The Crusades - WordPress.com
... The Holy Roman Empire was neither holy, nor Roman, nor an empire because A. The emperors were not crowned by the popes B. The byzantine emperors did not acknowledge the Holy Roman empire C. The people who lived there did not practice Christianity D. It did not restore imperial unity to Western Europ ...
... The Holy Roman Empire was neither holy, nor Roman, nor an empire because A. The emperors were not crowned by the popes B. The byzantine emperors did not acknowledge the Holy Roman empire C. The people who lived there did not practice Christianity D. It did not restore imperial unity to Western Europ ...
PPT Lecture 12 The Byzantine Empire and Western
... decline of old warbands as many could not afford the best equipment (chainmail, warhorse, sword and lance) ...
... decline of old warbands as many could not afford the best equipment (chainmail, warhorse, sword and lance) ...
Schedule 9/14/10
... Answer the Question, How did Feudalism and the Manor economy emerge and shape medieval life? ...
... Answer the Question, How did Feudalism and the Manor economy emerge and shape medieval life? ...
The Decline of Empires - Rincon History Department
... Consequences of Gupta decline • Regionalism continued • Hun invaders become Hindu, incorporated into warrior caste. – Hun leaders ruled regional territories ...
... Consequences of Gupta decline • Regionalism continued • Hun invaders become Hindu, incorporated into warrior caste. – Hun leaders ruled regional territories ...
Byzantine Empire
... 5. What is the name of the area that Greece is located in? 6. What was the capital of the Eastern Empire? 7. Use the map on the next page. What name does this city become in the Middle Ages? 8. See slide 14 to find out what is the city’s name today. ...
... 5. What is the name of the area that Greece is located in? 6. What was the capital of the Eastern Empire? 7. Use the map on the next page. What name does this city become in the Middle Ages? 8. See slide 14 to find out what is the city’s name today. ...
Byzantine Empire
... 5. What is the name of the area that Greece is located in? 6. What was the capital of the Eastern Empire? 7. Use the map on the next page. What name does this city become in the Middle Ages? 8. See slide 14 to find out what is the city’s name today. ...
... 5. What is the name of the area that Greece is located in? 6. What was the capital of the Eastern Empire? 7. Use the map on the next page. What name does this city become in the Middle Ages? 8. See slide 14 to find out what is the city’s name today. ...
topic 8 Early Middle Ages and East Asia
... After the fall of the Western Roman Empire Europe was in disorder and change During 400-1500AD the world was in transition and this period is referred to as the Middle ...
... After the fall of the Western Roman Empire Europe was in disorder and change During 400-1500AD the world was in transition and this period is referred to as the Middle ...
Unit 5 Reading and Questions the middle ages Historians disagree
... Although the Romans called them barbarians, German-speaking nomads defeated the Romans because the empire had grown weak, and it could no longer defend its vast borders. But the Germanic tribes were illiterate (could not read and write), and warriors were loyal only to their local chiefs, which made ...
... Although the Romans called them barbarians, German-speaking nomads defeated the Romans because the empire had grown weak, and it could no longer defend its vast borders. But the Germanic tribes were illiterate (could not read and write), and warriors were loyal only to their local chiefs, which made ...
File
... everyone and everything; concept of trial options (trial by oath and trial by ordeal) • Merovingian's founded and built many monasteries, churches and palaces and spread Christianity throughout Western Europe • IMPACT = Eventually dynasty declined as kings relaxed power and became more like figure h ...
... everyone and everything; concept of trial options (trial by oath and trial by ordeal) • Merovingian's founded and built many monasteries, churches and palaces and spread Christianity throughout Western Europe • IMPACT = Eventually dynasty declined as kings relaxed power and became more like figure h ...
Overview and Foundation: SS 8-T300-16-17
... bottom of the system were serfs, peasants who were not free to leave the lord’s land without permission. Western Europe During the Middle Ages For 500 years, much of Europe was part of the Roman Empire. When Rome fell to invading barbarians in 476 C.E., Europe was left with no central government or ...
... bottom of the system were serfs, peasants who were not free to leave the lord’s land without permission. Western Europe During the Middle Ages For 500 years, much of Europe was part of the Roman Empire. When Rome fell to invading barbarians in 476 C.E., Europe was left with no central government or ...
MIDDLE AGES
... TASK 3: Does the modern meaning of the word ‘vandalism’ correspond with the actions of the tribe carrying the name Vandals? ...
... TASK 3: Does the modern meaning of the word ‘vandalism’ correspond with the actions of the tribe carrying the name Vandals? ...
The European Middle Ages Study Guide-Chapter 13
... centered around the land (fief) given to a lord or knight. The land was worked by peasants and were self-sufficient in ...
... centered around the land (fief) given to a lord or knight. The land was worked by peasants and were self-sufficient in ...
Medieval Book Notes Recap - Watertown City School District
... The center of European trade will shift to Venice, making it a rich and powerful trading ...
... The center of European trade will shift to Venice, making it a rich and powerful trading ...
Chapter 12 Europe and the Byzantine Empire
... invasions of Germanic tribes, these tribes settled throughout Western Europe. Most of the tribes converted to Christianity quickly, though politically they continued to run their own shows. They formed alliance and expanded, sometime enough to be considered kingdoms. The most significant of the earl ...
... invasions of Germanic tribes, these tribes settled throughout Western Europe. Most of the tribes converted to Christianity quickly, though politically they continued to run their own shows. They formed alliance and expanded, sometime enough to be considered kingdoms. The most significant of the earl ...
The Middle Ages in Europe
... The Western Roman Empire fell to Germanic invaders in 476 C.E. – historians mark this as the start of the Middles Ages/Dark Ages – the time between the Roman Empire and the Renaissance in Europe. The early Middle Ages may be called “Dark” in the sense that the unity the Roman Empire brought to Europ ...
... The Western Roman Empire fell to Germanic invaders in 476 C.E. – historians mark this as the start of the Middles Ages/Dark Ages – the time between the Roman Empire and the Renaissance in Europe. The early Middle Ages may be called “Dark” in the sense that the unity the Roman Empire brought to Europ ...
Germanic Kingdoms Unite under Charlemagne
... Population Shifts – Cities didn’t have strong leadership, nobles moved away to rural areas, as did the common population. People had to grow their own food. ...
... Population Shifts – Cities didn’t have strong leadership, nobles moved away to rural areas, as did the common population. People had to grow their own food. ...
Dancing in the Dark Ages (Middle Age Europe)
... • which was an important event in world history due to the fact that it prevented Muslim expansion throughout Western Europe. • Think about it – it would be a different world, wouldn’t it? Why? • founding father of heavy cavalry (Also known as Knights), and ...
... • which was an important event in world history due to the fact that it prevented Muslim expansion throughout Western Europe. • Think about it – it would be a different world, wouldn’t it? Why? • founding father of heavy cavalry (Also known as Knights), and ...
Early Middle Ages
... Christianity Rules Pope Gregory the Great Made the papacy an office of political & spiritual power Foresaw a churchly kingdom, ruled by a pope – this idea became a central part of the Middle Ages Charles Martel – “The ...
... Christianity Rules Pope Gregory the Great Made the papacy an office of political & spiritual power Foresaw a churchly kingdom, ruled by a pope – this idea became a central part of the Middle Ages Charles Martel – “The ...
Lecture Notes: What Changed in the Middle Ages?
... • Under the Romans, laws were public and created by representatives of the people. Laws, such as the Twelve Tables were posted in the forum for all to see and follow. In the early Middle Ages, judgments were made by the local lord who settled all disputes on his property or fief. Disputes between no ...
... • Under the Romans, laws were public and created by representatives of the people. Laws, such as the Twelve Tables were posted in the forum for all to see and follow. In the early Middle Ages, judgments were made by the local lord who settled all disputes on his property or fief. Disputes between no ...
WHI.10 Middle Ages presentation
... A. Early Medieval Society 1. foundations: a) Roman heritage; constantly looking back and trying to recreate the “glory” of Rome b) Christianity; the Roman Catholic Church provided the central social and moral structure c) Germanic customs; the rise of the Warrior Culture ...
... A. Early Medieval Society 1. foundations: a) Roman heritage; constantly looking back and trying to recreate the “glory” of Rome b) Christianity; the Roman Catholic Church provided the central social and moral structure c) Germanic customs; the rise of the Warrior Culture ...
A New Civilization Emerges in Western Europe
... northern Italy, however, it is a hollow term. Local lords start to go their own way, and monarchies of individual states begin to arise. ...
... northern Italy, however, it is a hollow term. Local lords start to go their own way, and monarchies of individual states begin to arise. ...
Raiders, Traders and Crusaders
... stormed forth, terrorizing well established societies which were accustomed to war, but not to the startling tactics of the Vikings. They even sailed as far west as North America. ...
... stormed forth, terrorizing well established societies which were accustomed to war, but not to the startling tactics of the Vikings. They even sailed as far west as North America. ...
CHAPTER 11 – THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE AND WESTERN EUROPE
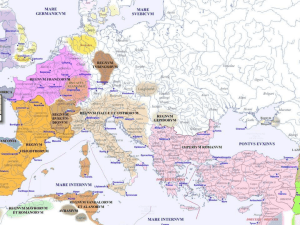
... The eastern empire, also called the Byzantine Empire, survived until 1453. It was composed of over 1500 cities, the greatest of which was Constantinople. Imperial policy was always to centralize and conform. Justinian’s revision of Roman law contributed to this process. Justinian’s code was a fourf ...
... The eastern empire, also called the Byzantine Empire, survived until 1453. It was composed of over 1500 cities, the greatest of which was Constantinople. Imperial policy was always to centralize and conform. Justinian’s revision of Roman law contributed to this process. Justinian’s code was a fourf ...
Slide 1
... Son, Pepin, begins Carolingian Dynasty — family that ruled 751–987 after helping the Pope fight the Lombards ...
... Son, Pepin, begins Carolingian Dynasty — family that ruled 751–987 after helping the Pope fight the Lombards ...
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages or Early Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from the 5th century to the 10th century. The Early Middle Ages followed the decline of the Western Roman Empire and preceded the High Middle Ages (c. 1001–1300). The period saw a continuation of trends begun during late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, and increased immigration. The period has been labelled the ""Dark Ages"", a characterization highlighting the relative scarcity of literary and cultural output from this time, especially in Northwestern Europe. However, the Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantine Empire, continued to survive, and in the 7th century the Islamic caliphates conquered swaths of formerly Roman territory.Many of these trends were reversed later in the period. In 800 the title of emperor was revived in Western Europe by Charlemagne, whose Carolingian Empire greatly affected later European social structure and history. Europe experienced a return to systematic agriculture in the form of the feudal system, which introduced such innovations as three-field planting and the heavy plow. Barbarian migration stabilized in much of Europe, although the north was greatly affected by the Viking expansion.