summary of the survey results
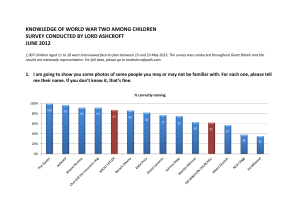
... Less than half of respondents aged 17-18 knew that the Second World War began in 1939 (45%). ...
... Less than half of respondents aged 17-18 knew that the Second World War began in 1939 (45%). ...
World War II..Ch.32
... These laws made it legal to sell arms or lend money to nations at war. Although the United States had not yet entered the war, Roosevelt and Churchill met secretly and issued a joint declaration called the Atlantic Charter. It upheld free trade among nations and the right of people to choose their o ...
... These laws made it legal to sell arms or lend money to nations at war. Although the United States had not yet entered the war, Roosevelt and Churchill met secretly and issued a joint declaration called the Atlantic Charter. It upheld free trade among nations and the right of people to choose their o ...
World War II Terms - Parkway C-2
... nationalist - Joined a political party known as the National Socialists, or Nazis - Organized a revolt in 1923 that failed and he was sent to prison - Hitler outlined his plans in a book called Mein Kampf “My Struggle” - blamed intellectuals, Communists, and Jews for Germany’s defeat and postwar pro ...
... nationalist - Joined a political party known as the National Socialists, or Nazis - Organized a revolt in 1923 that failed and he was sent to prison - Hitler outlined his plans in a book called Mein Kampf “My Struggle” - blamed intellectuals, Communists, and Jews for Germany’s defeat and postwar pro ...
Chapter 31 - Warren County Schools
... a. Atomic bombs - August 1945 a. Threat that Japanese would fight to the death V. War's End and the Emergence of the Superpower Standoff A. Introduction 1. Wanted to avoid failed peace treaties of World War I 2. Established United Nations a. More representative of world than League of Nations a. US ...
... a. Atomic bombs - August 1945 a. Threat that Japanese would fight to the death V. War's End and the Emergence of the Superpower Standoff A. Introduction 1. Wanted to avoid failed peace treaties of World War I 2. Established United Nations a. More representative of world than League of Nations a. US ...
Chapter 31
... a. Atomic bombs - August 1945 a. Threat that Japanese would fight to the death V. War's End and the Emergence of the Superpower Standoff A. Introduction 1. Wanted to avoid failed peace treaties of World War I 2. Established United Nations a. More representative of world than League of Nations a. US ...
... a. Atomic bombs - August 1945 a. Threat that Japanese would fight to the death V. War's End and the Emergence of the Superpower Standoff A. Introduction 1. Wanted to avoid failed peace treaties of World War I 2. Established United Nations a. More representative of world than League of Nations a. US ...
WWII
... • Germany withdrew from the League of Nations • Mussolini attacked Ethiopia • Fascism gained support in Spain and triggered a civil war ...
... • Germany withdrew from the League of Nations • Mussolini attacked Ethiopia • Fascism gained support in Spain and triggered a civil war ...
... Sudetnland (home to many Germans), Czech’s refused and Hitler threatened war. Munich Conference – French and British leaders met with Hitler in Sept. 1938. Appeased Hitler by persuading the Czech’s to give up the Sudetenland to preserve peace. “The Government had to choose between shame and war, the ...
World War II Section 1 - Geneva Area City Schools
... World War II 5.Threats to Czechoslovakia Section 1 Another German-speaking population • Sudetenland eager to be a part of Germany. German speaking. • Hitler threatened the Czech government. Encouraged Czech citizens to revolt. • Czechs prepared for war Avoiding conflict: Munich Conference • Septemb ...
... World War II 5.Threats to Czechoslovakia Section 1 Another German-speaking population • Sudetenland eager to be a part of Germany. German speaking. • Hitler threatened the Czech government. Encouraged Czech citizens to revolt. • Czechs prepared for war Avoiding conflict: Munich Conference • Septemb ...
WWII Notes - Bismarck Public Schools
... race are the ideal race They launch the Holocaust: systematic murder of Jews & others Anti-Semitism: hatred of Jewish people Nuremberg laws: deprive Jews of their rights of citizenship, giving the status of “subjects” of Hitler’s Reich (1935) ...
... race are the ideal race They launch the Holocaust: systematic murder of Jews & others Anti-Semitism: hatred of Jewish people Nuremberg laws: deprive Jews of their rights of citizenship, giving the status of “subjects” of Hitler’s Reich (1935) ...
World War II
... • June 1940, France is forced to surrender in the same railway car in the forest at Campiegne, where Germany signed the Armistice in 1918. Then Hitler orders the railway car blown up. • The British Expeditionary forces are pushed back to Dunkirk Belgium with the backs to the Sea ...
... • June 1940, France is forced to surrender in the same railway car in the forest at Campiegne, where Germany signed the Armistice in 1918. Then Hitler orders the railway car blown up. • The British Expeditionary forces are pushed back to Dunkirk Belgium with the backs to the Sea ...
world war i
... avoidable. Write an essay in which you assess what took place from 1870 to 1935 and whether or not either of the wars might have been avoided. In discussing the question, be sure to consider the role played by key individuals, as well as the broader events shaping history. 2. Who do you think was re ...
... avoidable. Write an essay in which you assess what took place from 1870 to 1935 and whether or not either of the wars might have been avoided. In discussing the question, be sure to consider the role played by key individuals, as well as the broader events shaping history. 2. Who do you think was re ...
Chap 13 : WW2 in Europe
... Hitler turned his attention to the USSR after his failed attempt to conquer Britain He had always been interested in gaining lands in the east He decided to launch his attack on the USSR in the spring of 1941 However, before he could carry out his planned invasion of the USSR, he had to go to the ai ...
... Hitler turned his attention to the USSR after his failed attempt to conquer Britain He had always been interested in gaining lands in the east He decided to launch his attack on the USSR in the spring of 1941 However, before he could carry out his planned invasion of the USSR, he had to go to the ai ...
Lesson 2
... c. Concluding Activity: Students will be asked how they believe WWII affected the interactions between the countries involved both then and at the present time. d. Homework: Students will be asked to color in the blank world map provided by coloring all those countries involved in the axis one color ...
... c. Concluding Activity: Students will be asked how they believe WWII affected the interactions between the countries involved both then and at the present time. d. Homework: Students will be asked to color in the blank world map provided by coloring all those countries involved in the axis one color ...
Chapter 26 Study Guide
... 9. Compared to the other nations that fought in the war, the United States fared much better. Why did the U.S. lose fewer lives than other nations that fought? Why did the U.S. economy come out of the war stronger than ...
... 9. Compared to the other nations that fought in the war, the United States fared much better. Why did the U.S. lose fewer lives than other nations that fought? Why did the U.S. economy come out of the war stronger than ...
WORLD WAR II
... Hitler total power ● all parties were outlawed except the Nazi party ● Announces himself dictator ...
... Hitler total power ● all parties were outlawed except the Nazi party ● Announces himself dictator ...
... Sudetnland (home to many Germans), Czech’s refused and Hitler threatened war. Munich Conference – French and British leaders met with Hitler in Sept. 1938. Appeased Hitler by persuading the Czech’s to give up the Sudetenland to preserve peace. “The Government had to choose between shame and war, the ...
Allied Powers
... hopping , where Allied forces took only the most strategically important islands, instead of ...
... hopping , where Allied forces took only the most strategically important islands, instead of ...
WHII_Major_Events_of_WWII
... E. Battle of Britain For the following nine months, the German air force (Luftwaffe) launched repeated bombing raids on British towns and cities. This was known as the BLITZ and was an attempt to bomb Britain into submission. ...
... E. Battle of Britain For the following nine months, the German air force (Luftwaffe) launched repeated bombing raids on British towns and cities. This was known as the BLITZ and was an attempt to bomb Britain into submission. ...
England - MrSparksWiki
... – Dreams of a new Roman empire (Wants to control the Mediterranean Sea ) – Fascist slogan: “A country is nothing without conquest” ...
... – Dreams of a new Roman empire (Wants to control the Mediterranean Sea ) – Fascist slogan: “A country is nothing without conquest” ...
Chapter 24 World War II
... German Aggression • 1938 – Germany tries to take over Czechoslovakia • Britain & France Object • Munich Pact oFrance agrees to let Germany take part of Czech in return for no further aggression oNo one asked the Czechs ...
... German Aggression • 1938 – Germany tries to take over Czechoslovakia • Britain & France Object • Munich Pact oFrance agrees to let Germany take part of Czech in return for no further aggression oNo one asked the Czechs ...
From Appeasement to War 16sect 1
... Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain into believing that he only wanted peace. ...
... Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain into believing that he only wanted peace. ...
Timeline
... is solidified by an Italy-Germany alliance in May 1939. This was extended in September, 1940 by a military alliance among Germany, Italy, and Japan—the so-called Berlin Pact. January 19, 1937: Japan withdraws from the Washington Conference Treaty. July 7, 1937: Full-scale war begins between China an ...
... is solidified by an Italy-Germany alliance in May 1939. This was extended in September, 1940 by a military alliance among Germany, Italy, and Japan—the so-called Berlin Pact. January 19, 1937: Japan withdraws from the Washington Conference Treaty. July 7, 1937: Full-scale war begins between China an ...
Appeasement

Appeasement in a political context is a diplomatic policy of making political or material concessions to an enemy power in order to avoid conflict.The term is most often applied to the foreign policy of the British Prime Ministers Ramsay Macdonald, Stanley Baldwin and Neville Chamberlain towards Nazi Germany between 1933 and 1939. Their policies of avoiding war with Germany have been the subject of intense debate for more than seventy years among academics, politicians and diplomats. The historians' assessments have ranged from condemnation for allowing Adolf Hitler's Germany to grow too strong, to the judgment that they had no alternative and acted in Britain's best interests. At the time, these concessions were widely seen as positive, and the Munich Pact concluded on 30 September 1938 among Germany, Britain, France, and Italy prompted Chamberlain to announce that he had secured ""peace for our time.""























