* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mr. Holmes Wonderful World of History
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
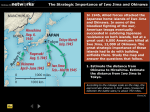
SSWH18 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the global political, economic, and social impact of WWII. Treaty of Versailles- Germans saw as unfair Reparations War-Guilt Clause Military Restrictions Loss of Territory Loss of Colonies Great Depression Aggression (Italy, Germany, Japan) LONG-TERM CAUSES: SHORT-TERM CAUSE: • Aug. 1939: Non-Aggression Pact (Germany & Soviet Union) • Blitzkrieg (lightening war) to subdue Poland • Sept. 01, 1939: Began with the invasion of Poland by Hitler • Sept. 03, 1939: Britain & France declared war on Germany • World War II: 1939-1945 ALLIES: AXIS: GREAT BRITAIN GERMANY FRANCE ITALY SOVIET UNION (switched) JAPAN UNITED STATES CANADA POLAND CHINA ALLIANCES: EUROPEAN THEATER: PACIFIC THEATER: Fighting was primarily landbased Fighting was primarily at sea Large scale bombing raids Island hopping & island invasions More countries involved More up-close fighting German soldiers tended to surrender when defeat was apparent Japanese land soldiers & Kamikaze pilots would fight to the death TWO LOCATIONS: December 07, 1941 surprise attack by the Japanese on US naval base in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii (USA) US stood in the way of a Pacific empire in Asia ended US neutrality, brought US into war MAJOR BATTLES: PEARL HARBOR 1st Battle: July 1942 2nd Battle: October-November 1942 Located in Egypt Allied Powers stopped the advancing Axis Powers, driving them back to Tunisia Decisive battle that lead to German surrender in North Africa in May 1943 MAJOR BATTLES: EL-ALAMEIN Hitler breaks Non-Aggression Pact; invades Soviet Union (June 1941) major turning point in war on Eastern front one of the costliest battles in WWII Germans unable to deal with winter in Russia Germans get trapped in city with no food or ammunition Jan. 1943: German commander surrenders MAJOR BATTLES: STALINGRAD June 06, 1944 major turning point on Western Front; opened a second front in Europe largest amphibious attack in history Allies attack on the beaches of Normandy, France Pages 946-947 MAJOR BATTLES: D-DAY August 07, 1942 Americans v. Japanese Located on the Solomon Islands, near Australia Took the Americans 6 months to cpature the island Allied victory allowed Australia to be protected & a safe sea route between US & Australia Part of island-hopping MAJOR BATTLES: GUADALCANAL June 19-20, 1944 America v. Japan Naval battle for control of the Philippine Islands Allied victory that helped to destroy Japanese planes MAJOR BATTLES: THE PHILIPPINES Racism, especially Anti-Semitism & Anti-Slavism Belief in the superiority of the white, Aryan race (Social Darwinism) Euthanasia & Eugenics Inventing common enemies: Jews, gypsies, homosexuals, disabled Belief in exterminating all inferior races NAZI IDEOLOGY: Jews were first sent to ghettos, then concentration camps (work camps) Wannsee Conference: Jan. 20, 1942; decision of the genocide of all European Jews Death camps were built & “undersirables” were sent there with efficient methods for killing men, women, & children THE FINAL SOLUTION: The Nazi massacre of over 6 million Jews & over 6 million other people Prisoners heads were shaved, they were stripped, women & children were separated from men Young, elderly, & sick were killed immediately Gas chambers, shootings, & crematoriums used Medical experiments common THE HOLOCAUST: The Holocaust is a reminder of the horrors of racism and intolerance DR. JOSEPH MENGEL First they came for the Jews And I did not speak outBecause I was not a Jew. Then they came for the Communists and I did not Speak out-because I was Not a communist. Then they came for the trade Unionists and I did not speak Out-because I was not A trade unionist. Then they came for meAnd there was no one left to Speak out for me. -Pastor Niemoeller French, British, & Americans advanced through France (west) Soviets advanced through Germany (east) heading towards Berlin Hitler began to lose support April 1945 Soviet troops and American troops met at the Elbe River & shook hands; war ends Germany surrenders May 07, 1945 V-E Day (May 08, 1945) EUROPEAN THEATER: Manhattan Project: name given to the atomic bomb creation project President Harry Truman decides to drop bombs to save American lives US dropped 2 atomic bombs on Japan 1. Hiroshima (90,000-160,000 died) 2. Nagaski (60,000-80,000 died) August 15, 1945: Japan surrenders (V-J Day) Introduced a new type of war: nuclear PACIFIC THEATER: Germany- 3 million combat deaths (3/4ths on the eastern front) Japan – over 1.5 combat deaths; 900,000 civilians dead Soviet Union - 13 million combat deaths U.S. – 300,000 combat deaths, over 100,000 other deaths COST OF WAR: TEHRAN: YALTA: Location: Iran, 1943 Lcoation: Soviet Union (Feb. 1945) Distrust among the Allies Stalin wanted to control Eastern Europe, Churchill & Roosevelt wanted self-determination (choose own government) Churchill & Roosevelt agreed to allow the borders under the NaziSoviet Pact stand (Poland) Stalin asks for a two-front war to be opened up, Churchhill & Roosevelt say they don’t have resouces, Stalin angry Soviet Union would help fight Japan Germany would be divided into 4 zones (US, France, GB, USSR) Stalin agreed to hold free elections in Eastern Europe THE BIG THREE: STALIN, CHURCHILL, & ROOSEVELT Location: Germany (July 16-Aug 02, 1945) Harry Truman represented US Purpose was how to punish Nazi Germany Other goals included post-war order, peace treaty issues, & countering effects of the war Demilitarization in Japan and Germany Nuremburg Trials – 22 Nazi leaders charged with “Crimes against Humanity” POTSDAM CONFERENCE: April 1945: delegates from 50 nations met in San Francisco to create UN 5 permanent members: US, Soviet Union, Britain, France, & China Prevents outbreak of diseases, helps education, protects refugees, & helps nations develop economically UNITED NATIONS: Causes of tension in Europe: Marshall Plan: *governments in Eastern Europe Aid package offered by US to send food & aid to Europe to help countries rebuild *conflicting ideologies (communism v. democracy) Helped Europe recover rapidly (billions of dollars) *mutual distrust Truman also offered it to USSR & Eastern Europe, Stalin declined & forbade any country from accepting it *German reparations Led to Cold War (US v. USSR) POST-WAR POLICIES: Emperor lost all political power Established a parliamentary democracy Education system opened to all people Legal equality for women Rebuilt cities & economy Began huge trading relationship with US MACARTHUR'S PLAN FOR JAPAN: