
Experimental Chemistry I
... 1.2 Titration (verification of results obtain from Experiment 1/1.1): Purpose: Find the concentrations of the Standardized Acid / Base with the help of titration. The reaction between a strong acid and a strong base can be basically considered as a neutralization reaction. In a neutralization reacti ...
... 1.2 Titration (verification of results obtain from Experiment 1/1.1): Purpose: Find the concentrations of the Standardized Acid / Base with the help of titration. The reaction between a strong acid and a strong base can be basically considered as a neutralization reaction. In a neutralization reacti ...
AVOGADRO EXAMS 1991 - 2002 PRACTICE BOOKLET
... 16. An element occurring in nature as a metal(such as copper or gold) is likely to (a) react readily with oxygen to from a protective oxide coating (b) be at the high end of the activity series of metals (c) cause strong acids to release hydrogen gas (d) undergo oxidation only with difficulty (e) lo ...
... 16. An element occurring in nature as a metal(such as copper or gold) is likely to (a) react readily with oxygen to from a protective oxide coating (b) be at the high end of the activity series of metals (c) cause strong acids to release hydrogen gas (d) undergo oxidation only with difficulty (e) lo ...
Quiz contsts questions chemistry
... H2 is passed over heated capric oxide, the latter loses 0.04 g of its weight. All measurements are done under similar conditions of temperature and pressure (at. wt., H=1, O=16). Which of the following law is obeyed by this data? (a) Gay Lussac’s law of gaseous volume (B) Law of constant composition ...
... H2 is passed over heated capric oxide, the latter loses 0.04 g of its weight. All measurements are done under similar conditions of temperature and pressure (at. wt., H=1, O=16). Which of the following law is obeyed by this data? (a) Gay Lussac’s law of gaseous volume (B) Law of constant composition ...
Isomers and Isomerism Isomers
... Louis Pasteur first used this method in 1848 to separate the stereoisomers of a crystalline tartaric acid salt. Separate solutions of the two separate isomers had the same specific rotation, but differed in the sign of rotation. This is a rather special method, which can’t be applied to all racemic ...
... Louis Pasteur first used this method in 1848 to separate the stereoisomers of a crystalline tartaric acid salt. Separate solutions of the two separate isomers had the same specific rotation, but differed in the sign of rotation. This is a rather special method, which can’t be applied to all racemic ...
STUDY MATERIAL 2016-17 CHEMISTRY CLASS XII
... empirical endeavour to help students learn more effectively and efficiently. It is designed to give proper platform to students for better practice and understanding of the chapters. This can suitably be used during revision. Ample opportunity has been provided to students through master cards and q ...
... empirical endeavour to help students learn more effectively and efficiently. It is designed to give proper platform to students for better practice and understanding of the chapters. This can suitably be used during revision. Ample opportunity has been provided to students through master cards and q ...
National German Competition and Problems of the IChO
... molecules X2 ( (X = Cl, Br, I). (Account only for the atom orbitals of the valence electrons.) If iodine is dissolved in different solvents the solutions show different colours. Iodine as an electron-pair acceptor forms Lewis acid-base adducts with the molecules of many solvents. These adducts show ...
... molecules X2 ( (X = Cl, Br, I). (Account only for the atom orbitals of the valence electrons.) If iodine is dissolved in different solvents the solutions show different colours. Iodine as an electron-pair acceptor forms Lewis acid-base adducts with the molecules of many solvents. These adducts show ...
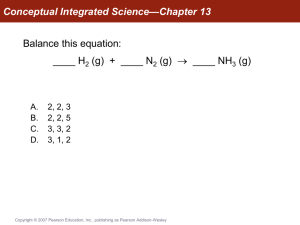
Conceptual Integrated Science—Chapter 13
... Conceptual Integrated Science—Chapter 13 The warm air from a lit birthday candle does not rise within an orbiting space station because there is no up or down. As a result, what happens to the burning candle and why? A. The warm air surrounding the candle speeds up the rate of reaction so that the ...
... Conceptual Integrated Science—Chapter 13 The warm air from a lit birthday candle does not rise within an orbiting space station because there is no up or down. As a result, what happens to the burning candle and why? A. The warm air surrounding the candle speeds up the rate of reaction so that the ...
SQA Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Principles of Chemical
... Which of the following statements applies to this equation? 1. Calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce calcium chloride solution, water and carbon dioxide. 2. One formula unit of calcium carbonate reacts with two formula units of hydrochloric acid to produce one formula unit each ...
... Which of the following statements applies to this equation? 1. Calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce calcium chloride solution, water and carbon dioxide. 2. One formula unit of calcium carbonate reacts with two formula units of hydrochloric acid to produce one formula unit each ...
Stoichiometry of Ozonation of Environmentally
... form secondary ozonides, addition to alcohols, water, and carboxylic acids to form alkoxy-, hydroxy-, and acyloxyhydroperoxides, respectively, and isomerization into carboxylic acids (16). In gas-phase ozonation reactions, carbonyl oxides may also undergo unimolecular decomposition to give OH radica ...
... form secondary ozonides, addition to alcohols, water, and carboxylic acids to form alkoxy-, hydroxy-, and acyloxyhydroperoxides, respectively, and isomerization into carboxylic acids (16). In gas-phase ozonation reactions, carbonyl oxides may also undergo unimolecular decomposition to give OH radica ...
Chemistry 133 Problem Set Introduction
... was the twenty-dollar gold piece known as the double eagle. By an act of Congress in 1849, each double eagle weighed 516 grains and was 0.900 fine (33.436 g and 90.0 % gold (the remainder was copper). In 1934, the United States increased the price of gold from $20.67 per Troy ounce to $35.00 per Tro ...
... was the twenty-dollar gold piece known as the double eagle. By an act of Congress in 1849, each double eagle weighed 516 grains and was 0.900 fine (33.436 g and 90.0 % gold (the remainder was copper). In 1934, the United States increased the price of gold from $20.67 per Troy ounce to $35.00 per Tro ...
Chapter 2 Matter and Components F11 110
... 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons, and thus in mass number. A sample of the element is treated as though its atoms have an average mass. ...
... 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons, and thus in mass number. A sample of the element is treated as though its atoms have an average mass. ...
Chapter 2 Matter and Components F11 110pt
... Type II: Use the name of the element AND its oxidation state (or charge); use roman numerals in parentheses to denote this; if you are talking about an ion by itself put ‘ion’ after the name: ...
... Type II: Use the name of the element AND its oxidation state (or charge); use roman numerals in parentheses to denote this; if you are talking about an ion by itself put ‘ion’ after the name: ...
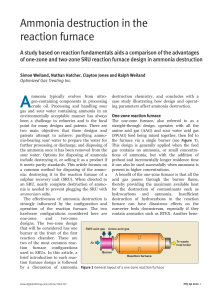
Ammonia destruction in the reaction furnace
... mmonia typically evolves from nitro- destruction chemistry, and concludes with a gen-containing components in processing case study illustrating how design and operatcrude oil. Processing and handling sour ing parameters affect ammonia destruction. gas and sour water containing ammonia in an environ ...
... mmonia typically evolves from nitro- destruction chemistry, and concludes with a gen-containing components in processing case study illustrating how design and operatcrude oil. Processing and handling sour ing parameters affect ammonia destruction. gas and sour water containing ammonia in an environ ...
12_chemistry_impq_CH13_amines_02
... 2. Which reaction is used for preparation of pure aliphatic & aralkyl primary amine ? 3. Name one reagent used for the separation of primary, secondary & tertiary amine ? 4. What amine salts are used for determing their molecular masses ? 5. What is the directive influence of amino group in arylamin ...
... 2. Which reaction is used for preparation of pure aliphatic & aralkyl primary amine ? 3. Name one reagent used for the separation of primary, secondary & tertiary amine ? 4. What amine salts are used for determing their molecular masses ? 5. What is the directive influence of amino group in arylamin ...
Complete Set
... From 2008-N-2, Ksp = [Ca2+(aq)][CO32-(aq)] = 3.3 × 10-9. Hence, [Ca2+(aq)] = Ksp / [CO32-(aq)] = 3.3 × 10-9 / (1.47 × 10-5) = 2.2 × 10-4 M [Ca2+] = 2.2 × 10-4 M The pH is expected to drop to about 7.8 by the end of the century as CO2 levels increase further. What effect will this have on the solubil ...
... From 2008-N-2, Ksp = [Ca2+(aq)][CO32-(aq)] = 3.3 × 10-9. Hence, [Ca2+(aq)] = Ksp / [CO32-(aq)] = 3.3 × 10-9 / (1.47 × 10-5) = 2.2 × 10-4 M [Ca2+] = 2.2 × 10-4 M The pH is expected to drop to about 7.8 by the end of the century as CO2 levels increase further. What effect will this have on the solubil ...
St. Xavier`s College – Autonomous Mumbai Syllabus for 3 Semester
... 3.1.1: Recapitulation of Arrhenius theory. 3.1. 2: Lowry-Bronsted concept: Bronsted acids and bases, acid-base properties of water, pH, strength of acids and bases, weak acids and acid ionization constants, weak bases and base ionization constants, relationship between ionization constants of acids ...
... 3.1.1: Recapitulation of Arrhenius theory. 3.1. 2: Lowry-Bronsted concept: Bronsted acids and bases, acid-base properties of water, pH, strength of acids and bases, weak acids and acid ionization constants, weak bases and base ionization constants, relationship between ionization constants of acids ...
updated chem cp final review key
... SOLVENT: the substance that does the dissolving SOLUTE: the substance that is dissolved Examples of solutions include steel, Kool-Aid, and air. A mixture that is not a solution is oil and water. 70. Give an example of a solid, liquid, and gas solution. Identify the solute and solvent. Solid: Steel. ...
... SOLVENT: the substance that does the dissolving SOLUTE: the substance that is dissolved Examples of solutions include steel, Kool-Aid, and air. A mixture that is not a solution is oil and water. 70. Give an example of a solid, liquid, and gas solution. Identify the solute and solvent. Solid: Steel. ...
Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective
... Our previous investigations on the conversion of tert-butanol revealed that the reactivity of tert-butanol could be greatly improved by the use of tetrafluoroborate ionic liquids as media [26,27]. Therefore, we consequently investigated the esterification reaction of tert-butanol in [BMIm]BF4 , whic ...
... Our previous investigations on the conversion of tert-butanol revealed that the reactivity of tert-butanol could be greatly improved by the use of tetrafluoroborate ionic liquids as media [26,27]. Therefore, we consequently investigated the esterification reaction of tert-butanol in [BMIm]BF4 , whic ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.



















![Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017897985_1-047f9869d5604c115b21339541ccfffe-300x300.png)