CHEM102 Chemistry II Spring 11-12 Mid
... 28) Which of the following can serve as the solvent in a solution? 28) ______ A) a liquid B) a gas C) a solid D) a mixture of comingled liquids E) all of the above 29) If the concentration of H3O+ is 3.5 × 10-3 M, the concentration of OH- is ________ M. 29) ______ A) 3.5 × 10-11 B) 1.0 × 10-12 C) 2. ...
... 28) Which of the following can serve as the solvent in a solution? 28) ______ A) a liquid B) a gas C) a solid D) a mixture of comingled liquids E) all of the above 29) If the concentration of H3O+ is 3.5 × 10-3 M, the concentration of OH- is ________ M. 29) ______ A) 3.5 × 10-11 B) 1.0 × 10-12 C) 2. ...
9.1-10.5 Organic Chemistry
... Read pg. 384 Lab Exercise 9.A – complete the parts in red Purpose: To test the generalization that aromatic hydrocarbons react like saturated rather than unsaturated hydrocarbons Design: cyclohexane, cyclohexene and benzene are all mixed with potassium permanganate (purple). Evidence for a react ...
... Read pg. 384 Lab Exercise 9.A – complete the parts in red Purpose: To test the generalization that aromatic hydrocarbons react like saturated rather than unsaturated hydrocarbons Design: cyclohexane, cyclohexene and benzene are all mixed with potassium permanganate (purple). Evidence for a react ...
Organic and Bio-Molecular Chemistry
... in the air, nitrogen and oxygen, to the strangest and most complex compounds produced by microorganisms. Organic and Bio-Molecular Chemistry concerns in particular, as indicated by the name, the wide variety of compounds that constitute the living organisms; it includes however also structurally rel ...
... in the air, nitrogen and oxygen, to the strangest and most complex compounds produced by microorganisms. Organic and Bio-Molecular Chemistry concerns in particular, as indicated by the name, the wide variety of compounds that constitute the living organisms; it includes however also structurally rel ...
avogadro exam 1994 - University of Waterloo
... 33. Sodium hypochlorite is prepared by the reaction 2 NaOH + Cl2 → NaCl + NaClO + H2O If 71 g of chlorine, Cl2, is bubbled into a solution containing 50 g of sodium hydroxide, which component limits the quantity of sodium hypochlorite formed? ...
... 33. Sodium hypochlorite is prepared by the reaction 2 NaOH + Cl2 → NaCl + NaClO + H2O If 71 g of chlorine, Cl2, is bubbled into a solution containing 50 g of sodium hydroxide, which component limits the quantity of sodium hypochlorite formed? ...
CHAPTER 4: CHEMICAL QUANTITIES and AQUEOUS REACTIONS
... and iron (III) phosphate are soluble in water or not. Aluminum nitrate – Soluble (rule 1) Iron (III) phosphate – Not soluble (rule 6) ...
... and iron (III) phosphate are soluble in water or not. Aluminum nitrate – Soluble (rule 1) Iron (III) phosphate – Not soluble (rule 6) ...
Lecture 25 Notes
... The hydronium ion A hydrogen ion (H+) does not exist by itself in an aqueous solution • In water, H+ combines with a polar H2O molecule to form a hydrated hydrogen ion (H3O+) called a hydronium ion ...
... The hydronium ion A hydrogen ion (H+) does not exist by itself in an aqueous solution • In water, H+ combines with a polar H2O molecule to form a hydrated hydrogen ion (H3O+) called a hydronium ion ...
chemistry 103 - chem.uwec.edu
... solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. Because acetic acid is a weak acid, we can ignore the small amount of dissociation and assume at equilibrium that [CH3CO2H] = 1.0 M It is also important to keep in mind that there is a lot of acetate ion present, and this will suppress the dissociation ...
... solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. Because acetic acid is a weak acid, we can ignore the small amount of dissociation and assume at equilibrium that [CH3CO2H] = 1.0 M It is also important to keep in mind that there is a lot of acetate ion present, and this will suppress the dissociation ...
E:\My Documents\sch4u\SCH4U review McKay answers.wpd
... 2) You are given a 100.0 mL sample of 0.0010 M silver nitrate and 100.0 mL of solution made by dissolving 6.4X10-4 g of sodium carbonate (not sodium bicarbonate) in enough water to make 100.0 mL of solution. If the two solutions are mixed at 25/C, will a precipitate of silver carbonate form? (Ans; ...
... 2) You are given a 100.0 mL sample of 0.0010 M silver nitrate and 100.0 mL of solution made by dissolving 6.4X10-4 g of sodium carbonate (not sodium bicarbonate) in enough water to make 100.0 mL of solution. If the two solutions are mixed at 25/C, will a precipitate of silver carbonate form? (Ans; ...
FORMULA WRITNG
... 1) Write balanced equations (molecular, total ionic, and net ionic) for the reaction between each of the following solutions. If no reaction occurs, write “NR” for No Reaction. a. barium nitrate and sodium phosphate molecular: total ionic: net ionic: b. silver nitrate and sodium sulfide molecular: t ...
... 1) Write balanced equations (molecular, total ionic, and net ionic) for the reaction between each of the following solutions. If no reaction occurs, write “NR” for No Reaction. a. barium nitrate and sodium phosphate molecular: total ionic: net ionic: b. silver nitrate and sodium sulfide molecular: t ...
Net ionic equation
... A base is a substance that forms OH- ion when added to water (Arrhenius definition). A strong soluble base is a soluble hydroxide compound that completely dissociates when added to water. An insoluble base is an insoluble hydroxide compound. There are also a few substances that act as weak bases in ...
... A base is a substance that forms OH- ion when added to water (Arrhenius definition). A strong soluble base is a soluble hydroxide compound that completely dissociates when added to water. An insoluble base is an insoluble hydroxide compound. There are also a few substances that act as weak bases in ...
Document
... The pressure of the system is assumed to be held constant, at normal pressure (1 atm). As you can see from the graph below, at normal pressure water freezes at 0ºC and boils at 100ºC. The plateaus on this diagram represent the points where water is being converted from one phase to another; at these ...
... The pressure of the system is assumed to be held constant, at normal pressure (1 atm). As you can see from the graph below, at normal pressure water freezes at 0ºC and boils at 100ºC. The plateaus on this diagram represent the points where water is being converted from one phase to another; at these ...
Common Student Misconceptions
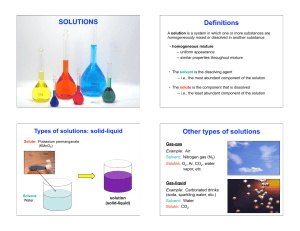
... A substance with a solubility of less than 0.01 mol/L is regarded as being insoluble. Experimental observations have led to empirical guidelines for predicting the solubility. Solubility guidelines for common ionic compounds in water: • Compounds containing alkali metal ions or ammonium ion are solu ...
... A substance with a solubility of less than 0.01 mol/L is regarded as being insoluble. Experimental observations have led to empirical guidelines for predicting the solubility. Solubility guidelines for common ionic compounds in water: • Compounds containing alkali metal ions or ammonium ion are solu ...
Chapter 4
... completely ionize in water - good conductors of electricity Weak bases are substances that act as bases but remain mostly molecular at equilibrium in water The dissociation of a weak base in solution is written using a double arrow to indicate that the dissociation does not go to completion Ammonia, ...
... completely ionize in water - good conductors of electricity Weak bases are substances that act as bases but remain mostly molecular at equilibrium in water The dissociation of a weak base in solution is written using a double arrow to indicate that the dissociation does not go to completion Ammonia, ...
Liquid–liquid extraction

Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) consists in transferring one (or more) solute(s) contained in a feed solution to another immiscible liquid (solvent). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called raffinate.Liquid–liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid into another liquid phase. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.The term partitioning is commonly used to refer to the underlying chemical and physical processes involved in liquid–liquid extraction, but on another reading may be fully synonymous with it. The term solvent extraction can also refer to the separation of a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent. In that case, a soluble compound is separated from an insoluble compound or a complex matrix.Solvent extraction is used in nuclear reprocessing, ore processing, the production of fine organic compounds, the processing of perfumes, the production of vegetable oils and biodiesel, and other industries.Liquid–liquid extraction is possible in non-aqueous systems: In a system consisting of a molten metal in contact with molten salts, metals can be extracted from one phase to the other. This is related to a mercury electrode where a metal can be reduced, the metal will often then dissolve in the mercury to form an amalgam that modifies its electrochemistry greatly. For example, it is possible for sodium cations to be reduced at a mercury cathode to form sodium amalgam, while at an inert electrode (such as platinum) the sodium cations are not reduced. Instead, water is reduced to hydrogen. A detergent or fine solid can be used to stabilize an emulsion, or third phase.