Receptors
... green or blue vs yellow) – Sensations of one color (e.g., red) inhibits sensation of its complementary color (i.e., green) – Explains negative afterimages & color blindness ...
... green or blue vs yellow) – Sensations of one color (e.g., red) inhibits sensation of its complementary color (i.e., green) – Explains negative afterimages & color blindness ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a certain threshold potential, the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a ...
... This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a certain threshold potential, the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a ...
Technical Definitions
... This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a certain threshold potential, the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a ...
... This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a certain threshold potential, the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a ...
Lecture ppt 1 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... • Two regions with additional gray called “cortex” ________________________________ – Cerebrum: “cerebral cortex” – Cerebellum: “cerebellar cortex” ...
... • Two regions with additional gray called “cortex” ________________________________ – Cerebrum: “cerebral cortex” – Cerebellum: “cerebellar cortex” ...
nervous system
... and relays that information to the proper region of the cerebrum for further processing e.) Hypothalamus: control center for recognition and analysis for hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temperature; also controls the coordination of the nervous and endocrine system 2. Spinal Cord: main comm ...
... and relays that information to the proper region of the cerebrum for further processing e.) Hypothalamus: control center for recognition and analysis for hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temperature; also controls the coordination of the nervous and endocrine system 2. Spinal Cord: main comm ...
Chapter 16A
... • Visceral pain is usually felt in or just under the skin that overlies the stimulated organ (referred pain) – localized damage (cutting) intestines may cause no pain, but diffuse visceral stimulation can be severe • distension of a bile duct from a gallstone • distension of the ureter from a ki ...
... • Visceral pain is usually felt in or just under the skin that overlies the stimulated organ (referred pain) – localized damage (cutting) intestines may cause no pain, but diffuse visceral stimulation can be severe • distension of a bile duct from a gallstone • distension of the ureter from a ki ...
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
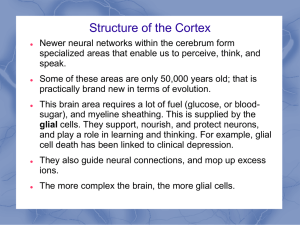
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
Slide ()
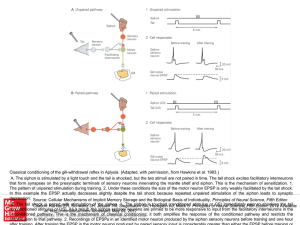
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
The Brain ppt module 4
... receives electrcal signals from receptors in the eye and changes them to basic visual sensation (ie light, shadow, texture) Visual Association Cortex interprets the basic sensations into complete meaningful perceptions such as people, objects or animals ...
... receives electrcal signals from receptors in the eye and changes them to basic visual sensation (ie light, shadow, texture) Visual Association Cortex interprets the basic sensations into complete meaningful perceptions such as people, objects or animals ...
The Nervous System - Centennial Christian School
... The Brain • Brain weighs about 3 pounds • Has hundreds of billions of neurons • You had the maximum number of neurons when you were born • 1000’s of neurons are lost every day and are never replaced • Don’t notice this until later in life when the loss is so large – This is why elderly people often ...
... The Brain • Brain weighs about 3 pounds • Has hundreds of billions of neurons • You had the maximum number of neurons when you were born • 1000’s of neurons are lost every day and are never replaced • Don’t notice this until later in life when the loss is so large – This is why elderly people often ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... released into the water. If the platform is removed, the normal animal will spend most of his time searching in the quadrant where the platform should be. Learning of this sort of spatial map depends on the hippocampus. If a genetically altered rat with a malfunctioning hippocampus is given the same ...
... released into the water. If the platform is removed, the normal animal will spend most of his time searching in the quadrant where the platform should be. Learning of this sort of spatial map depends on the hippocampus. If a genetically altered rat with a malfunctioning hippocampus is given the same ...
File
... • An impulse is sent to the spinal cord and acted on immediately. This impulse uses a pathway know as a reflex arc which does not involve the brain directly. • A message is sent to the brain shortly afterwards. • Actions that need to be carried out automatically and without thinking are very fast be ...
... • An impulse is sent to the spinal cord and acted on immediately. This impulse uses a pathway know as a reflex arc which does not involve the brain directly. • A message is sent to the brain shortly afterwards. • Actions that need to be carried out automatically and without thinking are very fast be ...
Mental activities
... change the environment so the signal can penetrate a cluttered environment ...
... change the environment so the signal can penetrate a cluttered environment ...
Clinicals - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Rapidly developing loss of cerebral function lasting more than 24 hours due to cerebrovascular disturbance. Extent of recovery varies. ...
... Rapidly developing loss of cerebral function lasting more than 24 hours due to cerebrovascular disturbance. Extent of recovery varies. ...
Unit 8 Review Sheet[1]
... - Retinal Disparity: Your brain receives two images of the world that are different your brain makes them one image. Monocular Cues: Depth cues that are available to either eye alone. Allows you to judge distance between objects. Optical Illusions: Why do they happen? (Physiological and cognitive) - ...
... - Retinal Disparity: Your brain receives two images of the world that are different your brain makes them one image. Monocular Cues: Depth cues that are available to either eye alone. Allows you to judge distance between objects. Optical Illusions: Why do they happen? (Physiological and cognitive) - ...
The Neuron - University of Connecticut
... CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES (or CEREBRUM): corpus callosum: connects hemispheres each hemisphere controls OPPOSITE SIDE of body cerebral cortex (= skin or bark): 1 to 3 mm thick; 2 or 3 ft square if flattened out higher motor, sensory, and intellectual functions ...
... CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES (or CEREBRUM): corpus callosum: connects hemispheres each hemisphere controls OPPOSITE SIDE of body cerebral cortex (= skin or bark): 1 to 3 mm thick; 2 or 3 ft square if flattened out higher motor, sensory, and intellectual functions ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... large bundle of neural fibers (myelinated axons, or white matter) connecting the two hemispheres ...
... large bundle of neural fibers (myelinated axons, or white matter) connecting the two hemispheres ...
Biology 232
... sensation – conscious or subconscious awareness of internal or external stimuli perception – conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations (occurs in thalamus and cerebral cortex) Basic Sensory Pathway 1) sensory receptor – specialized cell or dendrites that detect stimuli stimulus – change i ...
... sensation – conscious or subconscious awareness of internal or external stimuli perception – conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations (occurs in thalamus and cerebral cortex) Basic Sensory Pathway 1) sensory receptor – specialized cell or dendrites that detect stimuli stimulus – change i ...
Allochiria

Allochiria (from the Greek meaning ""other hand"") is a neurological disorder in which the patient responds to stimuli presented to one side of their body as if the stimuli had been presented at the opposite side. It is associated with spatial transpositions, usually symmetrical, of stimuli from one side of the body (or of the space) to the opposite one. Thus a touch to the left arm will be reported as a touch to the right arm, which is also known as somatosensory allochiria. If the auditory or visual senses are affected, sounds (a person's voice for instance) will be reported as being heard on the opposite side to that on which they occur and objects presented visually will be reported as having been presented on the opposite side. Often patients may express allochiria in their drawing while copying an image. Allochiria often co-occurs with unilateral neglect and, like hemispatial neglect, the disorder arises commonly from damage to the right parietal lobe.Allochiria is often confused with alloesthesia, also known as false allochiria. True allochiria is a symptom of dyschiria and unilateral neglect. Dyschiria is a disorder in the localization of sensation due to various degrees of dissociation and cause impairment in one side causing the inability to tell which side of the body was touched.
















![Unit 8 Review Sheet[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001686639_1-accaddf9a4bef8f1f5e508cc8efafb82-300x300.png)