* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
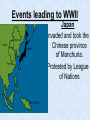
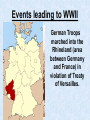
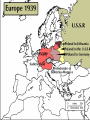
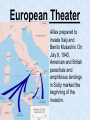
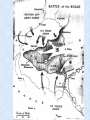
World War II LEADERS OF THE AXIS POWERS •ITALY- MUSSOLINI •JAPAN-HIROHITO •GERMANY-HITLER Events leading to WWII Italy Benito Mussolini seized power, became dictator and made Italy a fascist state Events leading to WWII Japan Invaded and took the Chinese province of Manchuria. Protested by League of Nations Events leading to WWII Germany Adolph Hitler became Fuehrer (leader) of Germany Events leading to WWII Hitler Destroyed the Republic Persecuted Jews Drove out political enemies Made Germany a totalitarian state (one party) state Events leading to WWII Mussolini’s army invaded and conquered Ethiopia in Africa Events leading to WWII German Troops marched into the Rhineland (area between Germany and France) in violation of Treaty of Versailles. Events leading to WWII Germany and Italy sent planes and troops to Francisco Franco, a revolutionary leader in Spain. Events leading to WWII Germany and Italy formed the Rome-Berlin Axis (Later Japan joined , making it the Rome-BerlinTokyo Axis) Events leading to WWII Japan began an undeclared war with china. Though the democracies condemned Japan’s action, the U.S. and England continued to ship vital war materials to her Events leading to WWII Hitler’s Legions marched into Austria and annexed it to Germany. Events leading to WWII Hitler threatened war if the Sudetenland (part of Czechoslovakia) were not turned over to Germany Events leading to WWII • France and England, anxious to avoid war, appeased Hitler and gave the area to him. • He then demanded and got the remainder of Czechoslovakia after signing a non-aggression pact with Russia Events leading to WWII • September 1, 1939 Germany attacks Poland • This marked the beginning of World War II • France and Great Britain declare war on Germany • Russia invades Poland from the east and seized the Baltic states. The Axis Powers Germany Italy Japan The Allied Powers France Great Britain Russia The United States attempts to remain Neutral (isolationism) As Germany and Japan gained ground, the U.S. changes her policy from one of strict neutrality to one of aiding the Allies “Short of War” Events leading to WWII Lend Lease Act, 1941, authorized the President to send aid to the Allies. The U.S. became the “arsenal of democracy” Events leading to WWII The U.S. Made preparations for defense in case of war Billions of dollars were appropriated for strengthening the Army, Navy, and Air Force. In 1940, the Selective Service Act was passed to raise an army of fighting men. Western Front April 1940, Germany invades and occupies Denmark (four hours) and Norway (four days) May 1940, Hitler invades Holland (three days) and Belgium (fourteen days). His army skirts the Marginal Line of France and races to the English Channel Norway Denmark Holland Belgium Western Front • June 1940, France is forced to surrender in the same railway car in the forest at Campiegne, where Germany signed the Armistice in 1918. Then Hitler orders the railway car blown up. • The British Expeditionary forces are pushed back to Dunkirk Belgium with the backs to the Sea • Through a supreme effort the entire army is evacuated by the British Navy but all their equipment is lost. Western Front July 1940- Hitler begins preparations for the invasion of England. Winston Churchill becomes Prime Minister of England (Great Britain) and vows to fight on. Western Front • August 1940Germany begins the Blitzkrieg (Lightning War) against England by trying to bomb her into submission Western Front • September 1940The Royal Air Force (RAF) Turns back the German Air Force and forces them to give up round-the- clock bombing. Now the Germans can only carry out nightly terror raids. Western Front October 1940- Hitler gives up plans to invade Great Britain and decides to turn against Russia. He plans to defeat England with submarines by cutting off supplies. His U-boast sink more than a British ship a day Western Front • June 1941- Hitler invades Russia. His army drives a thousand miles into Russia. At a spot fifteen miles form Moscow, he is stopped by the Russian Winter. Start of WWII Western Front • 1941- Mussolini invades Egypt and is thrown out by the British. • 1941- Italy and Hitler invade and conquers Hungary, Romania, Yugoslavia, Albania, Greece, and Crete. – This is done with the leadership of Field Marshall Rommell for Germany, known as “the desert fox”. Germany Field Marshall Rommell, “The Desert Fox” Events leading American involvement in WWII December 1941- The U.S. placed an embargo on all war materials sold to Japan. (Oil, steel, iron, etc) because of their refusal to stop her aggression against China. Japan knows she cannot exist without these material so she decide on radical action. Two of Japan’s top diplomats are dispatched to Washington D.C., in early December 1941, to try to negotiate a compromise .In the meantime the Japanese Fleet sets sail. December 7, 1941 December 7, 1941 • “A Day that will live in Infamy” • U.S. Naval and Military installations in Hawaiian Islands are surprise attacked by the Japanese without a declaration of war. • All eight U.S. battleships were sunk or badly damaged. • The U.S. world War II battle cry becomes “remember pearl harbor” December 8, 1941 • The U.S. congress Declares war on Japan December 11, 1941 • Germany and Italy declare war on the U.S. World War II America enters the war Two Front War European Theater Attempt to defeat Germany and Italy in Europe Pacific Theater Attempt to stop Japanese aggression in the Pacific Region Philippines Within hours of attacking Pearl Harbor, Japan attacks the Philippines. U.S. forces are forced to surrender to Japanese. American General Douglas McArthur vows, “I shall return!” Bataan Death March of surrendered U.S. Troops Battle of Midway • Japan attacks Midway Island (American Naval station) in an attempt to wipe out the entire U.S. fleet. • The critical Battle of Midway on June 4, 1942 turned the tide in the Americans' favor and they now controlled the Pacific. U.S.S. Yorktown, during the Battle of Midway Pacific Theater • The allied powers leapfrogged from island to island until they controlled the island of Saipan, the last island that protected the Japanese mainland. Raid on Tokyo Jimmy Doolittle led the audacious April 1942 bombing raid on Japan from the decks of an aircraft carrier. Although little damage resulted, his action raised American morale European Theater • Allies prepared to invade Italy and Benito Mussolini. On July 9, 1943, American and British parachute and amphibious landings in Sicily marked the beginning of the invasion. European Theater - Italy U.S. -General George Patton Britain-General Montgomery European Theater • Allies led by General Dwight D. Eisenhower make a secretive massive assault on France near Normandy. • The secret operation is code nicknamed “Operation Overlord”, which became known through history as D-Day D-Day D-Day • June 6, 1944 • More than 150,000 Allied soldiers stormed the beaches of Normandy in an early phase of the largest amphibious military operation in history • Although the Allied troops suffered heavy losses, including a casualty rate of 90% in several companies attacking Omaha Beach, they broke through German defenses after heavy fighting. NORMANDY, FRANCE European Theater The Battle of the Bulge Germans mounted one final, desperate offensive through the Ardennes Forest, in Belgium, against the relatively weak center of the American lines European Theater The Battle of the Bulge U.S. Division Commander of the surrounded 101st Airborne were asked to surrender to the Germans. He sent back his reply, “Nuts” European Theater The Battle of the Bulge After 10 days of fighting, the Allies had crushed the German offensive. The Battle of the Bulge was a major defeat for the German Army; it opened the door for Allied invasion of Germany Death of a President • President Roosevelt dies April 1945, his Vice President Harry Truman succeeds him as President. European Theater • By early 1945, the combined effect of Allied bombing, invading Americans and British troops from the West, and vengeful Soviets in the East had reduced much of Germany to rubble. • The Soviets carried out the attack on Berlin, capturing it by the end of April. Hitler committed suicide in his bunker beneath Berlin on April 30 as the Soviets closed in. On May 8, remaining German forces finally surrendered unconditionally to the Allies. European Theater VE Day“Victory in Europe” May 8 1945 the war was officially over in Europe. Pacific Theater Japan still remained undefeated. The prospect of invading the island nation was daunting, especially in the face of projected bitter resistance from the Japanese people. Pacific Theater Roosevelt had gathered hundreds of scientists to develop a weapon of destruction, the A-Bomb. This secret group was code named the “Manhattan Project” Pacific Theater • August 6, 1945 the U.S. dropped the first Atomic Bomb on Hiroshima, Japan. • August 8, 1945 the U.S. dropped the second Atomic bomb on Nagasaki, Japan. Pacific Theater • On September 2, 1945, Japan surrendered aboard the U.S.S. Missouri. The War is Over! VJ Day September 2, 1945 Marked the end of the war Although more than 400,000 American soldiers were killed (nearly 300,000 in combat), these losses paled in comparison with those of other nations, particularly the Soviet Union, Japan, and Germany. American civilians also suffered comparatively little