* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 22 Power Point
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
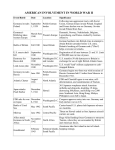
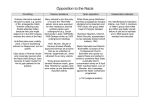
Chapter 22 Dictators Defy the League of Nations Meiji Period – modernization & westernization Spread of militarism after WWI Wanted to dominate the Asian “Sphere of Influence” Imperialist expansion Hideki Tojo – military-style dictator Japan expands in Asia 1911 overthrow of the Manchu Dynasty Chinese republic – Sun Yat-sen, organizer of the Kuomintang or Nationalist Party. Chiang Kai-shek leads after Sun Yatsen dies. Civil war breaks out when communists under Mao Zedong challenge the Nationalist Republic. The two sides suspend their civil war when Japan takes advantage of the strife to invade China in 1937. They join together to fight Japan, but Japan is prepared and strong. U.S. sends aid through the “Flying Tigers.” League of Nations condemns the invasion but has no enforcement authority. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I36cglDOtJg Italy is forever trying to return to the glory of the Roman Empire. Expand by invading Ethiopia which had defeated Italy in the 19th century. Italy had advanced weapons; Ethiopia didn’t. League of Nations imposed economic sanctions, but to no real effect. Hitler has established the Third Reich. Sought lebensraum – “living space” for the Aryan nation. Rebuild German military; establish draft Seize & fortify the Rhineland. France was upset but did nothing to intervene. Photo: www.bbc.co.uk Rome-Berlin Axis 1936 Line not a partition but an axis around which all European states can revolve. Anti-Comintern Pact (Germany & Japan) Axis Powers GERMANY ITALY JAPAN Fascist Francisco Franco revolted against Spain’s republican government. (1936) Supported by Germany & Italy Tried out new weapons and tactics. Guernica, Picasso’s depiction of the Spanish Civil War Anschluss is forbidden by the Treaty of Versailles. 1938 Hitler demands a Nazi chancellor for Austria & gets one. New chancellor “requests” Hitler to send German troops to “reestablish order.” Sudetenland with many German speakers, some of whom had fled Nazi aggression. Hitler demanded it. Neville Chamberlain, PM of Britain tries to resolve. Hitler promises not to make further territorial claims. Munich Conference, September 1938 Chamberlain and the French PM Daladier give the Sudetenland to Hitler. Note: Czechoslovakia had no representation at the conference. Chamberlain & Hitler @ Munich 1938 Chamberlain justified appeasement, claiming victory because they had avoided war. Winston Churchill said it was a total defeat and would lead to European subjugation by the Nazis. Winston Churchill A week after Munich, Hitler demanded the “Polish Corridor.” British and French resist and agree to defend Poland. They also get Russia to agree. Hitler expected them to give in since they had before. Axis Successes WWII begins with the German invasion of Poland. Britain & France declare war on Germany. Hitler took Poland in less than 4 weeks. How? Panzers – tank divisions Wehrmacht – German Army Blitzkrieg – lightning warfare, fast and decisive strikes Luftwaffe – German air force After the takeover of Poland, a lull or “sitzkrieg” (sitting war) occurred in which neither side launched an offensive. April 1940 Germany attacked Denmark and Norway to prevent England and France from using them as bases. The “Fifth Column” or traitors helped the Nazis take Denmark & Norway. Maginot Line Germans simply trek through the Ardennes Forest using blitzkrieg. (map page) Allies are pushed back to Dunkirk. Miracle at Dunkirk (page ) Many French flee to Britain in the Dunkirk evacuation. French government under Field Marshal Henri Petain surrenders on June 22, 1940. Most of France is occupied by Nazis Southern France is governed by Petain for the Germans at Vichy. (Vichy France) Mussolini invades Egypt and is repelled. Hitler sends in help: Field Marshall Erwin Rommel, the Desert Fox. Lacks supplies but almost conquers Alexandria, Egypt. Erwin Rommel Day bombing Night bombing Total warfare – targeting civilians in cities Narnia clip http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SQ0fGS 01Pdg http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LsKD GM5KTBY Our Finest Hour – Churchill http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MkTw 3_PmKtc&feature=related Fight them on the Beaches… - Churchill Gave Britain 50 WWI destroyers Lend-Lease Act 1941 Atlantic Charter (see text page 581) Germany could not manage to defeat the British navy or gain control of the French navy, whose ships had been scuttled or captured by the British so they Germans couldn’t get them. An invasion of a well-defended island would be difficult without a strong navy. Ultimately, Hitler chose not to invade Britain after he had bombed it because he turned his attention to Russia. Invasion of Russia German-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact 1939. Germany invaded one part of Poland and Russia invaded the other. Germans betrayed the Russians. Spring 1941 invasion. Reasons: • Lebensraum • Oil Nazis underestimated the Russians. Russian industry Length of time it would take Russian winter German army unprepared Russians retreat before the Germans. Scorched earth tactics Russian casualties: 4-5 million by December Germans almost reached Moscow. Winter arrived first. -40 degrees fahrenheit Stalingrad – Russians are heavily assaulted but refuse to surrender. Russians defeat the Germans after months of fierce fighting. Russians began receiving supplies from the other Allies through Iran, which helped them greatly. United States held the Philippines, Guam, Hawaii, and some other small Pacific islands. Japanese could not dominate Asia with the U.S. presence in the Pacific. Plan to cripple the U.S. fleet so Japan could gain dominance. Japanese were angry at U.S. interference with their plans in China. They were also offended by the embargo the U.S. had placed on Japan preventing the country from getting badly needed oil. (Typically viewed as an act of war) December 7, 1941 surprise attack. Battleships damaged and destroyed. Airfields wrecked. Aircraft carriers are out to sea instead of in port. Caused the American people to support U.S. entry into WWII. President Roosevelt makes his “date which will live in infamy” speech. Congress officially declares war on Japan. Germany & Italy declare war on U.S. Japan had “awakened a sleeping giant.” North Africa to Italy Monty (British General Bernard Montgomery) defeated the Nazis in North Africa in 1942. U.S. sent forces to Algeria to defeat the Nazis under the command of General Dwight D. Eisenhower. First invaded the island of Sicily under Eisenhower. Mussolini resigned. Allies land on mainland Europe in the Italian peninsula in Sept. 1943. Italy surrenders, but German troops keep fighting in Italy. Mussolini was captured then rescued by the Nazis. Then Italian partisans who opposed the Nazis recaptured Mussolini and executed him. From Britain to Normandy Casablanca in January 1943 – Churchill & Roosevelt Tehran in late 1943 – “Big Three” Churchill, Roosevelt, & Stalin Decide to demand the unconditional surrender of Germany. Decide that U.S. & Britain would retake Europe through France and that USSR would close in on Germany from the east. Operation Overlord – Allied plan to invade France and begin the reconquest of Europe. Fake landing site @ Calais. • Dummy bases • Dummy tanks • Dummy invasion force • False messages • Naval maneuvers off Calais Real landing @ Normandy’s beaches. Five beaches • Omaha – U.S. • Utah – U.S. • Sword - British • Gold - British • Juno - British D-Day – June 6, 1944 Bombed the coastal targets Thousands of ships Paratroopers dropped behind enemy lines Help of the French Resistance Massive invasion force: 1 million men; 177,000 vehicles; 500,000 tons of supplies Allied victory seemed assured, but the Germans continued to resist for another year. Why? • “Miracle weapons:” V-1 rockets, jet aircraft, promise of the atomic bomb • Expected division among the Allies • Nazi fear of Communism strengthened the German resistance. Island to Island After Pearl, Japanese attack Pacific islands. Philippines Outnumbered, Americans try to defend a small section @ Luzon. Put up a strong defense, but ultimately captured. . General Douglas MacArthur escapes at the orders of President Roosevelt. “I shall return.” Troops forced to march some 70 miles under inhumane conditions. Hundreds die along the way. “Bataan Death March” The Japanese capture many Pacific islands: • Hong Kong • Malaysia • Singapore • Burma (not an island, but a British colony in SE Asia) • Dutch East Indies Japanese get over-extended. U.S. war production gets up to speed. U.S. starts to advance across the Pacific. Battle of the Coral Sea • Prevented the Japanese from invading Australia • First naval battle in history in which the ships involved never saw each other. • Why? All the damage was done by aircraft launched from carriers. Battle of Midway Island • Midway Island is about in the middle of the • • • • Pacific. Japanese were planning to attack the U.S. bases there. U.S. broke the Japanese codes and launched the offensive first. U.S. gained a decisive victory. Turning point in the war: Japanese never went on the offensive again. U.S. begins its island-hopping campaign. Recaptures islands held by Japanese Skips some islands; takes the ones which make good airbases. Trying to get within bombing reach of the Japanese mainland. War in the Pacific was brutal. • Banzai charges • Kamikazi pilots • Japanese refusal to surrender • Surrender = Loss of honor/face • Better to commit suicide or die fighting General MacArthur fulfills his promise. Returns to liberate the Philippines in fall of 1944. 1945 Successes • Iwo Jima: sulfurous island described by Marines as hell on earth. 216 Japanese finally surrender after two months of brutal fighting. They originally has 21,000-23,000 troops on the island. • Okinawa: puts our bombers within reach of the Japanese mainland. (Map p. 591) U.S. Marines raise the U.S. flag on Iwo Jima. 1943-44 Soviets push the Germans back toward Germany. As they go, they establish communist totalitarianism over the formerly Nazi dominated areas they have “liberated.” Allied troops liberate Paris. Bombing of German cities. http://video.pbs.org/video/1405744809/ By December 1944 the Allies reach the border of Germany. Germany’s last advance: The Battle of the Bulge Big Three @ Yalta (Crimea) • Germany to pay reparations • German war criminals to be tried in court • German military disarmed and disbanded • German divided into zones of occupation • Stalin & USSR to join the effort against Japan. Eisenhower orders allied troops to halt at the Elbe River. The Big Three had agreed at Yalta to allow the Russians to move into Berlin. April 30, 1945 – Hitler commits suicide. May 7, 1945 – Germans surrender. May 8, 1945 – VE Day (Victory in Europe) Allies liberate the concentration camps. They realize the extent of the holocaust. Liberation of Dachau 29 April 1945 The Victorious Allies meet again & issue an ultimatum to Japan: Surrender or face serious consequences. New Crew • U.S. President Harry Truman • U.K. PM Clement Attlee • USSR Premier Josef Stalin Although the war ended in Europe, the war in the Pacific continued. U.S. incendiary bombing of Tokyo. One night 80,000 people died. Japan refused to surrender. Incendiary bombing of Tokyo Allies dreaded invading Japan. They had been so fierce in resisting in the Pacific islands. They would rather die than surrender. They had prepared their civilian population to resist an Allied invasion. Prediction of a million Japanese casualties and perhaps that many Allied casualties. Development of the atomic bomb. Hope that it would shorten the war and prevent the massive loss of life from invasion. Dropped on Hiroshima on Aug. 6, 1945 70,000 people died. Rubble of Hiroshima Japanese still did not surrender. Second bomb dropped on Nagasaki on August 8, 1945. Soviets declare war on Japan on Aug. 8. Why? Japan surrenders on August 14, 1945. They ask only that their Emperor Hirohito retain his throne. General MacArthur and Emperor Hirohito V-J (Victory in Japan) Day: September 2, 1945 World War II ends. San Francisco Conference of the Allied Powers in 1945. Fifty governments agree to form the United Nations. Purpose: maintain international peace & security. United Nations headquarters is in New York City. Organized into 3 major bodies: • Secretariat – headed by the Secretary-General; administration • General Assembly – representative body which debate world issues annually • Security Council – executive power with 5 permanent members (US, Great Britain, France, China, Russia) and 10 nonpermanent members. Also has a bureaucracy made up of special agencies • World Health Organization • UNESCO • International Labor Organization • UNICEF • Etc. No more world wars so far Threat of M.A.D. (mutually assured destruction) may have been more of a preventer of war than the U.N. Matthew 5:9 Blessed are the peacemakers, for they will be called children of God. ---Jesus John 14:27-28 Peace I leave with you; my peace I give you. I do not give to you as the world gives. Do not let your hearts be troubled and do not be afraid. ---Jesus Isaiah 9:7 Of the greatness of his government and peace there will be no end. He will reign on David’s throne and over his kingdom, establishing and upholding it with justice and righteousness from that time on and forever. The zeal of the LORD Almighty will accomplish this.