1 1. (8 pts) Circle the formula (only one) that best fits each of the
... (4 pts) A substance does not conduct electricity unless it is melted. It is hard and has a high melting point. These properties are characteristic of which one of the following crystalline solids? Circle the correct answer. a) ionic ...
... (4 pts) A substance does not conduct electricity unless it is melted. It is hard and has a high melting point. These properties are characteristic of which one of the following crystalline solids? Circle the correct answer. a) ionic ...
CHE 1031 Lab Manual
... experiments in a laboratory. It is in the laboratory that facts are discovered and concepts, ideas and theories are tested. In this course, an attempt will be made to correlate the classroom and the ...
... experiments in a laboratory. It is in the laboratory that facts are discovered and concepts, ideas and theories are tested. In this course, an attempt will be made to correlate the classroom and the ...
Chapter 6
... cause we treat HCl as if it completely dissociates in aqueous solutions. In water, the common strong acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl), hydroiodic acid (HI), hydrobromic acid (HBr), nitric acid (HNO3), perchloric acid (HClO4), and the first proton of sulfuric acid (H2SO4). ...
... cause we treat HCl as if it completely dissociates in aqueous solutions. In water, the common strong acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl), hydroiodic acid (HI), hydrobromic acid (HBr), nitric acid (HNO3), perchloric acid (HClO4), and the first proton of sulfuric acid (H2SO4). ...
3.Redox
... solution would be required to react with 6.00 g of Cu? How many mL of a 6.0M HNO3 stock solution would be required to prepare this solution? 13. How many mL of a 0.532 M H2SO4 solution would be required to titrate 62.0 mL of a 0.784 M KOH solution. 14. A 35.0 g sample of a mixture of KCl and NaCl re ...
... solution would be required to react with 6.00 g of Cu? How many mL of a 6.0M HNO3 stock solution would be required to prepare this solution? 13. How many mL of a 0.532 M H2SO4 solution would be required to titrate 62.0 mL of a 0.784 M KOH solution. 14. A 35.0 g sample of a mixture of KCl and NaCl re ...
Granta Design • CES Edupack 2009 • Durability - CORE
... There are, however, exceptions, notably aluminium, that forms non-protective aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3. Resistance to acid and alkali attack is ranked on a 4-point scale from 1 (Unacceptable) to 4 (Excellent resistance). Notes attached to individual environments give more details. See also Durabi ...
... There are, however, exceptions, notably aluminium, that forms non-protective aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3. Resistance to acid and alkali attack is ranked on a 4-point scale from 1 (Unacceptable) to 4 (Excellent resistance). Notes attached to individual environments give more details. See also Durabi ...
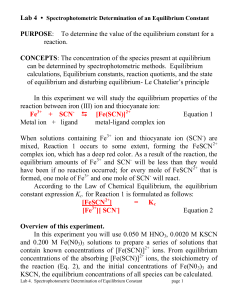
PURPOSE: To determine the value of the equilibrium constant for a
... Since the Fe3+ concentration is great excess in part A, this error would have no impact on the outcome. The SCN- concentration determines the concentration of FeSCN2+. 8. An error was made in preparing the KSCN solution in Part A. Its concentration was 0.003 molar but was labeled as 0.002 molar. How ...
... Since the Fe3+ concentration is great excess in part A, this error would have no impact on the outcome. The SCN- concentration determines the concentration of FeSCN2+. 8. An error was made in preparing the KSCN solution in Part A. Its concentration was 0.003 molar but was labeled as 0.002 molar. How ...
Chemistry - talcher autonomous college
... (16 Lectures) Unit-III CHEMICAL BONDING-I (i) lonic bond: General characteristics, types of ions, size effects, radius ratio rule and its limitations. Packing of ions in crystals. Born-Landé equation with derivation and importance of Kapustinskii expression for lattice energy. Madelung constant, Bor ...
... (16 Lectures) Unit-III CHEMICAL BONDING-I (i) lonic bond: General characteristics, types of ions, size effects, radius ratio rule and its limitations. Packing of ions in crystals. Born-Landé equation with derivation and importance of Kapustinskii expression for lattice energy. Madelung constant, Bor ...
Study Modules XII Chemistry 2017
... The energy gap between the valence band and conduction band in an insulator is very large while in a conductor, the energy gap is very small or there is overlapping between valence band and conduction band. 6. CaCl2 will introduce Schottky defect if added to AgCl crystal. Explain. Two Ag+ ions will ...
... The energy gap between the valence band and conduction band in an insulator is very large while in a conductor, the energy gap is very small or there is overlapping between valence band and conduction band. 6. CaCl2 will introduce Schottky defect if added to AgCl crystal. Explain. Two Ag+ ions will ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Jhunjhunu
... 1. The oxide of a metal M was water soluble. When a blue litmus strip was dipped in this solution, it did not undergo any change in colour. Predict the nature of the oxide. 2. Why does bee-sting cause pain and irritation? What relief can be given in such a case immediately? 3. Is the distilled water ...
... 1. The oxide of a metal M was water soluble. When a blue litmus strip was dipped in this solution, it did not undergo any change in colour. Predict the nature of the oxide. 2. Why does bee-sting cause pain and irritation? What relief can be given in such a case immediately? 3. Is the distilled water ...
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
Version A
... 5. If the temperature increases from 10°C to 60°C at a constant pressure of 0.4 atmosphere, which of the processes occurs? ...
... 5. If the temperature increases from 10°C to 60°C at a constant pressure of 0.4 atmosphere, which of the processes occurs? ...
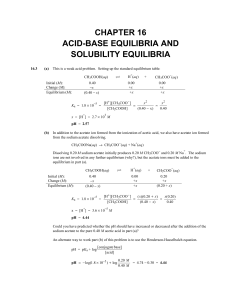
CHAPTER 16 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA AND SOLUBILITY
... Could you have predicted whether the pH should have increased or decreased after the addition of the sodium acetate to the pure 0.40 M acetic acid in part (a)? An alternate way to work part (b) of this problem is to use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. pH = pKa + log ...
... Could you have predicted whether the pH should have increased or decreased after the addition of the sodium acetate to the pure 0.40 M acetic acid in part (a)? An alternate way to work part (b) of this problem is to use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. pH = pKa + log ...
Alkaloids
... These methods are recommended for determination of: 1- Very weak bases which can not be determined by volumetric methods e.g. caffeine and colchicine. 2- Mixtures of alkaloids that are obtained from the same plant but differ greatly in their molecular weight e.g. Cinchona and Rawolfia alkaloids. The ...
... These methods are recommended for determination of: 1- Very weak bases which can not be determined by volumetric methods e.g. caffeine and colchicine. 2- Mixtures of alkaloids that are obtained from the same plant but differ greatly in their molecular weight e.g. Cinchona and Rawolfia alkaloids. The ...
IChO_Comp_Prob_Answ 1997
... routine material studied in most high schools around the world. But this is how it should be since the competitors involved are among the best that our countries have to offer. However, it is felt that even these topics and the level of expertise expected can be mastered by our students without sign ...
... routine material studied in most high schools around the world. But this is how it should be since the competitors involved are among the best that our countries have to offer. However, it is felt that even these topics and the level of expertise expected can be mastered by our students without sign ...
A Dictionary of the New Chymical Nomenclature
... Gas, oxygenated muriatic acid Dephlogisticated marine acid, of Scheele Gas Prussic acid ...
... Gas, oxygenated muriatic acid Dephlogisticated marine acid, of Scheele Gas Prussic acid ...
29th INTERNATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD PREPARATORY
... routine material studied in most high schools around the world. But this is how it should be since the competitors involved are among the best that our countries have to offer. However, it is felt that even these topics and the level of expertise expected can be mastered by our students without sign ...
... routine material studied in most high schools around the world. But this is how it should be since the competitors involved are among the best that our countries have to offer. However, it is felt that even these topics and the level of expertise expected can be mastered by our students without sign ...
Appendix
... Appendix Appendix 1: Normality Appendix 2: Propagation of Uncertainty Appendix 3: Single-Sided Normal Distribution Appendix 4: Critical Values for the t-Test Appendix 5: Critical Values for the F-Test Appendix 6: Critical Values for Dixon’s Q-Test Appendix 7: Critical Values for Grubb’ ...
... Appendix Appendix 1: Normality Appendix 2: Propagation of Uncertainty Appendix 3: Single-Sided Normal Distribution Appendix 4: Critical Values for the t-Test Appendix 5: Critical Values for the F-Test Appendix 6: Critical Values for Dixon’s Q-Test Appendix 7: Critical Values for Grubb’ ...
Document
... • To make solutions of lower concentrations from these stock solutions, more solvent is added the amount of solute doesn’t change, just the volume of solution moles solute in solution 1 = moles solute in solution 2 ...
... • To make solutions of lower concentrations from these stock solutions, more solvent is added the amount of solute doesn’t change, just the volume of solution moles solute in solution 1 = moles solute in solution 2 ...
Practice Exam I FR Answers and Explanations
... Perchloric acid has four oxygen atoms compared to only three found in chloric acid. Since oxygen is so highly electronegative it causes the net pull away from hydrogen to be greater with each additional oxygen, making it easier for water molecules to surround and remove the hydrogen of perchloric ac ...
... Perchloric acid has four oxygen atoms compared to only three found in chloric acid. Since oxygen is so highly electronegative it causes the net pull away from hydrogen to be greater with each additional oxygen, making it easier for water molecules to surround and remove the hydrogen of perchloric ac ...
chemistry (9189)
... Some of the options are more obviously quantitative/mathematical in nature, whereas others have a greater descriptive content. Similarly, choice of option may also be influenced by other subjects being studied alongside chemistry. This deliberate variety is seen as a virtue of the complete syllabus. ...
... Some of the options are more obviously quantitative/mathematical in nature, whereas others have a greater descriptive content. Similarly, choice of option may also be influenced by other subjects being studied alongside chemistry. This deliberate variety is seen as a virtue of the complete syllabus. ...
Chapter 2 Geochemical Reactions
... implied in the term geochemistry. These processes include dissolution of air-borne material and gases, weathering at the Earth’s surface, biodegradation and nutrient cycling in the soil, mineral dissolution in the subsurface, and mixing with seawater or deep crustal water. Human activity also plays ...
... implied in the term geochemistry. These processes include dissolution of air-borne material and gases, weathering at the Earth’s surface, biodegradation and nutrient cycling in the soil, mineral dissolution in the subsurface, and mixing with seawater or deep crustal water. Human activity also plays ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.