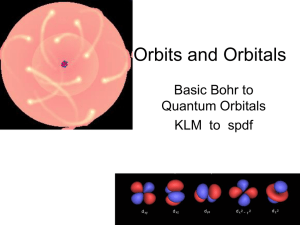
Chemistry 102 Summary June 25th - Bohr model only works for one
... Specific wave functions are called orbitals. Orbitals define the allowed energy states where electrons can reside. There are four basic shapes: s, p, d and f Shapes represent where an electron will reside 90 % of the time in that allowed energy state. From Heisenberg – the exact location cannot be d ...
... Specific wave functions are called orbitals. Orbitals define the allowed energy states where electrons can reside. There are four basic shapes: s, p, d and f Shapes represent where an electron will reside 90 % of the time in that allowed energy state. From Heisenberg – the exact location cannot be d ...
1. Consider an electron moving between two atoms making up a
... (b) Write down completeness and orthonormality relations for the ONB {| i}. Note that these states have both a continuous index and a discrete one, so that one has to do the correct kind of summation, and use the correct delta function for each index. (c) Express an arbitrary state vector |i ...
... (b) Write down completeness and orthonormality relations for the ONB {| i}. Note that these states have both a continuous index and a discrete one, so that one has to do the correct kind of summation, and use the correct delta function for each index. (c) Express an arbitrary state vector |i ...
THE UNIVERSITY OF LETHBRIDGE DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY
... and is not merely water of crystallization as the “bottle label” formula would indicate. Dispersion forces are of much less importance. The true formula for this compound is likely to be either [Mn(OH)4]Cl2 (ionic) or [Mn(OH)4Cl2] (molecular) d) Convert liquid NH3 to gaseous NH3. Hydrogen bonding do ...
... and is not merely water of crystallization as the “bottle label” formula would indicate. Dispersion forces are of much less importance. The true formula for this compound is likely to be either [Mn(OH)4]Cl2 (ionic) or [Mn(OH)4Cl2] (molecular) d) Convert liquid NH3 to gaseous NH3. Hydrogen bonding do ...
The variational principle and simple properties of the ground
... with ␣ T ⫽1/2 2 , thus leading to the exact solution 共14兲. In summary, we have stressed the power of the variational method by deriving general properties of the ground-state wave function of a one-body Hamiltonian in a simple way. This information can be used to constrain the form of a trial wave ...
... with ␣ T ⫽1/2 2 , thus leading to the exact solution 共14兲. In summary, we have stressed the power of the variational method by deriving general properties of the ground-state wave function of a one-body Hamiltonian in a simple way. This information can be used to constrain the form of a trial wave ...
class 2.pptx
... neutrons, but the same number of protons in their nuclei and the same number of electrons have essentially identical ...
... neutrons, but the same number of protons in their nuclei and the same number of electrons have essentially identical ...
Quantum Mechanical Model
... Quantum Mechanical Model • As the energy of an electron increases, so does the quantum number (n) • Each principle energy level is also split up into one or more sublevels • Chart on Pg. 145 [http://www.chemistry.mcmaster.ca/esam/Chapter_4/fig4-2.jpg] ...
... Quantum Mechanical Model • As the energy of an electron increases, so does the quantum number (n) • Each principle energy level is also split up into one or more sublevels • Chart on Pg. 145 [http://www.chemistry.mcmaster.ca/esam/Chapter_4/fig4-2.jpg] ...
Waves and the Schroedinger Equation
... written a representation of a wave-particle entity as a sinusoidal function. This is our attempt to describe the spatial and time dependence of an entity. However, this is one particular solution to the more general representation of the represenation of a state of an entitity (particle, wave, etc). ...
... written a representation of a wave-particle entity as a sinusoidal function. This is our attempt to describe the spatial and time dependence of an entity. However, this is one particular solution to the more general representation of the represenation of a state of an entitity (particle, wave, etc). ...