Surface Infrared Spectroscopic Study of ATP Synthesis in Mitochondria
... monitoring for ATP synthesis in mitochondria and its application to drug screening for mitochondrial toxicants. In the present study, we have monitored ATP synthesis in isolated mitochondria by using IRAS in the multiple internal reflection (MIR) geometry. We have constructed a system for real-time ...
... monitoring for ATP synthesis in mitochondria and its application to drug screening for mitochondrial toxicants. In the present study, we have monitored ATP synthesis in isolated mitochondria by using IRAS in the multiple internal reflection (MIR) geometry. We have constructed a system for real-time ...
Molecular Evolution and Structure of a
... a-Actinin is a ubiquitous actin cross-linker belonging to the spectrin superfamily (Blanchard, Ohanian, and Critchley 1989; Dubreuil 1991). It has been identified in most eukaryotic organisms, from human (Beggs et al. 1992; Mills et al. 2001) and mouse (Mills et al. 2001) to fly (Drosophila melanoga ...
... a-Actinin is a ubiquitous actin cross-linker belonging to the spectrin superfamily (Blanchard, Ohanian, and Critchley 1989; Dubreuil 1991). It has been identified in most eukaryotic organisms, from human (Beggs et al. 1992; Mills et al. 2001) and mouse (Mills et al. 2001) to fly (Drosophila melanoga ...
Design of gRNA and construction of gRNA expression vectors
... enhancer or silencer, the binding site of gRNA can directly be juxtaposed to the regions because of less probability of inhibition of their function. (b) The binding site should not be conserved among species because conserved regions are often binding sites of conserved binding molecules. In this r ...
... enhancer or silencer, the binding site of gRNA can directly be juxtaposed to the regions because of less probability of inhibition of their function. (b) The binding site should not be conserved among species because conserved regions are often binding sites of conserved binding molecules. In this r ...
Cell Host & Microbe
... and an early immune response, i.e., ROS production. BIK1 also associates with the PRR EFR that recognizes the bacterial elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu), as well as with PEPR1 and PEPR2, which are receptors of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) (Liu et al., 2013); therefore, it appears that BI ...
... and an early immune response, i.e., ROS production. BIK1 also associates with the PRR EFR that recognizes the bacterial elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu), as well as with PEPR1 and PEPR2, which are receptors of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) (Liu et al., 2013); therefore, it appears that BI ...
Spring 2008 - public.asu.edu
... particular interest for applications such as fuel cell electrolytes, bio-preservation media and pharmaceutical materials [1,2], to name only a few. Made by neutralizing a Brönsted acid with a Brönsted base of suitable pKa value, these protic ILs (PILs) may have either inorganic [3] or organic [4] ca ...
... particular interest for applications such as fuel cell electrolytes, bio-preservation media and pharmaceutical materials [1,2], to name only a few. Made by neutralizing a Brönsted acid with a Brönsted base of suitable pKa value, these protic ILs (PILs) may have either inorganic [3] or organic [4] ca ...
Towards the Discovery of New Antimicrobials: the Bifunctional
... [4] Zavascki, P., Carvalhaes, G., Picão, C., and Gales, C. (2010). Mul@drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii: resistance mechanisms and implica@ons for therapy. Expert Review of AnD-InfecDve Therapy, 8(1), pp. 71-93. [5] Schwartz, B., Markwalder, J., Seitz, S., Wang, Y ...
... [4] Zavascki, P., Carvalhaes, G., Picão, C., and Gales, C. (2010). Mul@drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii: resistance mechanisms and implica@ons for therapy. Expert Review of AnD-InfecDve Therapy, 8(1), pp. 71-93. [5] Schwartz, B., Markwalder, J., Seitz, S., Wang, Y ...
Ch. 10 - Photosynthesis
... Which of the following is NOT a product of the light reactions of photosynthesis? A. oxygen B. sugar C. NADPH D. ATP E. All of the above are products of the light reactions ...
... Which of the following is NOT a product of the light reactions of photosynthesis? A. oxygen B. sugar C. NADPH D. ATP E. All of the above are products of the light reactions ...
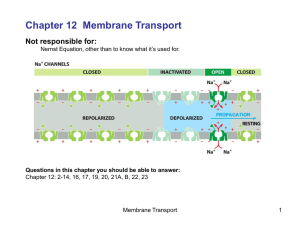
What is “membrane potential”
... Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
... Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
Print
... postulated membrane potential-regulated proton flux, and Hastings (4) illustrated this mechanism explicitly as a cartoon proton channel in 1978. Bioluminescent marine creatures like Noctiluca emit light when stimulated, producing nocturnal luminescence (5). This light is emitted from numerous small ...
... postulated membrane potential-regulated proton flux, and Hastings (4) illustrated this mechanism explicitly as a cartoon proton channel in 1978. Bioluminescent marine creatures like Noctiluca emit light when stimulated, producing nocturnal luminescence (5). This light is emitted from numerous small ...
Cell and Organelle Movement
... A. Myosin II, first identified in skeletal muscle, fig. 16-51 1. Responsible for generating force for muscle contraction and cytokenesis 2. Elongated protein composed of two heavy chains and two light chains a. Heavy chain composed of a globular head domain followed by an extended long amino acid se ...
... A. Myosin II, first identified in skeletal muscle, fig. 16-51 1. Responsible for generating force for muscle contraction and cytokenesis 2. Elongated protein composed of two heavy chains and two light chains a. Heavy chain composed of a globular head domain followed by an extended long amino acid se ...
The Cell Membrane
... It is the R groups of the amino acids that determine the location of the protein's side chains in a cell membrane. ...
... It is the R groups of the amino acids that determine the location of the protein's side chains in a cell membrane. ...
Anaerobic Protist Metabolism Amitochondriate Biochemistry
... formation to the respiratory chain (electron transport, membrane associated, O2 as final e- acceptor). As electrons move through complexes, a proton gradient is generated which drives ATP formation. Chemiosmotic theory - P. Mitchell, 1978. Substrate level phosphorylation - direct phosphorylation of ...
... formation to the respiratory chain (electron transport, membrane associated, O2 as final e- acceptor). As electrons move through complexes, a proton gradient is generated which drives ATP formation. Chemiosmotic theory - P. Mitchell, 1978. Substrate level phosphorylation - direct phosphorylation of ...
Name
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
The Light-Dependent Reactions: Generating ATP
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
8.3 122-125
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
Bio 8.3 HW Process of PS
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
... Describe what happens during the light-dependent reactions. Describe what happens during the light-independent reactions. Identify factors that affect the rate at which photosynthesis occurs. ...
View Full Text-PDF
... Majority of the problems in treating Tuberculosis (TB) is the appearance of drug resistant TB strains, including strains with multiple drug resistance (MDR) and more recently, strains with extensive drug resistance (XDR). From the various MDR mechanisms, main focus is on efflux pumps as they contrib ...
... Majority of the problems in treating Tuberculosis (TB) is the appearance of drug resistant TB strains, including strains with multiple drug resistance (MDR) and more recently, strains with extensive drug resistance (XDR). From the various MDR mechanisms, main focus is on efflux pumps as they contrib ...
Enzymes - A Level Notes
... temperature, so that if body temperature is raised, by fever or exercise, the enzymes are not denatured During hibernation, metabolism slows down so less energy is used pH - H+ ions may disrupt the hydrogen and ionic bonds that maintain the tertiary structure of the enzyme. The enzyme becomes de ...
... temperature, so that if body temperature is raised, by fever or exercise, the enzymes are not denatured During hibernation, metabolism slows down so less energy is used pH - H+ ions may disrupt the hydrogen and ionic bonds that maintain the tertiary structure of the enzyme. The enzyme becomes de ...
Open questions in the origin of eukaryotes
... Large genomes, e.g. Myxococcus xanthus (9.14 Mb): >1500 selective specific duplications: • cell‐cell signaling • small molecule signaling • integrative transcription control ...
... Large genomes, e.g. Myxococcus xanthus (9.14 Mb): >1500 selective specific duplications: • cell‐cell signaling • small molecule signaling • integrative transcription control ...
How Do Plant Mitochondria Avoid Importing Chloroplast Proteins
... known sizes of subunits in the yeast complex. In particular, no homologs of Tom37 or Tom22 were apparent and there was an additional protein of around 9 kD. The absence of Tom37 from the plant complex was not so surprising, since this subunit is also missing from the N. crassa complex, and the Tom37 ...
... known sizes of subunits in the yeast complex. In particular, no homologs of Tom37 or Tom22 were apparent and there was an additional protein of around 9 kD. The absence of Tom37 from the plant complex was not so surprising, since this subunit is also missing from the N. crassa complex, and the Tom37 ...
5_Muscle
... What molecule serves as the energy source for fermentation? Where does the muscle cell get these molecules? ...
... What molecule serves as the energy source for fermentation? Where does the muscle cell get these molecules? ...
Ion Channel Structure and Function (part 1)
... Location: plasma membrane of excitable and non-excitable cells Function: as a generalization, Kir help maintain the resting membrane potential and control excitability of neurons and muscle cells; transepithelial K+ transport (Kir1.1, Kir7.1), G protein coupled (serotonin, metabotropic glutamate, et ...
... Location: plasma membrane of excitable and non-excitable cells Function: as a generalization, Kir help maintain the resting membrane potential and control excitability of neurons and muscle cells; transepithelial K+ transport (Kir1.1, Kir7.1), G protein coupled (serotonin, metabotropic glutamate, et ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... and specificity of enzymes Binding energy (GB)--- the energy derived from enzyme-substrate interaction 1. Much of the catalytic power of enzymes is ultimately derived from the free energy released in forming multiple weak bonds and interactions between an enzyme and its substrate. This binding ener ...
... and specificity of enzymes Binding energy (GB)--- the energy derived from enzyme-substrate interaction 1. Much of the catalytic power of enzymes is ultimately derived from the free energy released in forming multiple weak bonds and interactions between an enzyme and its substrate. This binding ener ...
Leukaemia Section Acute basophilic leukemia / t(X;6)(p11;q23) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Molecular cytogenetics (FISH) revealed unbalanced and more complex rearrangements than those observed on karyotype (see Table 1 above). ...
... Molecular cytogenetics (FISH) revealed unbalanced and more complex rearrangements than those observed on karyotype (see Table 1 above). ...
P-type ATPase

The P-type ATPases, also known as E1-E2 ATPases, are a large group of evolutionarily related ion and lipid pumps that are found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. They are α-helical bundle primary transporters referred to as P-type ATPases because they catalyze auto- (or self-) phosphorylation of a key conserved aspartate residue within the pump. In addition, they all appear to interconvert between at least two different conformations, denoted by E1 and E2.Most members of this transporter family are specific for the pumping of a large array of cations, however one subfamily is involved in flipping phospholipids to maintain the asymmetric nature of the biomembrane.Prominent examples of P-type ATPases are the sodium-potassium pump (Na+,K+-ATPase), the plasma membrane proton pump (H+-ATPase), the proton-potassium pump (H+,K+-ATPase), and the calcium pump (Ca2+-ATPase).