World History II
... 7) How did U.S. policy toward Japanese-Americans during WWII undermine its own national ideals and values, as otherwise embodied in law by the Constitution? ...
... 7) How did U.S. policy toward Japanese-Americans during WWII undermine its own national ideals and values, as otherwise embodied in law by the Constitution? ...
Chapter 17 Study Guide
... d. They began to bomb London and other cities. ____ 14. What was one reason why the Spanish Civil War was called a “dress rehearsal” for World War II? a. The Nazis used the war to test their new weapons. b. Supporters of the Spanish Loyalists supported the Axis powers. c. The forces of democracy def ...
... d. They began to bomb London and other cities. ____ 14. What was one reason why the Spanish Civil War was called a “dress rehearsal” for World War II? a. The Nazis used the war to test their new weapons. b. Supporters of the Spanish Loyalists supported the Axis powers. c. The forces of democracy def ...
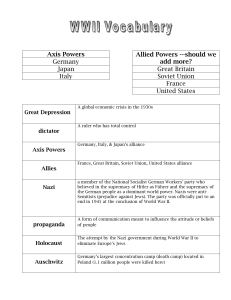
World War II Vocabulary
... Germany was forced to fight British and American troops from the West and Russia from the East. This divided Germany’s army in two and helped the Allies gain the advantage in Europe ...
... Germany was forced to fight British and American troops from the West and Russia from the East. This divided Germany’s army in two and helped the Allies gain the advantage in Europe ...
Section 3 - Mr. Cosbey
... met again at Yalta, in the southern Soviet Union. • There they planned war strategy in an atmosphere of distrust. • Stalin wanted control of Eastern Europe to protect the Soviet Union form future aggression. • Churchill and Roosevelt wanted self-determination for the people of Eastern Europe, but th ...
... met again at Yalta, in the southern Soviet Union. • There they planned war strategy in an atmosphere of distrust. • Stalin wanted control of Eastern Europe to protect the Soviet Union form future aggression. • Churchill and Roosevelt wanted self-determination for the people of Eastern Europe, but th ...
Ch 17 Sect 4 Notes-#14
... 1. In 1933, Nazi leader Adolf Hitler became dictator of Germany 2. Benito Mussolini had come to power in Italy 3. Military rulers had taken control of Japan 4. All three of these countries were attempting to build empires and would become allies. B. Japan invaded China in 1931 C. Italy had invaded N ...
... 1. In 1933, Nazi leader Adolf Hitler became dictator of Germany 2. Benito Mussolini had come to power in Italy 3. Military rulers had taken control of Japan 4. All three of these countries were attempting to build empires and would become allies. B. Japan invaded China in 1931 C. Italy had invaded N ...
Essential Question
... England was wounded Hitler broke the from German attacks in Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression the Battle of Britain Pact & marched into Russia ...
... England was wounded Hitler broke the from German attacks in Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression the Battle of Britain Pact & marched into Russia ...
Course outline Part 3 in MS Word format
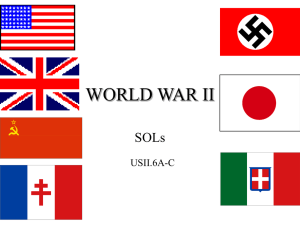
... The Allies: (Left-leaning, Socialist, and Centrist countries) Britain France Soviet Union China (Rep.) USA (Dec. 1941) The Axis: (Far Right / Fascist countries) Germany Japan Italy World War II: in Europe 1942-43: US and British forces: advance across North Africa invade Sicily begin long, slow inva ...
... The Allies: (Left-leaning, Socialist, and Centrist countries) Britain France Soviet Union China (Rep.) USA (Dec. 1941) The Axis: (Far Right / Fascist countries) Germany Japan Italy World War II: in Europe 1942-43: US and British forces: advance across North Africa invade Sicily begin long, slow inva ...
Chapter 20 Study Guide – The United States
... 1. Mussolini, Stalin, Hitler – types of government – fascist, totalitarian, etc. 2. Militarism, racism, extreme nationalism in Japan b. Military aggression 1. Japan invades Manchuria 2. Italy invades Ethiopia 3. Ineffectiveness of the League of Nations 4. Hitler’s defiance of Treaty of Versailles 5. ...
... 1. Mussolini, Stalin, Hitler – types of government – fascist, totalitarian, etc. 2. Militarism, racism, extreme nationalism in Japan b. Military aggression 1. Japan invades Manchuria 2. Italy invades Ethiopia 3. Ineffectiveness of the League of Nations 4. Hitler’s defiance of Treaty of Versailles 5. ...
April 15 – April 19 Chapter 32
... – Germans take the city, then surrounded by the Soviets – Soviets loose over 1 million men but capture the ...
... – Germans take the city, then surrounded by the Soviets – Soviets loose over 1 million men but capture the ...
Intensive Review - Standard 7
... The United States placed an oil _____________________ on Japan for launching aggressive warfare in Manchuria, China, and the Pacific. Japan, seeing the embargo as a threat to its ability to maintain a navy, attacked the U.S. Pacific Fleet at _________________ Harbor on _____________ ____, 1941. The ...
... The United States placed an oil _____________________ on Japan for launching aggressive warfare in Manchuria, China, and the Pacific. Japan, seeing the embargo as a threat to its ability to maintain a navy, attacked the U.S. Pacific Fleet at _________________ Harbor on _____________ ____, 1941. The ...
World War II - Cloudfront.net
... V1 rocket – pilot less plane V2- first long rang ballistic missile Battle of the Bulge Last major German offensive Each side lost 700,000 men German unable to sustain the offensive ...
... V1 rocket – pilot less plane V2- first long rang ballistic missile Battle of the Bulge Last major German offensive Each side lost 700,000 men German unable to sustain the offensive ...
Poles walk among the ruins of besieged Warsaw.
... Britain and France responded by declaring war on Germany on September 3. Within a month, Poland was defeated by a combination of German and Soviet forces and was partitioned between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. ...
... Britain and France responded by declaring war on Germany on September 3. Within a month, Poland was defeated by a combination of German and Soviet forces and was partitioned between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. ...
4 Fighting World War II in Europe
... England was wounded Hitler broke the from German attacks in Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression the Battle of Britain Pact & marched into Russia ...
... England was wounded Hitler broke the from German attacks in Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression the Battle of Britain Pact & marched into Russia ...
USII.7abc Test Review with Answers
... Fascism is a political philosophy in which total power is given to a dictator and individual freedoms are denied. Fascist dictators included: Hitler (Germany), Mussolini (Italy), and Tojo (Japan). These dictators led the countries that became known as the Axis Powers. ...
... Fascism is a political philosophy in which total power is given to a dictator and individual freedoms are denied. Fascist dictators included: Hitler (Germany), Mussolini (Italy), and Tojo (Japan). These dictators led the countries that became known as the Axis Powers. ...
world war ii - thewayitwas
... • Rise of Fascism – Fascism = “total power is given to a dictator” – Germany – Adolf Hitler – Italy – Benito Mussolini – Japan – Hideki Tojo *Became the Axis Powers (Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis) ...
... • Rise of Fascism – Fascism = “total power is given to a dictator” – Germany – Adolf Hitler – Italy – Benito Mussolini – Japan – Hideki Tojo *Became the Axis Powers (Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis) ...
World War 2 Study Guide Identify in detail: Sudetenland Battle of
... Answer the following questions: 1. List the Allied Powers. 2. List the Axis Powers. 3. What area of Czechoslovakia did Hitler demand? Did he get it? 4. What was the agreement between Hitler and Mussolini? 5. What event spurred France and Great Britain to declare war on Germany? 6. What country did H ...
... Answer the following questions: 1. List the Allied Powers. 2. List the Axis Powers. 3. What area of Czechoslovakia did Hitler demand? Did he get it? 4. What was the agreement between Hitler and Mussolini? 5. What event spurred France and Great Britain to declare war on Germany? 6. What country did H ...
WWII Test 2017 Test Review Guide
... 22. Why did Stalin want Britain and the United States to open a second front in France? ...
... 22. Why did Stalin want Britain and the United States to open a second front in France? ...
Exit Slip Exit Slip
... Exit Slip Name:___________________________________________Date_______________________ Use your knowledge from today’s activities to answer the following questions: 1. Major Allied Powers were: _______________, __________________, ________________ 2. Major Axis Powers were:__________________, _______ ...
... Exit Slip Name:___________________________________________Date_______________________ Use your knowledge from today’s activities to answer the following questions: 1. Major Allied Powers were: _______________, __________________, ________________ 2. Major Axis Powers were:__________________, _______ ...
Total Costs of World War II
... surrender of all German armed forces at Eisenhower's headquarters in Reims early on May 7. By then the German forces in Italy had already surrendered (on May 2), as had those in Holland, north Germany, and Denmark (May 4). The U.S. and British governments declared May 8, 1945 V-E (Victory in Europe) ...
... surrender of all German armed forces at Eisenhower's headquarters in Reims early on May 7. By then the German forces in Italy had already surrendered (on May 2), as had those in Holland, north Germany, and Denmark (May 4). The U.S. and British governments declared May 8, 1945 V-E (Victory in Europe) ...
schenk WH WW2 test.xlsx
... German defeat fought in order to gain control of crucial shipping ports and factories that produced Soviet military equipment. ...
... German defeat fought in order to gain control of crucial shipping ports and factories that produced Soviet military equipment. ...
The allies turn the tide - Brunswick City Schools / Homepage
... bombing Britain relentlessly, German forces had pushed far into the Soviet Union, and the Japanese were advancing in the Pacific. • However, through extraordinary efforts and a few key ...
... bombing Britain relentlessly, German forces had pushed far into the Soviet Union, and the Japanese were advancing in the Pacific. • However, through extraordinary efforts and a few key ...
Allies of World War II

The Allies of World War II, called the United Nations from the 1 January 1942 declaration, were the countries that opposed the Axis powers together during the Second World War (1939–1945). The Allies promoted the alliance as seeking to stop German, Japanese and Italian aggression.The anti-German coalition at the start of the war (1 September 1939) consisted of France, Poland and Great Britain, soon to be joined by the British Commonwealth (Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa). Poland was a minor factor after its defeat in 1939; France was a minor factor after its defeat in 1940. After first having cooperated with Germany in partitioning Poland whilst remaining neutral in the Allied-Axis conflict, the Soviet Union perforce joined the Allies in June 1941 after being invaded by Germany. The United States provided war material and money all along, and officially joined in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. As of 1942, the ""Big Three"" leaders of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States controlled Allied policy; relations between the UK and the U.S. were especially close. China had been already at war with Japan since 1937 but officially joined the Allies in 1941. The Big Three and China were referred as a ""trusteeship of the powerful"", then were recognized as the Allied ""Big Four"" in Declaration by United Nations and later the ""Four Policemen"" of ""United Nations"" for the Allies. Other key Allies included British India, the Netherlands, and Yugoslavia as well as Free France; there were numerous others. Together they called themselves the ""United Nations"" and in 1945 created the modern UN.