General Neurophysiology - Department of Physiology
... near its nest back to the others with its beak. The sight of the displaced egg triggers this mechanism. If the egg is taken away, the animal continues with the behavior, pulling its head back as if an imaginary egg is still being maneuvered by the underside of its beak ...
... near its nest back to the others with its beak. The sight of the displaced egg triggers this mechanism. If the egg is taken away, the animal continues with the behavior, pulling its head back as if an imaginary egg is still being maneuvered by the underside of its beak ...
A.P. Psychology 4 (E)
... Vestibular Sense: o The sense of body movement and position, including the sense of balance o Located in the inner ear ...
... Vestibular Sense: o The sense of body movement and position, including the sense of balance o Located in the inner ear ...
Seriousness/Agitation/Sadness or Depression
... Because drugs take 3-4 weeks for full effect, it is essential that patients continue to take their medication, even though in the beginning they may not see any difference in their mental state. Some of these drugs can cause dryness of the mouth, blurring of vision and constipation which settle down ...
... Because drugs take 3-4 weeks for full effect, it is essential that patients continue to take their medication, even though in the beginning they may not see any difference in their mental state. Some of these drugs can cause dryness of the mouth, blurring of vision and constipation which settle down ...
Slide ()
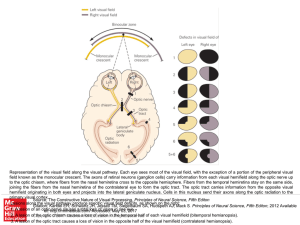
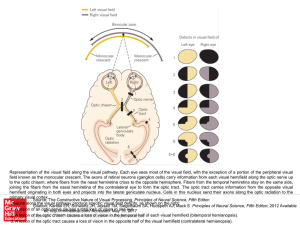
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
1 Central Nervous System: Brain one of largest organs in body (~3
... sensory processing areas a. primary sensory (somatosensory) cortex receives information from skin sensors when stimulated patient reports “feeling” in some part of body muscle, tendon and joint sensations, and touch provides feedback to motor cortex spatial discrimination motor and sensory cortex, l ...
... sensory processing areas a. primary sensory (somatosensory) cortex receives information from skin sensors when stimulated patient reports “feeling” in some part of body muscle, tendon and joint sensations, and touch provides feedback to motor cortex spatial discrimination motor and sensory cortex, l ...
The Nervous System - Science with Mr. Enns
... A reflex is a rapid, automatic response that happens without conscious control. Reflexes protect the body from harm. Reflexes are complex actions that bypass the brain They involve the spinal cord and other nerves ONLY ...
... A reflex is a rapid, automatic response that happens without conscious control. Reflexes protect the body from harm. Reflexes are complex actions that bypass the brain They involve the spinal cord and other nerves ONLY ...
Flash Card Fever!
... action of a neurotransmitter chemical that opposes the action of a neurotransmitter increases the likelihood that a neuron will fire decreases the likelihood that a neuron will fire voltage change at the receptor site on a ...
... action of a neurotransmitter chemical that opposes the action of a neurotransmitter increases the likelihood that a neuron will fire decreases the likelihood that a neuron will fire voltage change at the receptor site on a ...
Introduction to Perception
... Figure 1.4 Comparison of signal transmission by cell phone and the nervous system. (a) Cell phone #1 sends an electrical signal that stands for “hello.” The signal that reaches cell phone #2 is the same as the signal sent from cell phone #1. (b) The nervous system sends electrical signals that stan ...
... Figure 1.4 Comparison of signal transmission by cell phone and the nervous system. (a) Cell phone #1 sends an electrical signal that stands for “hello.” The signal that reaches cell phone #2 is the same as the signal sent from cell phone #1. (b) The nervous system sends electrical signals that stan ...
session1vocabulary
... The messages carried by neurons. Consists of both electrical (along the nerve) and chemical (across the "gap"). Pain impulse, pleasure impulse, hot or cold. Dendrite The thread like extension on a neuron carrying impulses towards the cell body. The "top" part of the nerve ...
... The messages carried by neurons. Consists of both electrical (along the nerve) and chemical (across the "gap"). Pain impulse, pleasure impulse, hot or cold. Dendrite The thread like extension on a neuron carrying impulses towards the cell body. The "top" part of the nerve ...
Disorders of the Nervous System
... The space between the arachnoid and pia mater contains cerebrospinal fluid – CSF, which protects the organs from injury. It is formed in capillaries that filter fluid from blood circulating in the brain and is collected in four cavities within the cerebral hemisphere called ventricles. The average a ...
... The space between the arachnoid and pia mater contains cerebrospinal fluid – CSF, which protects the organs from injury. It is formed in capillaries that filter fluid from blood circulating in the brain and is collected in four cavities within the cerebral hemisphere called ventricles. The average a ...
Stimulus Control of Operant Behavior
... Some procedures include delayed matching to sample – Matching accuracy decreases as a function of time ...
... Some procedures include delayed matching to sample – Matching accuracy decreases as a function of time ...
Afferent (Sensory) Division Part 1
... – Ion channels or second messengers that initiate membrane potential change is sensory receptors – Depolarizations trigger impulses to the CNS ...
... – Ion channels or second messengers that initiate membrane potential change is sensory receptors – Depolarizations trigger impulses to the CNS ...
Bio 111 Lab 8: The Nervous System and the Senses
... (or areas): frontal (solving problems, making decisions about appropriate behavior, planning), parietal (expressing thoughts and feelings), temporal (hearing, converting sensory information into memory), occipital (vision). The two hemispheres of the cerebrum engage in different activities: the left ...
... (or areas): frontal (solving problems, making decisions about appropriate behavior, planning), parietal (expressing thoughts and feelings), temporal (hearing, converting sensory information into memory), occipital (vision). The two hemispheres of the cerebrum engage in different activities: the left ...
unit 2 – nervous system / senses - Greater Atlanta Christian Schools
... 1. resting membrane potential – describes an unstimulated neuron -“polarized” b/c of electrical charge difference that exists on each side of the cell membrane - inside cell: -ve ; high amt. of K+ - outside cell: +ve; high amt of Na+ - cell membrane permeability K+ > Na+ - Na+/ K+ exchange pump ...
... 1. resting membrane potential – describes an unstimulated neuron -“polarized” b/c of electrical charge difference that exists on each side of the cell membrane - inside cell: -ve ; high amt. of K+ - outside cell: +ve; high amt of Na+ - cell membrane permeability K+ > Na+ - Na+/ K+ exchange pump ...
the nervous system powerpoint
... controled by motor area Right hemisphere controls left side of body Left hemisphere controls right side Motor nerves cross sides in spinal cord ...
... controled by motor area Right hemisphere controls left side of body Left hemisphere controls right side Motor nerves cross sides in spinal cord ...
How Exposure Therapy Works
... Exposure therapy is a way of treating phobias and other conditions, like PTSD, by having the patient experience their fear over time, reducing the psychophysiological response ...
... Exposure therapy is a way of treating phobias and other conditions, like PTSD, by having the patient experience their fear over time, reducing the psychophysiological response ...
physio unit 9 [4-20
... = inability to judge neither shape nor form (bilateral destruction of somatosensory area 1) Amorphosynthesis = inability to recognize complex objects on the opposite side of the lesion from unilateral destruction of the somatosensory association area Weber-Fechner principle Discrimination ability of ...
... = inability to judge neither shape nor form (bilateral destruction of somatosensory area 1) Amorphosynthesis = inability to recognize complex objects on the opposite side of the lesion from unilateral destruction of the somatosensory association area Weber-Fechner principle Discrimination ability of ...
General Psychology - K-Dub
... •Now start your right foot doing the same motion synchronized with the hand. ...
... •Now start your right foot doing the same motion synchronized with the hand. ...
From Vision to Movement
... reverse everything you see left-to-right. You will even see your hand reversed, but of course the real objects are still in the same place so you have to learn to reach opposite to what you see. We have ...
... reverse everything you see left-to-right. You will even see your hand reversed, but of course the real objects are still in the same place so you have to learn to reach opposite to what you see. We have ...
Allochiria

Allochiria (from the Greek meaning ""other hand"") is a neurological disorder in which the patient responds to stimuli presented to one side of their body as if the stimuli had been presented at the opposite side. It is associated with spatial transpositions, usually symmetrical, of stimuli from one side of the body (or of the space) to the opposite one. Thus a touch to the left arm will be reported as a touch to the right arm, which is also known as somatosensory allochiria. If the auditory or visual senses are affected, sounds (a person's voice for instance) will be reported as being heard on the opposite side to that on which they occur and objects presented visually will be reported as having been presented on the opposite side. Often patients may express allochiria in their drawing while copying an image. Allochiria often co-occurs with unilateral neglect and, like hemispatial neglect, the disorder arises commonly from damage to the right parietal lobe.Allochiria is often confused with alloesthesia, also known as false allochiria. True allochiria is a symptom of dyschiria and unilateral neglect. Dyschiria is a disorder in the localization of sensation due to various degrees of dissociation and cause impairment in one side causing the inability to tell which side of the body was touched.