Fundamentals Diagnostic Quiz
... a) All the atoms of a given element are identical. b) The atoms of different elements have different masses. *c) All atoms are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. d) A compound is a specific combination of atoms of more than one element. e) In a chemical reaction, atoms are neither created ...
... a) All the atoms of a given element are identical. b) The atoms of different elements have different masses. *c) All atoms are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. d) A compound is a specific combination of atoms of more than one element. e) In a chemical reaction, atoms are neither created ...
Chemistry: An Introduction for Medical and Health Sciences - E
... of aspirin-like medicines in Britain. It cured the pains from various complaints. Herbal concoctions have been the basis of healing and also poisoning for centuries. Curare was used on the tips of poison darts to kill opponents, but in smaller quantities it was used as a muscle relaxant in surgery u ...
... of aspirin-like medicines in Britain. It cured the pains from various complaints. Herbal concoctions have been the basis of healing and also poisoning for centuries. Curare was used on the tips of poison darts to kill opponents, but in smaller quantities it was used as a muscle relaxant in surgery u ...
Chemistry - An Introduction for Medical and Hea..
... of aspirin-like medicines in Britain. It cured the pains from various complaints. Herbal concoctions have been the basis of healing and also poisoning for centuries. Curare was used on the tips of poison darts to kill opponents, but in smaller quantities it was used as a muscle relaxant in surgery u ...
... of aspirin-like medicines in Britain. It cured the pains from various complaints. Herbal concoctions have been the basis of healing and also poisoning for centuries. Curare was used on the tips of poison darts to kill opponents, but in smaller quantities it was used as a muscle relaxant in surgery u ...
Chemistry JAMB Past Questions
... 40 g NaOH in 100 g of water 40 g NaOH in 1000 g of water 20 g NaOH in 500 g of solution 20 g NaOH in 1000 g of solution 20 g NaOH in 80 g of solution. Which among the element 1. Carbon 2. Oxygen 3. Copper 4. Bromine 5. Zinc will NOT react with either water of stream? A. 1 and 2 B. 2 and 3 C. 3 and 4 ...
... 40 g NaOH in 100 g of water 40 g NaOH in 1000 g of water 20 g NaOH in 500 g of solution 20 g NaOH in 1000 g of solution 20 g NaOH in 80 g of solution. Which among the element 1. Carbon 2. Oxygen 3. Copper 4. Bromine 5. Zinc will NOT react with either water of stream? A. 1 and 2 B. 2 and 3 C. 3 and 4 ...
Tech Tip 0013 - Hydrates and Salts
... Confusion is not uncommon when reporting the final values calculated with using such standards. The analyst must first determine if the end result will be reported as the hydrate or salt, or as the compound without the hydrate or salt. This determines how the initial calibration curve is generated. ...
... Confusion is not uncommon when reporting the final values calculated with using such standards. The analyst must first determine if the end result will be reported as the hydrate or salt, or as the compound without the hydrate or salt. This determines how the initial calibration curve is generated. ...
Learning Outcomes Leaving Certificate Chemistry
... define ion, positive ion, negative ion appreciate the minute size of ions explain ionic bonding in terms of electron transfer represent ionic bonds using dot and cross diagrams describe the structure of a sodium chloride crystal having reviewed models associate ionic substances with their characteri ...
... define ion, positive ion, negative ion appreciate the minute size of ions explain ionic bonding in terms of electron transfer represent ionic bonds using dot and cross diagrams describe the structure of a sodium chloride crystal having reviewed models associate ionic substances with their characteri ...
REACTIONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION
... Not all substances that dissolve in water make the resulting solution conducting. Imagine preparing two aqueous solutions—one by dissolving a teaspoon of table salt (sodium chloride) in a cup of water and the other by dissolving a teaspoon of table sugar (sucrose) in a cup of water (! FIGURE 4.2). B ...
... Not all substances that dissolve in water make the resulting solution conducting. Imagine preparing two aqueous solutions—one by dissolving a teaspoon of table salt (sodium chloride) in a cup of water and the other by dissolving a teaspoon of table sugar (sucrose) in a cup of water (! FIGURE 4.2). B ...
CHAPTER-7
... 19. What is the effect of catalyst on the equilibrium in a reversible reaction? Ans. Catalyst has no effect. 20. What is reaction quotient? Ans. Qc = Product of concentration of products Product of concentration of reactants 21. In a reversible reaction K = Qc, what does it signify? Ans. The reactio ...
... 19. What is the effect of catalyst on the equilibrium in a reversible reaction? Ans. Catalyst has no effect. 20. What is reaction quotient? Ans. Qc = Product of concentration of products Product of concentration of reactants 21. In a reversible reaction K = Qc, what does it signify? Ans. The reactio ...
Physical Chemistry Problems. ©Mike Lyons 2009
... a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed by the system. Hence derive a relationship between the change in ...
... a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed by the system. Hence derive a relationship between the change in ...
CHEM181H1_06_2013_Y_P1
... (d) they communicate or attempt to communicate any information relating to the examination to another candidate while the examination is in progress. (e) they use a false name or identity number in an examination. (f) they commit any other fraudulent, deceitful or dishonest practice which would mi ...
... (d) they communicate or attempt to communicate any information relating to the examination to another candidate while the examination is in progress. (e) they use a false name or identity number in an examination. (f) they commit any other fraudulent, deceitful or dishonest practice which would mi ...
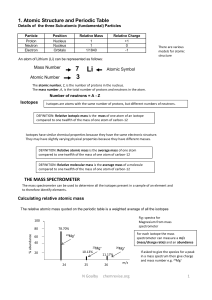
1. Atomic Structure and Periodic Table THE MASS SPECTROMETER
... reducing agents are electron donors oxidising agents are electron acceptors When naming oxidising and reducing agents always refer to full name of substance and not just name of element ...
... reducing agents are electron donors oxidising agents are electron acceptors When naming oxidising and reducing agents always refer to full name of substance and not just name of element ...
Web Appendix 6
... a single reactive hydrogen or hydroxide ion. For example, the equivalent weights of potassium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, and acetic acid are equal to their molar masses because each has but a single reactive hydrogen ion or hydroxide ion. Barium hydroxide, which contains two identical hydroxide i ...
... a single reactive hydrogen or hydroxide ion. For example, the equivalent weights of potassium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, and acetic acid are equal to their molar masses because each has but a single reactive hydrogen ion or hydroxide ion. Barium hydroxide, which contains two identical hydroxide i ...
The Chemistry of Solutions Page | 1 Unit 7: The Chemistry of
... When a soluble ionic compound is placed in water the ionic substance or salt will dissociate into its component ions. Ex. SrCl2 ...
... When a soluble ionic compound is placed in water the ionic substance or salt will dissociate into its component ions. Ex. SrCl2 ...
Chem 171-2-3: Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Problems 1
... Consider a Galvanic cell represented by the following line notation: Zn(s) | Zn2+ (aq) || Cu2+ (aq) | Cu (s). Which statement about this cell is not true? a. The mass of the zinc electrode will increase as the cell discharges. b. The copper electrode is the cathode. c. Electrons will flow through th ...
... Consider a Galvanic cell represented by the following line notation: Zn(s) | Zn2+ (aq) || Cu2+ (aq) | Cu (s). Which statement about this cell is not true? a. The mass of the zinc electrode will increase as the cell discharges. b. The copper electrode is the cathode. c. Electrons will flow through th ...
AP Exam Review Questions
... • Ans: V2 = 250 ml then you must subtract 100 ml (the initial volume of KCl) because it takes up space in the flask, therefore the answer is volume of water = 150 ml ...
... • Ans: V2 = 250 ml then you must subtract 100 ml (the initial volume of KCl) because it takes up space in the flask, therefore the answer is volume of water = 150 ml ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
... Χsolvent = 0.97649 = mol H2O / (mol H2O + mol Na+ and Br-) mol H2O = 250 g / 18.016 g/mol = 13.877 mol H2O Χsolvent = 0.97649 = 13.877 mol H2O / (13.877 mol H2O + mol Na+ and Br-) (13.877 mol H2O + mol Na+ and Br-) = 14.211 mol Na+ and Br- = 0.334 But we have 2 moles of ions for every mol of NaBr; w ...
... Χsolvent = 0.97649 = mol H2O / (mol H2O + mol Na+ and Br-) mol H2O = 250 g / 18.016 g/mol = 13.877 mol H2O Χsolvent = 0.97649 = 13.877 mol H2O / (13.877 mol H2O + mol Na+ and Br-) (13.877 mol H2O + mol Na+ and Br-) = 14.211 mol Na+ and Br- = 0.334 But we have 2 moles of ions for every mol of NaBr; w ...
Boronic acids facilitate rapid oxime condensations at neutral pH
... condensation is the size of required 2-FBPA motif. Although for most applications this should present no difficulties, examples where the compactness of the oxime is critical (such as, for example, as a functional isostere of peptide bonds)37 would not be possible. The ability to run conjugations at 1 ...
... condensation is the size of required 2-FBPA motif. Although for most applications this should present no difficulties, examples where the compactness of the oxime is critical (such as, for example, as a functional isostere of peptide bonds)37 would not be possible. The ability to run conjugations at 1 ...
pdf version - Joliet Junior College
... Review: What follows is a recap of the most important topics covered in CHM 101. We will use this material throughout CHM 102, so please ensure that you are familiar with the following questions, as well as the Ch3 & 4 HWK questions, before we move on to the Ch 11 material. Top Tip: Committing to a ...
... Review: What follows is a recap of the most important topics covered in CHM 101. We will use this material throughout CHM 102, so please ensure that you are familiar with the following questions, as well as the Ch3 & 4 HWK questions, before we move on to the Ch 11 material. Top Tip: Committing to a ...
Chemistry - Tumkur University
... equation. Industrial applications of enzymes and catalysts. (8 Lectures) Ionic Equilibria:Strong, moderate and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization, factors affecting degree of ionization, ionization constant and ionic product of water. Ionization of weak acids and bases, pH scale, common ion eff ...
... equation. Industrial applications of enzymes and catalysts. (8 Lectures) Ionic Equilibria:Strong, moderate and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization, factors affecting degree of ionization, ionization constant and ionic product of water. Ionization of weak acids and bases, pH scale, common ion eff ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.