APUSH Unit 10 Notes Filled In
... • the US decided to only take important islands to control the air and the sea • 50,000 and 110,000 casualties • allowed daily bombing of Japan ...
... • the US decided to only take important islands to control the air and the sea • 50,000 and 110,000 casualties • allowed daily bombing of Japan ...
Unit 12 – WWII: Study Guide
... (“My Struggle”). • It later became the basic book of Nazi goals and ideology. Nazi membership grew to almost a million. In 1933, Hitler was made Chancellor (Prime Minister) of Germany. Within a year, Hitler was master of Germany. He made Germany a one-party state and purged his ...
... (“My Struggle”). • It later became the basic book of Nazi goals and ideology. Nazi membership grew to almost a million. In 1933, Hitler was made Chancellor (Prime Minister) of Germany. Within a year, Hitler was master of Germany. He made Germany a one-party state and purged his ...
Chapter 17 Section 1
... for a wider European war. • Hitler and Mussolini sent arms and forces to support Franco, while the Soviet Union sent soldiers to help the Loyalists. • Nazi leaders used the war to test new bombers. • More than 500,000 people died in the struggle. • By 1939, Franco had won. He created a fascist dicta ...
... for a wider European war. • Hitler and Mussolini sent arms and forces to support Franco, while the Soviet Union sent soldiers to help the Loyalists. • Nazi leaders used the war to test new bombers. • More than 500,000 people died in the struggle. • By 1939, Franco had won. He created a fascist dicta ...
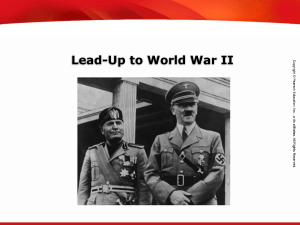
Chapter 13 The Rise of Dictators and World War II
... between Germany and Italy, and later would include Japan. 7. Benito Mussolini Dictator of Italy 8. General Hideki Tojo – Military leader of Japan. 9. Appeasement – the policy of meeting a nation’s demands to avoid war. 10. Lend - Lease Program – the policy in which the US sent war materials to the A ...
... between Germany and Italy, and later would include Japan. 7. Benito Mussolini Dictator of Italy 8. General Hideki Tojo – Military leader of Japan. 9. Appeasement – the policy of meeting a nation’s demands to avoid war. 10. Lend - Lease Program – the policy in which the US sent war materials to the A ...
Chapter 13 The Rise of Dictators and World War II
... between Germany and Italy, and later would include Japan. 7. Benito Mussolini Dictator of Italy 8. General Hideki Tojo – Military leader of Japan. 9. Appeasement – the policy of meeting a nation’s demands to avoid war. 10. Lend - Lease Program – the policy in which the US sent war materials to the A ...
... between Germany and Italy, and later would include Japan. 7. Benito Mussolini Dictator of Italy 8. General Hideki Tojo – Military leader of Japan. 9. Appeasement – the policy of meeting a nation’s demands to avoid war. 10. Lend - Lease Program – the policy in which the US sent war materials to the A ...
The Road to Revolution – Ch
... 1935 – Mussolini attacked Ethiopia; Mussolini and Hitler supported fascist Francisco Franco in his takeover of the Spanish government in the Spanish Civil War; Hitler remilitarized Germany (breaking the Treaty of Versailles) By 1938, Hitler had annexed Austria and Czechoslovakia and the Allies (most ...
... 1935 – Mussolini attacked Ethiopia; Mussolini and Hitler supported fascist Francisco Franco in his takeover of the Spanish government in the Spanish Civil War; Hitler remilitarized Germany (breaking the Treaty of Versailles) By 1938, Hitler had annexed Austria and Czechoslovakia and the Allies (most ...
1: Dictators key words Score: /8 3: Stalin Score: /10 2: Treaty of
... Stalin was the dictator of communist Russia, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) from 1929 to 1953. Under Stalin, the Soviet Union was transformed from a peasant society into an industrial and military superpower. However, he ruled by terror, and millions of his own citizens died during h ...
... Stalin was the dictator of communist Russia, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) from 1929 to 1953. Under Stalin, the Soviet Union was transformed from a peasant society into an industrial and military superpower. However, he ruled by terror, and millions of his own citizens died during h ...
World War II - davis.k12.ut.us
... Spain: Franco’s fascists won the Spanish Civil War b. Soviet Union: Joseph Stalin took control of the communist nation a. ...
... Spain: Franco’s fascists won the Spanish Civil War b. Soviet Union: Joseph Stalin took control of the communist nation a. ...
THE UNITED KINGDOM AND THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
... a severe economic crises that paved the way for the rise of the Nazy party. British people were worried about the rearmament of Germany because they didn’t want to involve in another war. In 1938 the Munich agreement annexed Austria to Germany. Soon after the latter invaded part of Czechoslovakia. B ...
... a severe economic crises that paved the way for the rise of the Nazy party. British people were worried about the rearmament of Germany because they didn’t want to involve in another war. In 1938 the Munich agreement annexed Austria to Germany. Soon after the latter invaded part of Czechoslovakia. B ...
AP EH CH - Wichita Falls ISD
... withdrawal of Germany from the Geneva Disarmament Conference and withdrawal from the League of Nations 6. by the beginning of 1935, Hitler became convinced that Germany could break some of the provisions of the Versailles Treaty without serious opposition from the French or British 7. on March 9, 19 ...
... withdrawal of Germany from the Geneva Disarmament Conference and withdrawal from the League of Nations 6. by the beginning of 1935, Hitler became convinced that Germany could break some of the provisions of the Versailles Treaty without serious opposition from the French or British 7. on March 9, 19 ...
World War II - SUNY UlsterSUNY Ulster
... accepted German annexation of Sudetenland at Munich Conference Aug. 1939: Germany & USSR agreed to divide eastern Europe in Ribbentrop-Molotov Pact Sept. 1, 1939: Germany invaded Poland © 2000 Wadsworth / Thomson Learning Sept. 3, 1939: Britain & France declared war on Germany ...
... accepted German annexation of Sudetenland at Munich Conference Aug. 1939: Germany & USSR agreed to divide eastern Europe in Ribbentrop-Molotov Pact Sept. 1, 1939: Germany invaded Poland © 2000 Wadsworth / Thomson Learning Sept. 3, 1939: Britain & France declared war on Germany ...
Unit10_RiseofDictatorsReading
... Background: Italians were unhappy with the Treaty of Versailles that ended World War I. They thought they should have gotten more territory. Economic Situation: Poverty was widespread in Italy. How the Dictator Came to Power: Benito Mussolini was a newspaper editor who promised territorial expansion ...
... Background: Italians were unhappy with the Treaty of Versailles that ended World War I. They thought they should have gotten more territory. Economic Situation: Poverty was widespread in Italy. How the Dictator Came to Power: Benito Mussolini was a newspaper editor who promised territorial expansion ...
WWII notes - Montgomery County Schools
... -breaking the treaty he had with them -he was able to push the Russians almost to Moscow -Stalingrad- Russia turned the tide of the war with Germany *ended any real plan Hitler had of dominating Europe -the bitter Russian winter stopped them -Stalin knew he could not defeat Hitler alone so he asked ...
... -breaking the treaty he had with them -he was able to push the Russians almost to Moscow -Stalingrad- Russia turned the tide of the war with Germany *ended any real plan Hitler had of dominating Europe -the bitter Russian winter stopped them -Stalin knew he could not defeat Hitler alone so he asked ...
Hitler`s Cabinet - Kabatas Model United Nations Conference
... with the signing of the Anglo-German Naval Agreement on 18 June 1935. The lack of any significant protest by either the British or the French following the Italian invasion of Ethiopia encouraged Hitler to send 3,000 troops into the demilitarised zone of the Rhineland in violation of the Treaty of V ...
... with the signing of the Anglo-German Naval Agreement on 18 June 1935. The lack of any significant protest by either the British or the French following the Italian invasion of Ethiopia encouraged Hitler to send 3,000 troops into the demilitarised zone of the Rhineland in violation of the Treaty of V ...
Course Learning Outcomes for Unit V Reading
... http://gcveteransmemorial.org/photo-panels/.) Japan and Italy, though not major factors in any Great War alliance, felt disregarded in the previous treaties. Fueled by both desperation and outrage, these two joined with Germany, creating a new Axis alliance against the revitalized Alliance of Wester ...
... http://gcveteransmemorial.org/photo-panels/.) Japan and Italy, though not major factors in any Great War alliance, felt disregarded in the previous treaties. Fueled by both desperation and outrage, these two joined with Germany, creating a new Axis alliance against the revitalized Alliance of Wester ...
Hitler`s Words and Hitler`s Deeds - University of Toledo Digital
... Exactly five months after the writing of this letter, Hitler drove out to Rohm's villa in the early hours of the morning, roughly awakened him and had him shot there and then without the least pretence of trial. More than sixty' 12' of the oldest and most trusted leaders of the National-Socialist mo ...
... Exactly five months after the writing of this letter, Hitler drove out to Rohm's villa in the early hours of the morning, roughly awakened him and had him shot there and then without the least pretence of trial. More than sixty' 12' of the oldest and most trusted leaders of the National-Socialist mo ...
WWII Review
... 10. What book did Hitler write, and what did he say in it? 11. Why did Japan argue that it needed to expand its territory? 12. Where did Japan seek to expand its territory first? 13. Why did Japan say it needed to expand its territory? 14. During the 1930’s how did Hitler and Germany violate the Tre ...
... 10. What book did Hitler write, and what did he say in it? 11. Why did Japan argue that it needed to expand its territory? 12. Where did Japan seek to expand its territory first? 13. Why did Japan say it needed to expand its territory? 14. During the 1930’s how did Hitler and Germany violate the Tre ...
World War I: The Fighting Ends
... • Asked to pay huge reparations ($33 billion) • Forced to give up large amounts of land • Massive disarmament left them with only a defensive army ...
... • Asked to pay huge reparations ($33 billion) • Forced to give up large amounts of land • Massive disarmament left them with only a defensive army ...
Document-Based Question (DBQ)
... World War II in Europe. The war pitted Germany, Italy and Japan – the Axis Powers – against the Allies, which included Britain, France, the Soviet Union and the United States (after Dec. 7, 1941), among others. Earlier, an alliance called the Rome-Berlin Axis had been established between Germany and ...
... World War II in Europe. The war pitted Germany, Italy and Japan – the Axis Powers – against the Allies, which included Britain, France, the Soviet Union and the United States (after Dec. 7, 1941), among others. Earlier, an alliance called the Rome-Berlin Axis had been established between Germany and ...
American Foreign Diplomacy
... 1944, the Germans launched a last counteroffensive in the Ardennes Forest Resulted in the Battle of the Bulge Temporarily slowed the Allied advance In the east, the Soviets had finally pushed into Germany American & Russian troops met at the Elbe River, 100 miles west of Berlin On April 30, 1945, Hi ...
... 1944, the Germans launched a last counteroffensive in the Ardennes Forest Resulted in the Battle of the Bulge Temporarily slowed the Allied advance In the east, the Soviets had finally pushed into Germany American & Russian troops met at the Elbe River, 100 miles west of Berlin On April 30, 1945, Hi ...
Hitler`s Rise to Power - MsPhillips
... unfair. In this climate, Hitler began building the National Socialist Party (the Nazi party). However, as long as the German economy could offer reasonably full employment groups like Hitler’s could not gain power. Unfortunately this situation changed with the onset of the Great Depression. By 1930 ...
... unfair. In this climate, Hitler began building the National Socialist Party (the Nazi party). However, as long as the German economy could offer reasonably full employment groups like Hitler’s could not gain power. Unfortunately this situation changed with the onset of the Great Depression. By 1930 ...
World War II Background Information to read with PPP
... Japanese Aggression and the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere – European powers were too busy to protect their colonies in East Asia and Japan took advantage of this and continued their policy of imperialist expansion. In 1940 Japan launched an initiative known as the Greater East Asia Co-Pros ...
... Japanese Aggression and the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere – European powers were too busy to protect their colonies in East Asia and Japan took advantage of this and continued their policy of imperialist expansion. In 1940 Japan launched an initiative known as the Greater East Asia Co-Pros ...
Chap. 27 PPT
... – Stalin wanted a second front opened in Western Europe Yalta Conference (Feb. 1945) – agreement let Soviets control elections in Eastern Europe in exchange for agreeing to declare war on Japan Potsdam Conference (July 1945) – discussed establishment of post-war order, peace treaties, and effect ...
... – Stalin wanted a second front opened in Western Europe Yalta Conference (Feb. 1945) – agreement let Soviets control elections in Eastern Europe in exchange for agreeing to declare war on Japan Potsdam Conference (July 1945) – discussed establishment of post-war order, peace treaties, and effect ...
Appeasement

Appeasement in a political context is a diplomatic policy of making political or material concessions to an enemy power in order to avoid conflict.The term is most often applied to the foreign policy of the British Prime Ministers Ramsay Macdonald, Stanley Baldwin and Neville Chamberlain towards Nazi Germany between 1933 and 1939. Their policies of avoiding war with Germany have been the subject of intense debate for more than seventy years among academics, politicians and diplomats. The historians' assessments have ranged from condemnation for allowing Adolf Hitler's Germany to grow too strong, to the judgment that they had no alternative and acted in Britain's best interests. At the time, these concessions were widely seen as positive, and the Munich Pact concluded on 30 September 1938 among Germany, Britain, France, and Italy prompted Chamberlain to announce that he had secured ""peace for our time.""