The Barbarian Invasions
... The Franks were fortunate that the Carolingians gained the throne. Pepin the Short’s son became one of the greatest leaders of medieval Europe and helped to build the Frankish Kingdom into an empire. Charlemagne or Charles the Great became king of the Franks in 771 after the death of his father. Wit ...
... The Franks were fortunate that the Carolingians gained the throne. Pepin the Short’s son became one of the greatest leaders of medieval Europe and helped to build the Frankish Kingdom into an empire. Charlemagne or Charles the Great became king of the Franks in 771 after the death of his father. Wit ...
The Real Dark Ages Notes
... 54. What was the Christian general’s name? 55. What did Martel need to build his professional army? 56. Where did he get the money? 57. Which side attacked on the seventh day of the stand off? 58. Was happened to the Muslim general? 59. Which side on the Battle of Tours? 60. What relationship was Ch ...
... 54. What was the Christian general’s name? 55. What did Martel need to build his professional army? 56. Where did he get the money? 57. Which side attacked on the seventh day of the stand off? 58. Was happened to the Muslim general? 59. Which side on the Battle of Tours? 60. What relationship was Ch ...
MIDDLE AGES
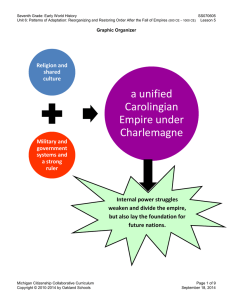
... Louis ‘the Pious’ (814-840) The son of Charlemagne had a difficult task to rule after the glorious era of his father. To make matters worse he had to face a new wave of invasions – Viking and Muslim. His rule seems to be a failure in comparison to Charlemagne but it was not only his fault. 843 Treat ...
... Louis ‘the Pious’ (814-840) The son of Charlemagne had a difficult task to rule after the glorious era of his father. To make matters worse he had to face a new wave of invasions – Viking and Muslim. His rule seems to be a failure in comparison to Charlemagne but it was not only his fault. 843 Treat ...
Development of Feudalism in Europe
... of Champagne by sending them the knights whose services I owe them from the fief which I hold from them. Feudalism, then, was this system of a vassal being paid in land for his service to a king, because the king was not strong enought to defende his kingdom. The Vassal owned the land and the people ...
... of Champagne by sending them the knights whose services I owe them from the fief which I hold from them. Feudalism, then, was this system of a vassal being paid in land for his service to a king, because the king was not strong enought to defende his kingdom. The Vassal owned the land and the people ...
The Dark Ages_Part 5-9 - 7thgradeworldhistoryperiod6
... 24. Was happened to the Muslim general? 25. Which side on the Battle of Tours? 26. What relationship was Charlemagne to Charles Martel? 27. Christmas Day, 800 AD – what happens Charlemagne? 800 AD 28. What does Charlemagne try to build up? 29. How many years did Charlemagne reign? 30. What did Cha ...
... 24. Was happened to the Muslim general? 25. Which side on the Battle of Tours? 26. What relationship was Charlemagne to Charles Martel? 27. Christmas Day, 800 AD – what happens Charlemagne? 800 AD 28. What does Charlemagne try to build up? 29. How many years did Charlemagne reign? 30. What did Cha ...
Christianity, Feudalism, and Manoralism the new one
... formed some time in the 3rd century A.D. Early on there was very little political unity among the Franks. Each group or tribe was ruled by its own chieftain and pursued its own course of migration and settlement. Some tribes remained east of the Rhine River in an area known as “Franconia.” Others cr ...
... formed some time in the 3rd century A.D. Early on there was very little political unity among the Franks. Each group or tribe was ruled by its own chieftain and pursued its own course of migration and settlement. Some tribes remained east of the Rhine River in an area known as “Franconia.” Others cr ...
Notes on Middle Ages - Anderson School District One
... of Spain - Charles Martel started the Reconquista or reconquest of Spain for Christians in 732 - In 1492 the Christian army of Spain pushed the Muslims completely out of Spain -Inquisition – Court held by the church in Spain - The king and queen of Spain would use the Inquisition to eliminate people ...
... of Spain - Charles Martel started the Reconquista or reconquest of Spain for Christians in 732 - In 1492 the Christian army of Spain pushed the Muslims completely out of Spain -Inquisition – Court held by the church in Spain - The king and queen of Spain would use the Inquisition to eliminate people ...
Early Middle Ages
... between monarchs and nobles in which land is given away in exchange for loyalty and military service Feudalism started in France and moved to other parts of Europe in the 1000s ...
... between monarchs and nobles in which land is given away in exchange for loyalty and military service Feudalism started in France and moved to other parts of Europe in the 1000s ...
The Middle Ages - nehs-ball
... • b. Greatest king was Charlemagne • 1. most powerful king in Western Europe • 2. encouraged learning ...
... • b. Greatest king was Charlemagne • 1. most powerful king in Western Europe • 2. encouraged learning ...
The Early Middle Ages
... brilliant, but ruthless, leadership of Clovis. Clovis eventually conquered the lands from the Pyrenees Mountains to the Rhine River in Central Europe. Upon the urging of his wife, Clovis became a Christian. This brought the support of the church in Rome. Instead of overthrowing the existing Roman po ...
... brilliant, but ruthless, leadership of Clovis. Clovis eventually conquered the lands from the Pyrenees Mountains to the Rhine River in Central Europe. Upon the urging of his wife, Clovis became a Christian. This brought the support of the church in Rome. Instead of overthrowing the existing Roman po ...
middle-ages-germanic-kingdoms
... By 719, Charles held more power than the king as mayor of the palace Charles was part of the Franks and therefore was Christian ...
... By 719, Charles held more power than the king as mayor of the palace Charles was part of the Franks and therefore was Christian ...
Frankish Kingdom
... Charlemagne has justly been called one of the founders of modern Europe. To a certain extent this view is founded upon his enthusiasm for learning. Charlemagne was convinced that only correctness in everything produced correct results. As a consequence of this view, he saw to it that the Holy Script ...
... Charlemagne has justly been called one of the founders of modern Europe. To a certain extent this view is founded upon his enthusiasm for learning. Charlemagne was convinced that only correctness in everything produced correct results. As a consequence of this view, he saw to it that the Holy Script ...
The Frankish Kingdom and Charlemagne
... area in the Netherlands and northern Germany Friesland inhabited by Frisians ...
... area in the Netherlands and northern Germany Friesland inhabited by Frisians ...
The Age of Charlemagne
... As Charlemagne’s power grew, so too did his prestige as the most powerful Christian ruler. One monk even described Charlemagne’s empire as the “kingdom of Europe.” In a.d. 800, Charlemagne acquired a new title—emperor of the Romans. Charlemagne’s coronation as Roman emperor—over 300 years after the ...
... As Charlemagne’s power grew, so too did his prestige as the most powerful Christian ruler. One monk even described Charlemagne’s empire as the “kingdom of Europe.” In a.d. 800, Charlemagne acquired a new title—emperor of the Romans. Charlemagne’s coronation as Roman emperor—over 300 years after the ...
The Frankish Empire The Germanic tribe known as the Franks
... Although the treaty successfully ended the civil war, it created an official division of the Frankish empire into three separate kingdoms, which were to be ruled by Louis the Pious’s sons Lothar I, Charles the Bald, and Louis the German, which would become the modern-day nations of Italy, France, an ...
... Although the treaty successfully ended the civil war, it created an official division of the Frankish empire into three separate kingdoms, which were to be ruled by Louis the Pious’s sons Lothar I, Charles the Bald, and Louis the German, which would become the modern-day nations of Italy, France, an ...
The Frankish Empire The Germanic tribe known as the Franks
... Although the treaty successfully ended the civil war, it created an official division of the Frankish empire into three separate kingdoms, which were to be ruled by Louis the Pious’s sons Lothar I, Charles the Bald, and Louis the German, which would become the modern-day nations of Italy, France, an ...
... Although the treaty successfully ended the civil war, it created an official division of the Frankish empire into three separate kingdoms, which were to be ruled by Louis the Pious’s sons Lothar I, Charles the Bald, and Louis the German, which would become the modern-day nations of Italy, France, an ...
Development of Feudalism - iMiddle7thgradeWorldHistory
... • Became king of all Frankish territory at 29 • Carolingian Dynasty is named after him • Great military leader and a smart, organized ruler • Very intelligent, but struggled all his life to learn to read and write • Deeply religious Christian • Was 6’ 4” tall, athletic, • 4 wives; 18 children ...
... • Became king of all Frankish territory at 29 • Carolingian Dynasty is named after him • Great military leader and a smart, organized ruler • Very intelligent, but struggled all his life to learn to read and write • Deeply religious Christian • Was 6’ 4” tall, athletic, • 4 wives; 18 children ...
File
... • Charlemagne (Charles the Great) who was a military general and restored Pope Leo III who had been exiled • In return, Leo placed a crown on Charlemagne and named him the “Emperor of the Romans” which secured the relationship between Frankish kings and the papacy • Charlemagne became the first rule ...
... • Charlemagne (Charles the Great) who was a military general and restored Pope Leo III who had been exiled • In return, Leo placed a crown on Charlemagne and named him the “Emperor of the Romans” which secured the relationship between Frankish kings and the papacy • Charlemagne became the first rule ...
HONORS Early Middle Ages Notes for kids
... 1. The changes in the ___________ monarchy were unique. During the Middle Ages, kings in other European countries also worked to gain more power, but their experiences were different from those of he English rulers. 2. After Charlemagne, kings of _______ did not rule much territory - _______________ ...
... 1. The changes in the ___________ monarchy were unique. During the Middle Ages, kings in other European countries also worked to gain more power, but their experiences were different from those of he English rulers. 2. After Charlemagne, kings of _______ did not rule much territory - _______________ ...
Student Handout #1 - The Carolingian Empire and Charlemagne
... At the end of Charlemagne’s rule, different members of his family were given power over different parts of the empire. The Carolingians, as you may have noted, believed that power and control of land should be inherited from father to son (along with certain names like Pepin and Charles!). This caus ...
... At the end of Charlemagne’s rule, different members of his family were given power over different parts of the empire. The Carolingians, as you may have noted, believed that power and control of land should be inherited from father to son (along with certain names like Pepin and Charles!). This caus ...
Hist 331: Civil War and Reconstruction (Fall 2001)
... The Pope in 800 declared Charlemagne “Holy Roman Emperor” ...
... The Pope in 800 declared Charlemagne “Holy Roman Emperor” ...
Chapter Two Review (review – noun
... • The Frankish kings proved inept against this threat. • The mayor of the palace, Charles the Bastard, gathered as many Frankish knights, warriors, and peasants as he could and met the invaders at Tours. • Although outnumbered, the Franks prevailed and pushed the Islamic army back to Spain. • After ...
... • The Frankish kings proved inept against this threat. • The mayor of the palace, Charles the Bastard, gathered as many Frankish knights, warriors, and peasants as he could and met the invaders at Tours. • Although outnumbered, the Franks prevailed and pushed the Islamic army back to Spain. • After ...
The Middle Ages
... Problems for the Merovingians Frankish custom to divide your land among all your sons. Heirs began to kill each other for their inheritances. So busy fighting the governing was left to the MAYORS OF THE PALACE. ...
... Problems for the Merovingians Frankish custom to divide your land among all your sons. Heirs began to kill each other for their inheritances. So busy fighting the governing was left to the MAYORS OF THE PALACE. ...
Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–924) was the final stage in the history of the early medieval realm of the Franks, ruled by the Carolingian dynasty. The size of the empire at its zenith around 800 was 1,112,000 km2, with a population of between 10 and 20 million people.With its division in 843, it also represents the earliest stage in the history of the kingdom of France and the kingdom of Germany, which in the High Middle Ages would emerge as the powerful monarchies of continental Europe, Capetian France and the Holy Roman Empire, and by extension the predecessor of the modern nations of France and Germany. The beginning of the Carolingian era is marked by the coronation of Charlemagne, or Charles the Great by Pope Leo III at Christmas of the year 800, and its end with the death of Charles the Fat.Because Charlemagne and his ancestors had been rulers of the Frankish realm earlier (his grandfather Charles Martel had essentially founded the empire during his lifetime, and his father, Pepin the Short, was the first King of the Franks), the coronation did not actually constitute a new empire. Most historians prefer to use the term ""Frankish Kingdoms"" or ""Frankish Realm"" to refer to the area covering parts of today's Germany and France from the 5th to the 9th century.According to the American Heritage Dictionary, the term ""Carolingian"" comes from the French terms ""Carolingien"" and ""Carlovingien"", probably a blend of Carolus (Latin for Charles) and ""Mérovingien"".