ActivNutrients
... and clinical studies. Not only does this formula contain natural vitamin E—which has been proven to be up to 100% more bioavailable than synthetic dl-alpha-tocopherol—but it is also provides mixed tocopherols to more closely approximate how one might consume vitamin E in healthful foods.[9,10] Folat ...
... and clinical studies. Not only does this formula contain natural vitamin E—which has been proven to be up to 100% more bioavailable than synthetic dl-alpha-tocopherol—but it is also provides mixed tocopherols to more closely approximate how one might consume vitamin E in healthful foods.[9,10] Folat ...
European Laboratory of Nutrients, Bunnik, The Netherlands, Tel
... Vitamins belong , like elements, amino acids and fatty acids to the essential elements human beings need to be able to function properly and that a human being is unable to produce from food. Vitamins are crucial parts or many kinds or biochemical conversions in the body, such as co-factors in enzym ...
... Vitamins belong , like elements, amino acids and fatty acids to the essential elements human beings need to be able to function properly and that a human being is unable to produce from food. Vitamins are crucial parts or many kinds or biochemical conversions in the body, such as co-factors in enzym ...
Poster ECE`14 PsedohipoPTH [Modo de compatibilidad]
... Treatment with vitamin D or analogues is necessary to normalize serum calcium. Fixed preparations of calcium and vitamin D are not recommended. Treatment must get low-normal range of serum calcium. Use thiazides if there is significant hypercalciuria. In this cases, an ophthalmologic examination and ...
... Treatment with vitamin D or analogues is necessary to normalize serum calcium. Fixed preparations of calcium and vitamin D are not recommended. Treatment must get low-normal range of serum calcium. Use thiazides if there is significant hypercalciuria. In this cases, an ophthalmologic examination and ...
Canada`s food Guide Key Nutrients
... Found in the cell walls of plants, outer layers of whole grains and in the skin of Fruits and vegetables Fibre helps maintain healthy body weight, lower risk of disease and aids in digestion ...
... Found in the cell walls of plants, outer layers of whole grains and in the skin of Fruits and vegetables Fibre helps maintain healthy body weight, lower risk of disease and aids in digestion ...
Lactation (breast
... Describe health and development concerns that affect the nutritional needs of people in different stages of the life span. Pregnancy and Lactation: 1st Trimester: Folic Acid prevents neural tube defects---Protein, calcium & iron are most important---Gain 25 to 35 lbs.--Follow My Plate guidelines for ...
... Describe health and development concerns that affect the nutritional needs of people in different stages of the life span. Pregnancy and Lactation: 1st Trimester: Folic Acid prevents neural tube defects---Protein, calcium & iron are most important---Gain 25 to 35 lbs.--Follow My Plate guidelines for ...
Preventing Colds and Flu Naturally
... Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a potent anti-viral, anti-bacterial, and anti-parasitic agent. Oral vitamin C helps protect the body from developing infections, and high-dose intravenous vitamin C is an effective method of destroying and removing pathogenic microbes. Intravenous vitamin C has cured viral in ...
... Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a potent anti-viral, anti-bacterial, and anti-parasitic agent. Oral vitamin C helps protect the body from developing infections, and high-dose intravenous vitamin C is an effective method of destroying and removing pathogenic microbes. Intravenous vitamin C has cured viral in ...
Chapter 11
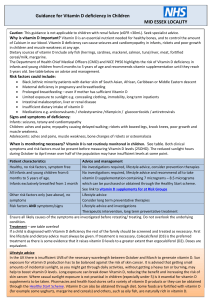
... increased risk of hip fractures Sources • Intestinal bacteria can make vitamin K but not enough to meet all of the body’s needs • Leafy green vegetables • Cabbage family vegetables ...
... increased risk of hip fractures Sources • Intestinal bacteria can make vitamin K but not enough to meet all of the body’s needs • Leafy green vegetables • Cabbage family vegetables ...
Lamb Meat - Alberta Lamb Producers
... protein. Requirements vary according to body size, nutritional status, and level of activity. All cells in the body contain protein. Protein is essential for the growth, development, maintenance and repair of body tissues. It is involved in the transport of oxygen and nutrients throughout the body, ...
... protein. Requirements vary according to body size, nutritional status, and level of activity. All cells in the body contain protein. Protein is essential for the growth, development, maintenance and repair of body tissues. It is involved in the transport of oxygen and nutrients throughout the body, ...
The power of blueberries and oranges
... found in food that are thought to be responsible for instigating cancers of the mouth, stomach, and colon. One Swiss study found that those who died of any type of cancer had vitamin C concentrations about 10 percent lower than those who died from other causes. It has been estimated that drinking 1 ...
... found in food that are thought to be responsible for instigating cancers of the mouth, stomach, and colon. One Swiss study found that those who died of any type of cancer had vitamin C concentrations about 10 percent lower than those who died from other causes. It has been estimated that drinking 1 ...
Dec 2006: The Role of Food Supplements in Preventing Chronic
... Folic Acid and Vitamin B12 Folic Acid and Heart Disease Although there have not been any clinical trials to show that folic acid lowers heart disease rates, we know that folic acid can lower high homocysteine levels. Higher homocysteine levels are associated with an increased risk of heart disease ( ...
... Folic Acid and Vitamin B12 Folic Acid and Heart Disease Although there have not been any clinical trials to show that folic acid lowers heart disease rates, we know that folic acid can lower high homocysteine levels. Higher homocysteine levels are associated with an increased risk of heart disease ( ...
Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies and Toxicities
... Cardio-Vascular: Interference with antiblood clotting medication Adult deficient, adequate, toxic values ...
... Cardio-Vascular: Interference with antiblood clotting medication Adult deficient, adequate, toxic values ...
Multivitamins in HIV Infection PDF
... Use, TB, OIs, malabsorption - Common deficiencies • B12 • Zinc ...
... Use, TB, OIs, malabsorption - Common deficiencies • B12 • Zinc ...
Guidance for Vitamin D deficiency in Children MID
... is insufficientisUVB of the necessary exposure for vitamin D production has to be balanced against the risk of skin cancer. It is advised that getting small amounts of incidental sunlight, as you might get through daily activities, without getting a heavy tan or burning, may help to boost vitamin D ...
... is insufficientisUVB of the necessary exposure for vitamin D production has to be balanced against the risk of skin cancer. It is advised that getting small amounts of incidental sunlight, as you might get through daily activities, without getting a heavy tan or burning, may help to boost vitamin D ...
Vitamin D leaflet (all ages)
... should continue to be given when babies are introduced to solid foods at 6 months. All children between 1-5 years are recommended to take a supplement containing vitamins A, C. and D. Multivitamin supplements containing vitamins A, C and D can therefore be taken instead of a single vitamin D supplem ...
... should continue to be given when babies are introduced to solid foods at 6 months. All children between 1-5 years are recommended to take a supplement containing vitamins A, C. and D. Multivitamin supplements containing vitamins A, C and D can therefore be taken instead of a single vitamin D supplem ...
Vitamin K
Vitamin K refers to a group of structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamins the human body needs for complete synthesis of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation, and also certain proteins that the body uses to control binding of calcium in bone and other tissues. The vitamin K-related modification of the proteins allows them to bind calcium ions, which they cannot do otherwise. Without vitamin K, blood coagulation is seriously impaired, and uncontrolled bleeding occurs. Low levels of vitamin K also weaken bones and promote calcification of arteries and other soft tissues.Chemically, the vitamin K family comprises 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone (3-) derivatives. Vitamin K includes two natural vitamers: vitamin K1 and vitamin K2. Vitamin K2, in turn, consists of a number of related chemical subtypes, with differing lengths of carbon side chains made of isoprenoid groups of atoms.Vitamin K1, also known as phylloquinone, phytomenadione, or phytonadione, is synthesized by plants, and is found in highest amounts in green leafy vegetables because it is directly involved in photosynthesis. It may be thought of as the ""plant"" form of vitamin K. It is active as a vitamin in animals and performs the classic functions of vitamin K, including its activity in the production of blood-clotting proteins. Animals may also convert it to vitamin K2.Vitamin K2, the main storage form in animals, has several subtypes, which differ in isoprenoid chain length. These vitamin K2 homologues are called menaquinones, and are characterized by the number of isoprenoid residues in their side chains. Menaquinones are abbreviated MK-n, where M stands for menaquinone, the K stands for vitamin K, and the n represents the number of isoprenoid side chain residues. For example, menaquinone-4 (abbreviated MK-4) has four isoprene residues in its side chain. Menaquinone-4 (also known as menatetrenone from its four isoprene residues) is the most common type of vitamin K2 in animal products since MK-4 is normally synthesized from vitamin K1 in certain animal tissues (arterial walls, pancreas, and testes) by replacement of the phytyl tail with an unsaturated geranylgeranyl tail containing four isoprene units, thus yielding menaquinone-4. This homolog of vitamin K2 may have enzyme functions distinct from those of vitamin K1.Bacteria in the colon (large intestine) can also convert K1 into vitamin K2. In addition, bacteria typically lengthen the isoprenoid side chain of vitamin K2 to produce a range of vitamin K2 forms, most notably the MK-7 to MK-11 homologues of vitamin K2. All forms of K2 other than MK-4 can only be produced by bacteria, which use these forms in anaerobic respiration. The MK-7 and other bacterially derived forms of vitamin K2 exhibit vitamin K activity in animals, but MK-7's extra utility over MK-4, if any, is unclear and is a matter of investigation.Three synthetic types of vitamin K are known: vitamins K3, K4, and K5. Although the natural K1 and all K2 homologues and synthetic K4 and K5 have proven nontoxic, the synthetic form K3 (menadione) has shown toxicity.


![Poster ECE`14 PsedohipoPTH [Modo de compatibilidad]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007957322_1-13955f29e92676d795b568b8e6827da6-300x300.png)