![02 Atomic Structure [ppt 1MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000821172_1-5bf1afd152b32026d524139a10b8292f-300x300.png)
02 Atomic Structure [ppt 1MB]
... a substance that is made up of the same kind of atoms is an element I can describe the basic structure of an atom and state the location and charge of the proton, electron and neutron within the atom structure I can state the relative masses of the proton, neutron and electron. I can explain what is ...
... a substance that is made up of the same kind of atoms is an element I can describe the basic structure of an atom and state the location and charge of the proton, electron and neutron within the atom structure I can state the relative masses of the proton, neutron and electron. I can explain what is ...
File
... A) low first ionization energy and low electronegativity B) low first ionization energy and high electronegativity C) high first ionization energy and low electronegativity D) high first ionization energy and high electronegativity 39. Which is a property of most nonmetallic solids? A) B) C) D) ...
... A) low first ionization energy and low electronegativity B) low first ionization energy and high electronegativity C) high first ionization energy and low electronegativity D) high first ionization energy and high electronegativity 39. Which is a property of most nonmetallic solids? A) B) C) D) ...
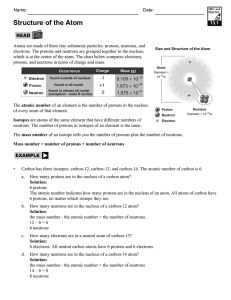
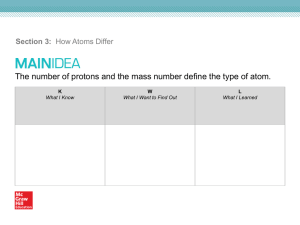
Units and Unit Conversions 6. Define the problem: If the nucleus
... Develop a plan: Look up the symbol for cobalt and find that symbol on the periodic table. The periodic table gives the atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons since the atom has no charge. The number of neutrons is the diff ...
... Develop a plan: Look up the symbol for cobalt and find that symbol on the periodic table. The periodic table gives the atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons since the atom has no charge. The number of neutrons is the diff ...
Chapter 3—Time and Geology
... Phanerozoic Eon (30): The eon of geologic time during which the Earth has been populated by abundant and diverse life. It is subdivided into Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic. The basal unit is 570 (or 544) million years and it continues through the present geologic time. Pleistocene Series (34): Th ...
... Phanerozoic Eon (30): The eon of geologic time during which the Earth has been populated by abundant and diverse life. It is subdivided into Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic. The basal unit is 570 (or 544) million years and it continues through the present geologic time. Pleistocene Series (34): Th ...
Radiometric Dating - Tulane University
... and solve for t . The answer is about 6 billion years. This argument tells when the elements were formed that make up the Earth, but does not really give us the age of the Earth. It does, however, give a maximum age of the Earth. 3. From the Pb-Pb isochron equation (11) we can make some arguments ab ...
... and solve for t . The answer is about 6 billion years. This argument tells when the elements were formed that make up the Earth, but does not really give us the age of the Earth. It does, however, give a maximum age of the Earth. 3. From the Pb-Pb isochron equation (11) we can make some arguments ab ...
Students will review concepts from their quiz and then correct it at
... A pure substance containing two or more kinds of __atoms__. The atoms are ___chemically___ combined in some way. Often times (but not always) they come together to form groups of atoms called molecules. A compound is always homogeneous (uniform). Compounds ___cannot___ be separated by physical means ...
... A pure substance containing two or more kinds of __atoms__. The atoms are ___chemically___ combined in some way. Often times (but not always) they come together to form groups of atoms called molecules. A compound is always homogeneous (uniform). Compounds ___cannot___ be separated by physical means ...
Groups of the Periodic Table
... Moving from left to right across a period, the elements become less metallic. This is related to the increase in the number of electrons in the outer shell of their atoms. The atoms become more likely to gain or share electrons, rather than lose them when they form compounds. Metals Metals tend to h ...
... Moving from left to right across a period, the elements become less metallic. This is related to the increase in the number of electrons in the outer shell of their atoms. The atoms become more likely to gain or share electrons, rather than lose them when they form compounds. Metals Metals tend to h ...
Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
... graduate research under the guidance of the man who discovered the electron, J. J. Thomson. Through his research with Thomson, Rutherford became interested in studying radioactivity. In 1898 he described two kinds of particles emitted from radioactive atoms, calling them alpha and beta particles. He ...
... graduate research under the guidance of the man who discovered the electron, J. J. Thomson. Through his research with Thomson, Rutherford became interested in studying radioactivity. In 1898 he described two kinds of particles emitted from radioactive atoms, calling them alpha and beta particles. He ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... Moving from left to right across a period, the elements become less metallic. This is related to the increase in the number of electrons in the outer shell of their atoms. The atoms become more likely to gain or share electrons, rather than lose them when they form compounds. Metals Metals tend to h ...
... Moving from left to right across a period, the elements become less metallic. This is related to the increase in the number of electrons in the outer shell of their atoms. The atoms become more likely to gain or share electrons, rather than lose them when they form compounds. Metals Metals tend to h ...
Chapter 4 Practice Test
... d. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios. The comparison of the number of atoms in a copper coin the size of a penny with the number of people on Earth is made to illustrate which of the following? a. that atoms are indivisible b. that atoms are very ...
... d. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios. The comparison of the number of atoms in a copper coin the size of a penny with the number of people on Earth is made to illustrate which of the following? a. that atoms are indivisible b. that atoms are very ...
1b Atomic Structure
... One of the reasons that certain isotopes are more abundant than others is because some isotopes spontaneously fall apart, or decay. Isotopes that disintegrate to become more stable atomic forms are called radioisotopes. Henry Becquerel and Marie Curie were the first scientists to discover radioisoto ...
... One of the reasons that certain isotopes are more abundant than others is because some isotopes spontaneously fall apart, or decay. Isotopes that disintegrate to become more stable atomic forms are called radioisotopes. Henry Becquerel and Marie Curie were the first scientists to discover radioisoto ...
unit-3-atoms-and-nuclear - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... For example, when fission of uranium=235 occurs, the 2 or 3 neutrons given off cause the fission of other uranium-235 nuclei. Continues until all atoms are split or neutrons fail to hit uranium-235 nuclei. (mass hits a certain level. The minimum amount of nuclide that provides the number of neutrons ...
... For example, when fission of uranium=235 occurs, the 2 or 3 neutrons given off cause the fission of other uranium-235 nuclei. Continues until all atoms are split or neutrons fail to hit uranium-235 nuclei. (mass hits a certain level. The minimum amount of nuclide that provides the number of neutrons ...
10/2/2013 1 5 Early Atomic Theory and Structure Chapter Outline
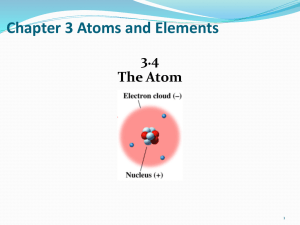
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. ...
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. ...
Chapter 5
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Atomic Structure - Kania´s Science Page
... If the atom gives up an electron we say that it has been oxidized (overall charge increases) If the atoms takes in an electron we say that it has been reduced (overall charge decreases) These come from Benjamin Franklin’s names of oxidation and reduction during a chemical reaction. Cation- + ions An ...
... If the atom gives up an electron we say that it has been oxidized (overall charge increases) If the atoms takes in an electron we say that it has been reduced (overall charge decreases) These come from Benjamin Franklin’s names of oxidation and reduction during a chemical reaction. Cation- + ions An ...
Nuts,Bolts and Isotopes- Average Atomic Mass Activity
... (for example carbon is composed of carbon atoms). However, not all of the atoms found in that element are the same. For example, carbon contains three different types of atoms (carbon-12, 13 and 14). Each atom has the same number of protons and electrons but differing numbers of neutrons. These are ...
... (for example carbon is composed of carbon atoms). However, not all of the atoms found in that element are the same. For example, carbon contains three different types of atoms (carbon-12, 13 and 14). Each atom has the same number of protons and electrons but differing numbers of neutrons. These are ...
- Orangefield ISD
... Isotopes and Mass Number All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons and electrons but the number of neutrons in the nucleus can differ. Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. In nature, most elements are found as mixtures ...
... Isotopes and Mass Number All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons and electrons but the number of neutrons in the nucleus can differ. Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. In nature, most elements are found as mixtures ...
Atomic Mass
... Thompson determined the proton’s characteristics. Thompson showed that atoms contained both positive and negative charges. This disproved the Dalton model of the atom which held that atoms were indivisible. But the mass of the atom could not be accounted for by the mass of protons inside it. There h ...
... Thompson determined the proton’s characteristics. Thompson showed that atoms contained both positive and negative charges. This disproved the Dalton model of the atom which held that atoms were indivisible. But the mass of the atom could not be accounted for by the mass of protons inside it. There h ...
Elements and Compounds Chapter 3
... Thompson determined the proton’s characteristics. Thompson showed that atoms contained both positive and negative charges. This disproved the Dalton model of the atom which held that atoms were indivisible. But the mass of the atom could not be accounted for by the mass of protons inside it. There h ...
... Thompson determined the proton’s characteristics. Thompson showed that atoms contained both positive and negative charges. This disproved the Dalton model of the atom which held that atoms were indivisible. But the mass of the atom could not be accounted for by the mass of protons inside it. There h ...
Reviewing Chemistry: Mastering the TEKS - Student
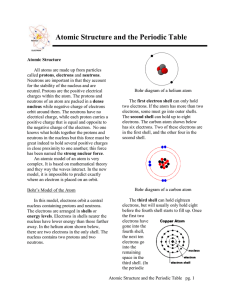
... The diagram above shows the results of Rutherford’s experiment in which he used a radioactive source to “shoot” alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold foil. Based on these results, what were Rutherford’s conclusions? ...
... The diagram above shows the results of Rutherford’s experiment in which he used a radioactive source to “shoot” alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold foil. Based on these results, what were Rutherford’s conclusions? ...
Catalyst (4 min) - Schurz High School
... Know the names, charges, masses and locations in the atom of the three subatomic particles Draw atoms – correct number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the correct places Be able to determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the atom Be able to name isotopes ...
... Know the names, charges, masses and locations in the atom of the three subatomic particles Draw atoms – correct number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the correct places Be able to determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the atom Be able to name isotopes ...
Chapter 4 Early Atomic Theory
... If two elements form more that one compound, the ratio of the second element that combines with 1 gram of the first element in each is a simple whole number. • In hydrogen peroxide 32.0 g oxygen reacts with 2.0 g hydrogen (H2O2) O:H = 16:1 • Ratio of the masses of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide and wat ...
... If two elements form more that one compound, the ratio of the second element that combines with 1 gram of the first element in each is a simple whole number. • In hydrogen peroxide 32.0 g oxygen reacts with 2.0 g hydrogen (H2O2) O:H = 16:1 • Ratio of the masses of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide and wat ...
Atoms
... particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form che ...
... particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form che ...
Atomic Structure_Bohr Flashcards
... 8. a. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in H-1 to H-2 to H-3. List any similarities and differences. b. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in C-12 to C-13 to C-14. List any similarities and differences. ...
... 8. a. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in H-1 to H-2 to H-3. List any similarities and differences. b. Compare the number of protons and neutrons in C-12 to C-13 to C-14. List any similarities and differences. ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.