Do Now
... 2. Understand the role of appeasement, nonintervention, (isolationism), and the domestic distractions in Europe and the United States prior to the outbreak of WWII. 3. Identify and locate the Allied and Axis powers on a map and discuss the major turning points of the war, the principals theaters of ...
... 2. Understand the role of appeasement, nonintervention, (isolationism), and the domestic distractions in Europe and the United States prior to the outbreak of WWII. 3. Identify and locate the Allied and Axis powers on a map and discuss the major turning points of the war, the principals theaters of ...
World War II
... Czechoslovakia), only after the invasion of Poland on Sept. 1, 1939 do Britain and France declare war on Germany to stop their expansion. • Poland falls to Germany • 1939 – summer of 1940 is known as the “Sitzkrieg”, or Sitting War, since no fighting takes place at this time. ...
... Czechoslovakia), only after the invasion of Poland on Sept. 1, 1939 do Britain and France declare war on Germany to stop their expansion. • Poland falls to Germany • 1939 – summer of 1940 is known as the “Sitzkrieg”, or Sitting War, since no fighting takes place at this time. ...
Slide 1
... problem though because they also spoke several other languages. Germany then agreed to meet in Munich to discuss Hitler's appeasement, which both France and Britain agreed to. But later on Chamberlain broke the agreement, forcing Germany to attack. ...
... problem though because they also spoke several other languages. Germany then agreed to meet in Munich to discuss Hitler's appeasement, which both France and Britain agreed to. But later on Chamberlain broke the agreement, forcing Germany to attack. ...
WORLD WAR II IN SUMMARY ( 1939 - 1945 ) - SHS-AP-World
... A. Massive German counterattack: Battle of the Bulge 1. Unexpected by Allies that Hitler would throw full force into offensive move instead of saving troops for final defense of Germany itself a) Pushed Allies back 40-50 miles, but only really delayed the Allied advance one month 2. "The Last Blitzk ...
... A. Massive German counterattack: Battle of the Bulge 1. Unexpected by Allies that Hitler would throw full force into offensive move instead of saving troops for final defense of Germany itself a) Pushed Allies back 40-50 miles, but only really delayed the Allied advance one month 2. "The Last Blitzk ...
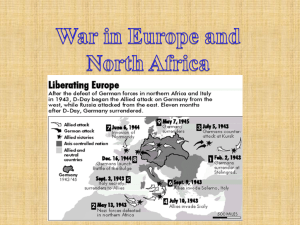
14_1 War in Europe and North Africa with Pair Share
... 1. Hitler broke his nonaggression pack with Stalin and invaded the Soviet Union in 1941. – The Soviets then joined the Allies as enemies of the Axis Powers. – At first the Soviets seemed unable to stop the German blitzkrieg; however, the bitterly cold Russian winter proved a great ally. – Still, the ...
... 1. Hitler broke his nonaggression pack with Stalin and invaded the Soviet Union in 1941. – The Soviets then joined the Allies as enemies of the Axis Powers. – At first the Soviets seemed unable to stop the German blitzkrieg; however, the bitterly cold Russian winter proved a great ally. – Still, the ...
Chapter 24 World War II: The Road to War
... 2. How did American involvement in the European conflict grow from 1939 to 1941? 3. Why did Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbor led to United States to declare war? 4. How much did President Roosevelt consider American public opinion when deciding how to respond to the conflict in Europe? 5. Why did he n ...
... 2. How did American involvement in the European conflict grow from 1939 to 1941? 3. Why did Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbor led to United States to declare war? 4. How much did President Roosevelt consider American public opinion when deciding how to respond to the conflict in Europe? 5. Why did he n ...
The Interwar Period
... Sun Yat-Sen dies. New Nationalist leader Chaing Kai-Shek declares war on Communists Mao and followers flee into mountains: The Long March In mountains Mao rebuilds Communist party ...
... Sun Yat-Sen dies. New Nationalist leader Chaing Kai-Shek declares war on Communists Mao and followers flee into mountains: The Long March In mountains Mao rebuilds Communist party ...
Momentum for the Allies
... By January of 1945, both the Soviet Union and the American forces were nearing Berlin. The Soviet Union reached the German capital first. By this time Hitler realized that his dream of a thousand year reich was over. He and a group of his closest advisors committed suicide in a bunker as the Soviets ...
... By January of 1945, both the Soviet Union and the American forces were nearing Berlin. The Soviet Union reached the German capital first. By this time Hitler realized that his dream of a thousand year reich was over. He and a group of his closest advisors committed suicide in a bunker as the Soviets ...
World War II
... Question of the Day Which of the following statements about the 1936 Summer Olympics is not accurate? (A) they were held in Berlin, Germany (B) German Jews were not allowed to compete (C) some Americans suggested the U.S. should boycott the Games as Adolf Hitler would use them to promote his goals ...
... Question of the Day Which of the following statements about the 1936 Summer Olympics is not accurate? (A) they were held in Berlin, Germany (B) German Jews were not allowed to compete (C) some Americans suggested the U.S. should boycott the Games as Adolf Hitler would use them to promote his goals ...
WHAP 1914-present review
... Nazis attempted to achieve their policy of eliminating entire races of people. Jews were deprived of citizenship and legal rights and forced into ghettoes. In 1942 the “final solution” started the systematic extermination of human beings. ...
... Nazis attempted to achieve their policy of eliminating entire races of people. Jews were deprived of citizenship and legal rights and forced into ghettoes. In 1942 the “final solution” started the systematic extermination of human beings. ...
World War II Teacher - New Smyrna Beach High School
... World War II Study Guide World War II Why? - WWII 1939 -1945 …………………USA INVOLVEMENT 1941-1945 -Four Reasons for WWII1-Treaty of Versailles a) Germany lost land to surrounding nations b) Reduced size of military c) War Reparations 2-World-Wide Depression a) The Depression made Germany’s debt even wor ...
... World War II Study Guide World War II Why? - WWII 1939 -1945 …………………USA INVOLVEMENT 1941-1945 -Four Reasons for WWII1-Treaty of Versailles a) Germany lost land to surrounding nations b) Reduced size of military c) War Reparations 2-World-Wide Depression a) The Depression made Germany’s debt even wor ...
Lord of the Flies
... 1936- Germany and Italy • Germany and Italy join forces (an alliance) in October of 1936 • Axis leaders Adolf Hitler and Italian prime minister Benito Mussolini meet in Munich, Germany, 1940 ...
... 1936- Germany and Italy • Germany and Italy join forces (an alliance) in October of 1936 • Axis leaders Adolf Hitler and Italian prime minister Benito Mussolini meet in Munich, Germany, 1940 ...
12. Nazi Germany - Hitler`s Foreign Policy
... This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not editable. For more detailed instructions, see the Getting Started presentation. ...
... This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not editable. For more detailed instructions, see the Getting Started presentation. ...
WWII European Front Notes Outline
... • FDR and Churchill concede E. European nations bordering USSR should be “Soviet friendly,” in exchange… – Soviets pledge free elections in all land liberated from Nazi Germany • FDR & Stalin divided and weak Germany – Churchill wants a strong Germany…why? • Lay out framework for United Nations (5 m ...
... • FDR and Churchill concede E. European nations bordering USSR should be “Soviet friendly,” in exchange… – Soviets pledge free elections in all land liberated from Nazi Germany • FDR & Stalin divided and weak Germany – Churchill wants a strong Germany…why? • Lay out framework for United Nations (5 m ...
Chapter 22 Power Point
... has established the Third Reich. Sought lebensraum – “living space” for the Aryan nation. Rebuild German military; establish draft Seize & fortify the Rhineland. France was upset but did nothing to intervene. ...
... has established the Third Reich. Sought lebensraum – “living space” for the Aryan nation. Rebuild German military; establish draft Seize & fortify the Rhineland. France was upset but did nothing to intervene. ...
PPTNotesAppeasement Trying to Keep the Peace
... aggression in the 1930s, Britain and France repeatedly made concessions,1) hoping to keep peace. Both nations were 2) dealing with serious economic problems as a result of the Great Depression. In addition, the horrors of World War I had created a 3) deep desire to avoid war. ...
... aggression in the 1930s, Britain and France repeatedly made concessions,1) hoping to keep peace. Both nations were 2) dealing with serious economic problems as a result of the Great Depression. In addition, the horrors of World War I had created a 3) deep desire to avoid war. ...
Europe Erupts in War
... pact with Hitler in 1939? What was the blitzkrieg? What was Germany planning during the ...
... pact with Hitler in 1939? What was the blitzkrieg? What was Germany planning during the ...
Coming of War
... Spanish Civil War − Spanish conflict fought from 1936 to 1939 appeasement − policy of granting concessions to a potential enemy in the hope that it will maintain peace Anschluss − union in which Hitler forced Austria to become part of Germany’s territory Munich Pact − agreement in which Britain and ...
... Spanish Civil War − Spanish conflict fought from 1936 to 1939 appeasement − policy of granting concessions to a potential enemy in the hope that it will maintain peace Anschluss − union in which Hitler forced Austria to become part of Germany’s territory Munich Pact − agreement in which Britain and ...
Economy of Nazi Germany

World War I caused economic and manpower losses on Germany led to a decade of economic woes, including hyperinflation in the mid-1920s. Following the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the German economy, like those of many other western nations, suffered the effects of the Great Depression, with unemployment soaring. When Hitler became Chancellor in 1933, he introduced new efforts to improve Germany's economy, including autarky and the development of the German agricultural economy by placing tariffs on agricultural imports.However, these changes—including autarky and nationalization of key industries—had a mixed record. By 1938, unemployment was practically extinct. Wages increased by 10.9% in real terms during this period. However, nationalization and a cutting off of trade meant rationing in key resources like poultry, fruit, and clothing for many Germans.In 1934 Hjalmar Schacht, the Reich Minister of Economics, introduced the Mefo bills, allowing Germany to rearm without spending Reichmarks but instead pay industry with Reichmarks and Mefo bills (Government IOU's) which they could trade with each other. Between 1933 and 1939, the total revenue was 62 billion marks, whereas expenditure (at times made up to 60% by rearmament costs) exceeded 101 billion, thus creating a huge deficit and national debt (reaching 38 billion marks in 1939) coinciding with the Kristallnacht and intensified persecutions of Jews and the outbreak of the war.