November 2016 (v1) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry A-level
... (f) Iron(III) ions can oxidise vanadium metal. Construct an equation for the reaction of an excess of iron(III) ions with vanadium metal. Use of the Data Booklet will be helpful. ...
... (f) Iron(III) ions can oxidise vanadium metal. Construct an equation for the reaction of an excess of iron(III) ions with vanadium metal. Use of the Data Booklet will be helpful. ...
CLASS X carbon and its compound
... Homopolar bond : A chemical bond formed between two non-metallic elements by the mutual sharing of one or more electron pairs is called covalent bond. 2. Covalency : The number of electron pairs which an atom of an element mutually shares with another atom or atoms of the same or different elements, ...
... Homopolar bond : A chemical bond formed between two non-metallic elements by the mutual sharing of one or more electron pairs is called covalent bond. 2. Covalency : The number of electron pairs which an atom of an element mutually shares with another atom or atoms of the same or different elements, ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... (a) An acidified solution of hydrogen peroxide is added to a solution of sodium iodide. (b) Chlorine gas is passed over powdered aluminum. (c) Solutons of mercury (I) nitrate and potassium sulfate are mixed. (d) A strip of magnesium metal is added to a solution of silver nitrate. (e) Solutions of le ...
... (a) An acidified solution of hydrogen peroxide is added to a solution of sodium iodide. (b) Chlorine gas is passed over powdered aluminum. (c) Solutons of mercury (I) nitrate and potassium sulfate are mixed. (d) A strip of magnesium metal is added to a solution of silver nitrate. (e) Solutions of le ...
Grade 11 Unit 8 - Amazon Web Services
... Plant and animal products. Plants and animals are themselves highly effective chemical factories and they synthesize many carbon compounds useful to man. These useful products include sugars, starches, plant oils and waxes, fats, gelatin, dyes, drugs, and fibers. Wood is a primary product of plant ( ...
... Plant and animal products. Plants and animals are themselves highly effective chemical factories and they synthesize many carbon compounds useful to man. These useful products include sugars, starches, plant oils and waxes, fats, gelatin, dyes, drugs, and fibers. Wood is a primary product of plant ( ...
FM 10-67-2 Chapter 7
... A primary standard is a known substance, with properties that make it useful, as a reference in standardization. The properties of a primary standard should include a high equivalent weight, usually greater than 50. It should be chemically stable and should not absorb atmospheric moisture readily. I ...
... A primary standard is a known substance, with properties that make it useful, as a reference in standardization. The properties of a primary standard should include a high equivalent weight, usually greater than 50. It should be chemically stable and should not absorb atmospheric moisture readily. I ...
X012/12/02
... Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this information is wrong, tell the Invigilator immediately. 5 If this information is correct, print your name and seat number in the boxes provided. 6 The answer to each question is either A ...
... Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this information is wrong, tell the Invigilator immediately. 5 If this information is correct, print your name and seat number in the boxes provided. 6 The answer to each question is either A ...
A.P. Chemistry Writing Chemical Reactions Generally students do
... chlorides are soluble except silver, lead and mercury(I) [AP H]. All sulfates are soluble except those of calcium, lead, barium, and strontium [C PBS]. All other salts should be considered only slightly soluble unless you learn otherwise. This is a beginning. Learn this now. It is likely that you wi ...
... chlorides are soluble except silver, lead and mercury(I) [AP H]. All sulfates are soluble except those of calcium, lead, barium, and strontium [C PBS]. All other salts should be considered only slightly soluble unless you learn otherwise. This is a beginning. Learn this now. It is likely that you wi ...
1. (a) Propan-1ol, C2H5CH2OH can be oxidised to propanoic acid
... X reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate solution to give a gas which turns lime water milky. It also reacts with a solution of sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid between 0 ºC and 5 ºC to produce a substance which reacts with phenol to give an orange ...
... X reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate solution to give a gas which turns lime water milky. It also reacts with a solution of sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid between 0 ºC and 5 ºC to produce a substance which reacts with phenol to give an orange ...
Solution Stoichiometry - Angelo State University
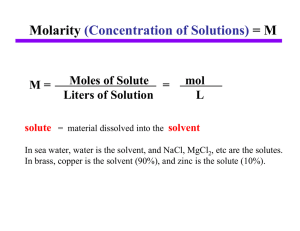
... • For a chemical reaction to occur, the reacting species have to come in close contact with each other. Most chemical reactions are performed in a solution (or in the gas phase) rather than in the solid state. • A solution consists of a smaller amount of one substance, the solute (usually a liquid o ...
... • For a chemical reaction to occur, the reacting species have to come in close contact with each other. Most chemical reactions are performed in a solution (or in the gas phase) rather than in the solid state. • A solution consists of a smaller amount of one substance, the solute (usually a liquid o ...
An Electrochemical Reactor for the CO2 Reduction in Gas
... energy sources (solar, wind, hydropower, etc.), then producing H2 by electrolysis and finally using this hydrogen to produce chemical and fuels from CO2. In a longer term vision, however, it is necessary to integrate all these steps in a single photoelectrocatalytic (PEC) device able to use directly ...
... energy sources (solar, wind, hydropower, etc.), then producing H2 by electrolysis and finally using this hydrogen to produce chemical and fuels from CO2. In a longer term vision, however, it is necessary to integrate all these steps in a single photoelectrocatalytic (PEC) device able to use directly ...
Equation Writing Information
... anions (-) and cations (+) as separate entities. You also omit the spectator ions - those ions that do not take part in the reaction. You wrote several different types of net ionic equations in ‘INTRODUCTORY’ Chemistry. On this handout, an attempt has been made to summarize the most important types ...
... anions (-) and cations (+) as separate entities. You also omit the spectator ions - those ions that do not take part in the reaction. You wrote several different types of net ionic equations in ‘INTRODUCTORY’ Chemistry. On this handout, an attempt has been made to summarize the most important types ...
Chapter 4 - profpaz.com
... This relationship is valid because the product of molarity times volume on each side equals the moles of solute, which remains constant during dilution. Molarity and volume, however, are inversely proportional during the dilution process. ...
... This relationship is valid because the product of molarity times volume on each side equals the moles of solute, which remains constant during dilution. Molarity and volume, however, are inversely proportional during the dilution process. ...
Chemistry SOL Review Test
... Unit 7: Chemical Equations (Ch. 11) 64) Use the activity series of metals to determine which of the following reactions will occur. If a reaction will take place, complete and balance the equation. If the reaction will not occur, write no reaction. a) 2 Al + 3 CuSO4 3 Cu + Al2(SO4)3 b) 6 Ag + 2 H3 ...
... Unit 7: Chemical Equations (Ch. 11) 64) Use the activity series of metals to determine which of the following reactions will occur. If a reaction will take place, complete and balance the equation. If the reaction will not occur, write no reaction. a) 2 Al + 3 CuSO4 3 Cu + Al2(SO4)3 b) 6 Ag + 2 H3 ...
Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... 1) Water is a very common solvent due to its wide availability and low cost (most of our world is water). 2) Many reactions take place in aqueous solution. The term aqueous means dissolved in water. 3) Hydration of solids in Water A) Solid dissolves (falls apart) through interaction of ions with wat ...
... 1) Water is a very common solvent due to its wide availability and low cost (most of our world is water). 2) Many reactions take place in aqueous solution. The term aqueous means dissolved in water. 3) Hydration of solids in Water A) Solid dissolves (falls apart) through interaction of ions with wat ...
The Hydroxylation of Aromatic Nitro Compounds by Alkalies
... should diminish the yield; but no such diminution occurs. The only remaining product is water; and this is now believed to render the potassium hydroxide incapable of further reaction by coating the surface. Wohl's statement that the hydroxylation proceeds in the absence of air Is true. but then the ...
... should diminish the yield; but no such diminution occurs. The only remaining product is water; and this is now believed to render the potassium hydroxide incapable of further reaction by coating the surface. Wohl's statement that the hydroxylation proceeds in the absence of air Is true. but then the ...
Liquid–liquid extraction

Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) consists in transferring one (or more) solute(s) contained in a feed solution to another immiscible liquid (solvent). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called raffinate.Liquid–liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid into another liquid phase. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.The term partitioning is commonly used to refer to the underlying chemical and physical processes involved in liquid–liquid extraction, but on another reading may be fully synonymous with it. The term solvent extraction can also refer to the separation of a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent. In that case, a soluble compound is separated from an insoluble compound or a complex matrix.Solvent extraction is used in nuclear reprocessing, ore processing, the production of fine organic compounds, the processing of perfumes, the production of vegetable oils and biodiesel, and other industries.Liquid–liquid extraction is possible in non-aqueous systems: In a system consisting of a molten metal in contact with molten salts, metals can be extracted from one phase to the other. This is related to a mercury electrode where a metal can be reduced, the metal will often then dissolve in the mercury to form an amalgam that modifies its electrochemistry greatly. For example, it is possible for sodium cations to be reduced at a mercury cathode to form sodium amalgam, while at an inert electrode (such as platinum) the sodium cations are not reduced. Instead, water is reduced to hydrogen. A detergent or fine solid can be used to stabilize an emulsion, or third phase.