. an outer coat of protein Viral Host Cell Infection 1. After a cell attaches to its host cell, it injects its her ...
... 2. Viruses require a host organism, or living cell, to reproduce. 3. Viruses are parasites because they harm living cells. A virus has two basic parts: 1. a core of hereditary material 2. an outer coat of protein Viral Host Cell Infection 1. After a cell attaches to its host cell, it injects its her ...
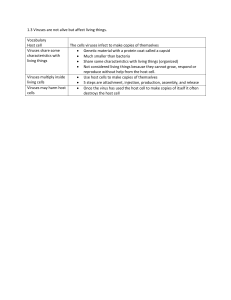
1.3 Viruses are not alive but affect living things. Vocabulary Host cell
... 1.3 Viruses are not alive but affect living things. Vocabulary Host cell Viruses share some characteristics with living things ...
... 1.3 Viruses are not alive but affect living things. Vocabulary Host cell Viruses share some characteristics with living things ...
Our selections for Fall 2005
... – Mixing of viruses that infect birds, pigs, produce new strains able to jump to humans. – New antigenic type leaves population unprotected – Numerous epidemics throughout history • Flu of 1918-1919 killed 20 million – Asia watched very carefully: bird flu? ...
... – Mixing of viruses that infect birds, pigs, produce new strains able to jump to humans. – New antigenic type leaves population unprotected – Numerous epidemics throughout history • Flu of 1918-1919 killed 20 million – Asia watched very carefully: bird flu? ...
Intro to Virology: March 15 2009
... developed the polio. 1910 Rous: identified the first oncogenic virus: avian flu he tested on birds and saw cancerous growths as a result he won a nobel prize for his discovery 50 years later 1915 Twort and dHerell identify bacteriophages viruses that infect bacteria 1935 Wendell Stanley crystalised ...
... developed the polio. 1910 Rous: identified the first oncogenic virus: avian flu he tested on birds and saw cancerous growths as a result he won a nobel prize for his discovery 50 years later 1915 Twort and dHerell identify bacteriophages viruses that infect bacteria 1935 Wendell Stanley crystalised ...
BACTERIA - Virus and Bacteria worksheet
... 5. ________________________ Made up of only protein only; cause of “Mad Cow disease” ...
... 5. ________________________ Made up of only protein only; cause of “Mad Cow disease” ...
Essential Knowledge 3.C.3: Viral replication results in genetic
... variation and viral infection can introduce genetic variation into the hosts. A. Viral replication differs from other reproductive strategies and generates genetic variation via various mechanisms. B. The reproductive cycles of viruses facilitate transfer of genetic information. ...
... variation and viral infection can introduce genetic variation into the hosts. A. Viral replication differs from other reproductive strategies and generates genetic variation via various mechanisms. B. The reproductive cycles of viruses facilitate transfer of genetic information. ...
notes chap. 24 virsuses - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
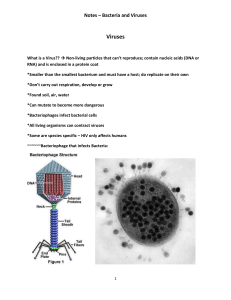
... Virulent – when a virus causes a disease Temperate – when a virus doesn’t cause disease right away (AIDS, cancer) Obligate intracellular parasite – (virus) must use a host for reproducing Nanometer (nm) – measurement for virus. 4000 can fit within a typed “o” ...
... Virulent – when a virus causes a disease Temperate – when a virus doesn’t cause disease right away (AIDS, cancer) Obligate intracellular parasite – (virus) must use a host for reproducing Nanometer (nm) – measurement for virus. 4000 can fit within a typed “o” ...
Viruses
... HIV doesn’t target just any cell, it goes right for the cells that want to kill it. “Helper" T cells are HIV's primary target. These cells help direct the immune system's response to various ...
... HIV doesn’t target just any cell, it goes right for the cells that want to kill it. “Helper" T cells are HIV's primary target. These cells help direct the immune system's response to various ...
4C Viruses
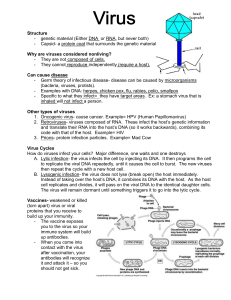
... 1. A virus is an obligate parasite that can only replicate inside another cell. Viruses are not living because they must live inside another cell and use the host’s machinery to reproduce and synthesize proteins. A virus consists of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) in a capsid (protein coat) and is much s ...
... 1. A virus is an obligate parasite that can only replicate inside another cell. Viruses are not living because they must live inside another cell and use the host’s machinery to reproduce and synthesize proteins. A virus consists of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) in a capsid (protein coat) and is much s ...
Chapter 5: Viruses and Monerans
... ignore its normal functions and to produce more virus particles instead. The virus particles then leave the host cell to infect other cells. 2. Would you classify viruses as living or nonliving? Explain. Arguments can be made for both sides. Because viruses are not cells, they cannot perform all the ...
... ignore its normal functions and to produce more virus particles instead. The virus particles then leave the host cell to infect other cells. 2. Would you classify viruses as living or nonliving? Explain. Arguments can be made for both sides. Because viruses are not cells, they cannot perform all the ...
What is a virus
... Why are viruses considered nonliving? - They are not composed of cells. - They cannot reproduce independently (require a host). Can cause disease - Germ theory of infectious disease- disease can be caused by microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, protists). - Examples with DNA: herpes, chicken pox, flu, ...
... Why are viruses considered nonliving? - They are not composed of cells. - They cannot reproduce independently (require a host). Can cause disease - Germ theory of infectious disease- disease can be caused by microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, protists). - Examples with DNA: herpes, chicken pox, flu, ...
Viruses - saddlespace.org
... Not capable of reproduction without a host So, are viruses living things? Most biologists say they are not…they are on the border of non-living and living. SPOOKY! ...
... Not capable of reproduction without a host So, are viruses living things? Most biologists say they are not…they are on the border of non-living and living. SPOOKY! ...
Viruses - Elgin Local Schools
... Viruses: Nucleic Acids: -DNA or RNA -single strand or double strand Capsid: proteins coat that enables infection of cell ...
... Viruses: Nucleic Acids: -DNA or RNA -single strand or double strand Capsid: proteins coat that enables infection of cell ...
Viruses - Elgin Local Schools
... Viruses: Nucleic Acids: -DNA or RNA -single strand or double strand Capsid: proteins coat that enables infection of cell ...
... Viruses: Nucleic Acids: -DNA or RNA -single strand or double strand Capsid: proteins coat that enables infection of cell ...
Viruses - Mr. Enns
... WANTED DEAD OR ALIVE?? Viruses are tiny, non-living particles that can reproduce ONLY inside a host cell. Viruses seem to be living because they can infect us and spread… ….but a virus has no nucleus and no organelles So its not classed as living! ...
... WANTED DEAD OR ALIVE?? Viruses are tiny, non-living particles that can reproduce ONLY inside a host cell. Viruses seem to be living because they can infect us and spread… ….but a virus has no nucleus and no organelles So its not classed as living! ...
viruses - Spanish Point Biology
... a) Attach – the ………..attaches to the …………….. of the host cell. b) Inject – the virus injects its ……….(or ……)through the cell wall/membrane into the host cell. c) Copy – the virus uses host cell’s ………. to copy its ………./RNA. d) Make – the virus uses the host cell’s ribosomes to make new ……… coats. e) ...
... a) Attach – the ………..attaches to the …………….. of the host cell. b) Inject – the virus injects its ……….(or ……)through the cell wall/membrane into the host cell. c) Copy – the virus uses host cell’s ………. to copy its ………./RNA. d) Make – the virus uses the host cell’s ribosomes to make new ……… coats. e) ...
20.1 viruses - OG
... 5. Once inside the viral genes are expressed. This may lead to the cells destruction. ...
... 5. Once inside the viral genes are expressed. This may lead to the cells destruction. ...