How Microcurrent Stimulation Produces ATP – One
... ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecules are the storage and distribution vehicles for energy in the body. The breakdown of ATP into ADP yields energy. It is the cleaving of the phosphate bond that yields the energy. This energy is utilized in almost all energy related cellular reactions. In addition ...
... ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecules are the storage and distribution vehicles for energy in the body. The breakdown of ATP into ADP yields energy. It is the cleaving of the phosphate bond that yields the energy. This energy is utilized in almost all energy related cellular reactions. In addition ...
Enzymes
... 2. pH also influences the reaction rate, each enzyme has an optimal pH falls between pH 6 - 8 for most enzymes. ...
... 2. pH also influences the reaction rate, each enzyme has an optimal pH falls between pH 6 - 8 for most enzymes. ...
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
... Analyze: Why are protists, plants, fungi and animals classified into the same domain but into different kingdoms? The Tree of Life The most recent classification system divides life into three domains, which include six kingdoms. The distances between branches are proportional to the number of diffe ...
... Analyze: Why are protists, plants, fungi and animals classified into the same domain but into different kingdoms? The Tree of Life The most recent classification system divides life into three domains, which include six kingdoms. The distances between branches are proportional to the number of diffe ...
University of Groningen Archaeal type IV prepilin-like signal
... be universally conserved (169), and functions at the cytoplasmic membrane of prokaryotes, the chloroplast thylakoid membrane, and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of eukaryotes (Figure 2). It consists of a protein-targeting pathway and a multisubunit protein-translocase complex that mediates the trans ...
... be universally conserved (169), and functions at the cytoplasmic membrane of prokaryotes, the chloroplast thylakoid membrane, and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of eukaryotes (Figure 2). It consists of a protein-targeting pathway and a multisubunit protein-translocase complex that mediates the trans ...
Cell transport with the environment
... Osmosis: The process of diffusion involving only the water molecule. Water molecules still move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without the involvement of ATP. ...
... Osmosis: The process of diffusion involving only the water molecule. Water molecules still move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without the involvement of ATP. ...
PREVIEW_on_Ng_etal_STRUCTURE-MK
... Pathogenic bacteria employ a plethora of virulence factors to disrupt the function of infected host cells (Dubin et al, 2013). Among such factors are the AB5 toxins, which are complexes between five copies of a B subunit employed for attachment to the host plasma membrane and a single catalytic A s ...
... Pathogenic bacteria employ a plethora of virulence factors to disrupt the function of infected host cells (Dubin et al, 2013). Among such factors are the AB5 toxins, which are complexes between five copies of a B subunit employed for attachment to the host plasma membrane and a single catalytic A s ...
Ch. 27 & 28 Notes
... Including places too acidic, too salty, too cold, or too hot for most other organisms ...
... Including places too acidic, too salty, too cold, or too hot for most other organisms ...
A planarian has a mutation that affects mitochondria. The planarian
... (C) The mitochondrion from planarian Y does not have a large enough surface area to hold electron-transferring proteins and is unable to adequately oxidize NADH and FADH2 to generate enough ATP. ...
... (C) The mitochondrion from planarian Y does not have a large enough surface area to hold electron-transferring proteins and is unable to adequately oxidize NADH and FADH2 to generate enough ATP. ...
Cell Energy Part 1 – ATP
... consumed & regenerated per second, per cell! (600 million molecules per minute!) If ATP was not continuously regenerated, you would need to consume an amount roughly equal to your bodyweight every day to meet the energy needs of your cells! ...
... consumed & regenerated per second, per cell! (600 million molecules per minute!) If ATP was not continuously regenerated, you would need to consume an amount roughly equal to your bodyweight every day to meet the energy needs of your cells! ...
Chapter18_Section03_edit
... The three domains are: • Eukarya, which is composed of protists, fungi, plants, and animals. • Bacteria, which corresponds to the kingdom Eubacteria. • Archaea, which corresponds to the kingdom Archaebacteria. ...
... The three domains are: • Eukarya, which is composed of protists, fungi, plants, and animals. • Bacteria, which corresponds to the kingdom Eubacteria. • Archaea, which corresponds to the kingdom Archaebacteria. ...
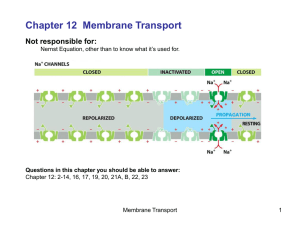
What is “membrane potential”
... Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
... Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
9700/04 - StudyGuide.PK
... (a) Describe the importance of ATP in cells, giving two examples of processes in which it is used. ...
... (a) Describe the importance of ATP in cells, giving two examples of processes in which it is used. ...
Name of Student: Dominik Sommerfeld
... comparing predicted consensus sequences with known substrate sequences, it has yet to be validated empirically by in vitro assays. Methodology: To test the accuracy of our algorithm, we used the PSSM for each of 488 typical human protein kinases to generate a list of ‘optimal’ substrate peptide sequ ...
... comparing predicted consensus sequences with known substrate sequences, it has yet to be validated empirically by in vitro assays. Methodology: To test the accuracy of our algorithm, we used the PSSM for each of 488 typical human protein kinases to generate a list of ‘optimal’ substrate peptide sequ ...
Outline for Lecture #5
... Becker fig. 8-5 (8-6). This allows you to find out what sort of protein (if any) is involved in transport. 1. If an enzyme-like protein (carrier or pump) is involved in transport, curve will be hyperbolic -- carrier or pump protein will saturate at high [X] just as an enzyme does. Why? If [X] is hi ...
... Becker fig. 8-5 (8-6). This allows you to find out what sort of protein (if any) is involved in transport. 1. If an enzyme-like protein (carrier or pump) is involved in transport, curve will be hyperbolic -- carrier or pump protein will saturate at high [X] just as an enzyme does. Why? If [X] is hi ...
enzymes
... • Substrate - The molecule that the enzyme attaches to • Active site - The spot on the enzyme that fits into the substrate ...
... • Substrate - The molecule that the enzyme attaches to • Active site - The spot on the enzyme that fits into the substrate ...
pdf file
... and the plasma membrane. Here, we report the identification of COD1/SPF1 (control of HMGCoA reductase degradation/SPF1) through genetic strategies intended to uncover genes involved in protein maturation and endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated degradation (ERAD), a quality control pathway that rid ...
... and the plasma membrane. Here, we report the identification of COD1/SPF1 (control of HMGCoA reductase degradation/SPF1) through genetic strategies intended to uncover genes involved in protein maturation and endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated degradation (ERAD), a quality control pathway that rid ...
– Cytoplasmic inclusions Liver, Hepatocyte
... artifact especially common in male rats that are not completely exsanguinated at necropsy. The cytoplasmic vacuoles contain plasma that has entered the hepatocyte cytoplasm (plasma influx) of affected hepatocytes (Li et al. 2003). Similar but more discrete eosinophilic hyalinized inclusions, which m ...
... artifact especially common in male rats that are not completely exsanguinated at necropsy. The cytoplasmic vacuoles contain plasma that has entered the hepatocyte cytoplasm (plasma influx) of affected hepatocytes (Li et al. 2003). Similar but more discrete eosinophilic hyalinized inclusions, which m ...
The Role of Enzymes in Maintaining Homeostasis • All enzymes are
... o Where else have we seen structures in a cell that rely on specificity? Cell membrane receptors (like antennae sticking out of cell membrane) have specific shapes that only recognize certain molecules controlling what enters and leaves the cell and allows for communication with other cells o Lock a ...
... o Where else have we seen structures in a cell that rely on specificity? Cell membrane receptors (like antennae sticking out of cell membrane) have specific shapes that only recognize certain molecules controlling what enters and leaves the cell and allows for communication with other cells o Lock a ...
Missy Cavallin September 14, 2007
... Lower the effectiveness of excitatory inputs on a cell when open Delayed rectifier type expressed in axons ...
... Lower the effectiveness of excitatory inputs on a cell when open Delayed rectifier type expressed in axons ...
2MemTrans
... B. potassium ions flow into the dendrite. C. voltage-gated Ca - channels open in the post-synaptic membrane. D. voltage-gated K - channels close along the axon. E. ligand-gated Na - channels open in the post-synaptic membrane. 3. A patch-clamp device is used to: A. measure the strength of an electro ...
... B. potassium ions flow into the dendrite. C. voltage-gated Ca - channels open in the post-synaptic membrane. D. voltage-gated K - channels close along the axon. E. ligand-gated Na - channels open in the post-synaptic membrane. 3. A patch-clamp device is used to: A. measure the strength of an electro ...
Biomarkers_04-Mechanisms-Membranes
... (similar logP higher toxicity, i.e. higher Values of 1/EC50 in comparison to neutral organics) ...
... (similar logP higher toxicity, i.e. higher Values of 1/EC50 in comparison to neutral organics) ...
A GTPase gate for protein import into chloroplasts
... in the dimer. Thus, a significant conformational shift or perhaps dimer dissociation may be required for GDP/GTP exchange. As a consequence, the conformational state of Toc34 may be directly regulated by bound nucleotide. It is tempting to speculate that this shift coupled with subsequent dimer-acti ...
... in the dimer. Thus, a significant conformational shift or perhaps dimer dissociation may be required for GDP/GTP exchange. As a consequence, the conformational state of Toc34 may be directly regulated by bound nucleotide. It is tempting to speculate that this shift coupled with subsequent dimer-acti ...
Surface Infrared Spectroscopic Study of ATP Synthesis in Mitochondria
... monitoring for ATP synthesis in mitochondria and its application to drug screening for mitochondrial toxicants. In the present study, we have monitored ATP synthesis in isolated mitochondria by using IRAS in the multiple internal reflection (MIR) geometry. We have constructed a system for real-time ...
... monitoring for ATP synthesis in mitochondria and its application to drug screening for mitochondrial toxicants. In the present study, we have monitored ATP synthesis in isolated mitochondria by using IRAS in the multiple internal reflection (MIR) geometry. We have constructed a system for real-time ...
P-type ATPase

The P-type ATPases, also known as E1-E2 ATPases, are a large group of evolutionarily related ion and lipid pumps that are found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. They are α-helical bundle primary transporters referred to as P-type ATPases because they catalyze auto- (or self-) phosphorylation of a key conserved aspartate residue within the pump. In addition, they all appear to interconvert between at least two different conformations, denoted by E1 and E2.Most members of this transporter family are specific for the pumping of a large array of cations, however one subfamily is involved in flipping phospholipids to maintain the asymmetric nature of the biomembrane.Prominent examples of P-type ATPases are the sodium-potassium pump (Na+,K+-ATPase), the plasma membrane proton pump (H+-ATPase), the proton-potassium pump (H+,K+-ATPase), and the calcium pump (Ca2+-ATPase).