Quantum Theory of Condensed Matter: Problem Set 1 Qu.1
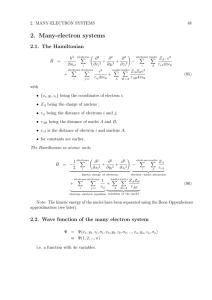
... (i) Use the standard theory for addition of angular momenta to find the exact energy levels. (ii) Use the Holstein-Primakoff transformation and harmonic approximation to calculate the low-lying excitation energies. (iii) Compare the exact and approximate calculations. Qu.2 Consider a Bose gas at zer ...
... (i) Use the standard theory for addition of angular momenta to find the exact energy levels. (ii) Use the Holstein-Primakoff transformation and harmonic approximation to calculate the low-lying excitation energies. (iii) Compare the exact and approximate calculations. Qu.2 Consider a Bose gas at zer ...
Section1 Final Key
... is always lower than the classical energy. T / F: A spherical harmonic function Ylm (θ, φ) is an eigenfunction of the L̂2 operator with eigenvalue h̄2 l(l + 1). T / F : Any linear combination of solutions to the time independent Schrödinger equation is also a solution of that equation. T / F: The e ...
... is always lower than the classical energy. T / F: A spherical harmonic function Ylm (θ, φ) is an eigenfunction of the L̂2 operator with eigenvalue h̄2 l(l + 1). T / F : Any linear combination of solutions to the time independent Schrödinger equation is also a solution of that equation. T / F: The e ...
Lecture Notes, Feb 24, 2016
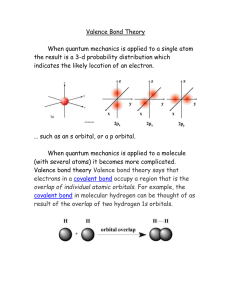
... Em − En , when it makes a quantum jump. The reverse is possible: An atom in a lower energy state can absorb a photon with the correct energy and make a transition to the higher state. The frequency of emitted or absorbed light when the atom jumps from the orbit n to m will be f = ...
... Em − En , when it makes a quantum jump. The reverse is possible: An atom in a lower energy state can absorb a photon with the correct energy and make a transition to the higher state. The frequency of emitted or absorbed light when the atom jumps from the orbit n to m will be f = ...