Chapter 28 Study Guide Again The Road To
... 10. Which country was going to have a plebiscite to decide whether to unite with Germany? 11. Who said, “I have no more territorial demands to make in Europe.”? 12. In which conference did he say this? 13. Which country did Germany invade that was the immediate cause of World War II? 14. Which two n ...
... 10. Which country was going to have a plebiscite to decide whether to unite with Germany? 11. Who said, “I have no more territorial demands to make in Europe.”? 12. In which conference did he say this? 13. Which country did Germany invade that was the immediate cause of World War II? 14. Which two n ...
7a: Causes of World War II
... – Fascist dictators included Adolf Hitler (Germany), Benito Mussolini (Italy), and Hideki Tojo (Japan). ...
... – Fascist dictators included Adolf Hitler (Germany), Benito Mussolini (Italy), and Hideki Tojo (Japan). ...
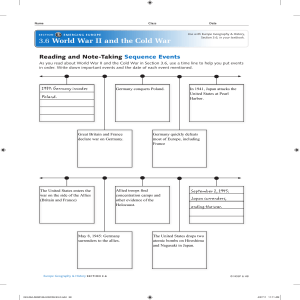
3.6 World War II and the Cold War
... As you read about World War II and the Cold War in Section 3.6, use a time line to help you put events in order. Write down important events and the date of each event mentioned. ...
... As you read about World War II and the Cold War in Section 3.6, use a time line to help you put events in order. Write down important events and the date of each event mentioned. ...
World War II
... sell, lease, or lend defense equipment to nations which the President considered vital to American security • Allowed FDR to help the British against Germany ...
... sell, lease, or lend defense equipment to nations which the President considered vital to American security • Allowed FDR to help the British against Germany ...
America – 1918-1945
... loaned equipment for fighting. Roosevelt used plain talk to convince Congress of the need to help. “If your neighbor’s house is on fire, wouldn’t you lend him your water hose and water? In fact, wouldn’t you hold the hose for him? If something happened to the hose he could pay you back after the fir ...
... loaned equipment for fighting. Roosevelt used plain talk to convince Congress of the need to help. “If your neighbor’s house is on fire, wouldn’t you lend him your water hose and water? In fact, wouldn’t you hold the hose for him? If something happened to the hose he could pay you back after the fir ...
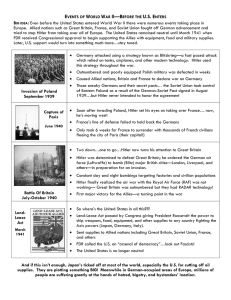
BIG IDEA: Even before the United States entered World War II there
... BIG IDEA: Even before the United States entered World War II there were numerous events taking place in Europe. Allied nations such as Great Britain, France, and Soviet Union fought off German advancement and tried to stop Hitler from taking over all of Europe. The United States remained neutral unt ...
... BIG IDEA: Even before the United States entered World War II there were numerous events taking place in Europe. Allied nations such as Great Britain, France, and Soviet Union fought off German advancement and tried to stop Hitler from taking over all of Europe. The United States remained neutral unt ...
world war ii
... ___________________. This decimated the Nazi troops. Stalin pleaded with England to open up a second front in Europe. England had its own battles to fight. Hitler wanted to invade England, but knew there would need to be an extensive bombing campaign first. This campaign is known as the Battle of __ ...
... ___________________. This decimated the Nazi troops. Stalin pleaded with England to open up a second front in Europe. England had its own battles to fight. Hitler wanted to invade England, but knew there would need to be an extensive bombing campaign first. This campaign is known as the Battle of __ ...
World War II - Reading Community Schools
... Which areas were under Axis control between 1939 and 1941? - Austria, Czechoslovakia, Poland, Norway, Denmark, the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Greece, Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, Hungary, parts of the USSR and North Africa. - Spain, Portugal, Switzerland, Ireland and Sweden were neutral countries -Brit ...
... Which areas were under Axis control between 1939 and 1941? - Austria, Czechoslovakia, Poland, Norway, Denmark, the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Greece, Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, Hungary, parts of the USSR and North Africa. - Spain, Portugal, Switzerland, Ireland and Sweden were neutral countries -Brit ...
World War II Notes
... communist. He will take power after Lenin’s death. The Soviet Union will become a member of the ALLIES. • These dictators led the countries that became known as the Axis Powers ...
... communist. He will take power after Lenin’s death. The Soviet Union will become a member of the ALLIES. • These dictators led the countries that became known as the Axis Powers ...
Hitler and the Rise of Germany
... Meanwhile, American scientists had successfully tested the world’s first atomic bomb. New U.S. President Truman decided to use an atomic bomb to save American lives. Two atomic bombs were dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, and the Japanese surrendered. ...
... Meanwhile, American scientists had successfully tested the world’s first atomic bomb. New U.S. President Truman decided to use an atomic bomb to save American lives. Two atomic bombs were dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, and the Japanese surrendered. ...
40068.1271171598.10-42-20
... • World War II was a global military conflict lasting from 1939 until ...
... • World War II was a global military conflict lasting from 1939 until ...
world war ii & cold war jeopardy ii
... Of the following countries, which nation was not controlled by the Soviet Union: Poland, Albania, Greece, or Hungary ...
... Of the following countries, which nation was not controlled by the Soviet Union: Poland, Albania, Greece, or Hungary ...
World War II - Winter Sports School in Park City
... 2 Conflicts: Japan in Asia, Germany in Europe An estimated 40-60 million people died Civilian populations as targets 56 Nations involved Two “Super Powers” emerged: U.S. and Soviet Union ...
... 2 Conflicts: Japan in Asia, Germany in Europe An estimated 40-60 million people died Civilian populations as targets 56 Nations involved Two “Super Powers” emerged: U.S. and Soviet Union ...
The United States and World War II
... • United States chose to remain out of the war and be isolationist • President Franklin Roosevelt wanted to help the Allies resist Axis aggression • After Germany defeated France, Roosevelt persuaded Congress to make some changes to the US neutrality laws: • Congress allowed the sale of arms on a c ...
... • United States chose to remain out of the war and be isolationist • President Franklin Roosevelt wanted to help the Allies resist Axis aggression • After Germany defeated France, Roosevelt persuaded Congress to make some changes to the US neutrality laws: • Congress allowed the sale of arms on a c ...
Outline
... . _________ _________- lasting from the late 1940s to the late 1980s, rose from disagreements between the U.S.S.R. and its World War II allies over post-war territorial settlements. . Korea was divided into _________________ and _________________ _____________ zones. . _____________________’s holdin ...
... . _________ _________- lasting from the late 1940s to the late 1980s, rose from disagreements between the U.S.S.R. and its World War II allies over post-war territorial settlements. . Korea was divided into _________________ and _________________ _____________ zones. . _____________________’s holdin ...
Fighting World War II
... Battle of the Bulge – American forces move into western Germany – Nazi counterattack in Dec. 1944 – General Patton brings reinforcements and U.S. stops German advance – Last chance for Germany to hold off ...
... Battle of the Bulge – American forces move into western Germany – Nazi counterattack in Dec. 1944 – General Patton brings reinforcements and U.S. stops German advance – Last chance for Germany to hold off ...
Peace
... Human Cost of the War • Approximately 55 Million people dead • The majority of people killed were civilians ...
... Human Cost of the War • Approximately 55 Million people dead • The majority of people killed were civilians ...
Beginning of second world war in 1939
... September 1939 to Poland. The United Kingdom and France proclaimed two days later war to Germany. The declared war on Germany the Soviet Union, which with signed Germany the pact about non-aggression, occupied East part of Poland. Territory of Poland was splitted Germany and SSSR. In April 1940 into ...
... September 1939 to Poland. The United Kingdom and France proclaimed two days later war to Germany. The declared war on Germany the Soviet Union, which with signed Germany the pact about non-aggression, occupied East part of Poland. Territory of Poland was splitted Germany and SSSR. In April 1940 into ...
great leaders of world war ii
... At the start of World War II, F.D.R. tried to keep the United States out of the conflict. Japan attacked the American Naval base at Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. President Roosevelt declared it “a day that will live in infamy.” The United States declared war on Japan on December 8, 1941. ...
... At the start of World War II, F.D.R. tried to keep the United States out of the conflict. Japan attacked the American Naval base at Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. President Roosevelt declared it “a day that will live in infamy.” The United States declared war on Japan on December 8, 1941. ...
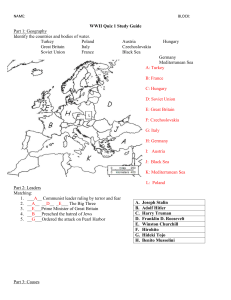
NAME: BLOCK: WWII Quiz 1 Study Guide Part 1: Geography Identify
... 2. __A__ __D__ _E___ The Big Three 3. __E___Prime Minister of Great Britain 4. __B___Preached the hatred of Jews 5. __G___Ordered the attack on Pearl Harbor ...
... 2. __A__ __D__ _E___ The Big Three 3. __E___Prime Minister of Great Britain 4. __B___Preached the hatred of Jews 5. __G___Ordered the attack on Pearl Harbor ...
29-4 notes - Mr. Shawiak
... August 8: The Soviet Union invaded Manchuria. The Japanese did not respond. August 9: The United States dropped a second atomic bomb on Nagasaki. This time, more than 40,000 people were killed August 10: Emperor Hirohito intervened and forced the government to surrender. ...
... August 8: The Soviet Union invaded Manchuria. The Japanese did not respond. August 9: The United States dropped a second atomic bomb on Nagasaki. This time, more than 40,000 people were killed August 10: Emperor Hirohito intervened and forced the government to surrender. ...
The Search for Peace
... Allied vs. Axis Deaths Allies • United States • Soviet Union • Great Britain • France ...
... Allied vs. Axis Deaths Allies • United States • Soviet Union • Great Britain • France ...
Allies of World War II

The Allies of World War II, called the United Nations from the 1 January 1942 declaration, were the countries that opposed the Axis powers together during the Second World War (1939–1945). The Allies promoted the alliance as seeking to stop German, Japanese and Italian aggression.The anti-German coalition at the start of the war (1 September 1939) consisted of France, Poland and Great Britain, soon to be joined by the British Commonwealth (Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa). Poland was a minor factor after its defeat in 1939; France was a minor factor after its defeat in 1940. After first having cooperated with Germany in partitioning Poland whilst remaining neutral in the Allied-Axis conflict, the Soviet Union perforce joined the Allies in June 1941 after being invaded by Germany. The United States provided war material and money all along, and officially joined in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. As of 1942, the ""Big Three"" leaders of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States controlled Allied policy; relations between the UK and the U.S. were especially close. China had been already at war with Japan since 1937 but officially joined the Allies in 1941. The Big Three and China were referred as a ""trusteeship of the powerful"", then were recognized as the Allied ""Big Four"" in Declaration by United Nations and later the ""Four Policemen"" of ""United Nations"" for the Allies. Other key Allies included British India, the Netherlands, and Yugoslavia as well as Free France; there were numerous others. Together they called themselves the ""United Nations"" and in 1945 created the modern UN.