
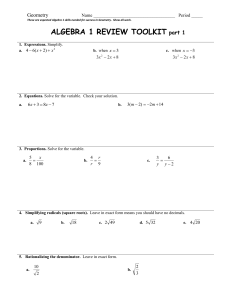
Solve systems of linear equations using the elimination method
... Learning Target I CAN solve systems of linear equations using the elimination method. ...
... Learning Target I CAN solve systems of linear equations using the elimination method. ...
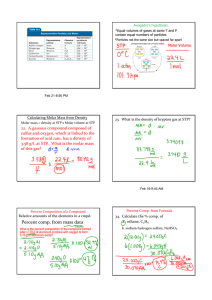
Course 3: Pressure – Volume – Temperature Relationship of Pure
... understand their P-V-T behavior and the energy requirements of processes within small margins of error Consider an engine piston full of ideal gas Total energy of the ideal gas can only be changed through transfer of energy across its boundary and work done on or by the system Heat is admitted to th ...
... understand their P-V-T behavior and the energy requirements of processes within small margins of error Consider an engine piston full of ideal gas Total energy of the ideal gas can only be changed through transfer of energy across its boundary and work done on or by the system Heat is admitted to th ...
Block 3 Drill Set - PHYS 242, General Physics II
... PHYSICS 242 BLOCK 3 DRILL SET, SPRING ‘17 NAME _____________________________ Slide this paper under the door of Marteena 308 any time before 7:50 AM Friday, February 3, or give it to me in Marteena 312 by 8:00 AM that day. Use one different equation from the Block 3 objectives for each problem. 1. A ...
... PHYSICS 242 BLOCK 3 DRILL SET, SPRING ‘17 NAME _____________________________ Slide this paper under the door of Marteena 308 any time before 7:50 AM Friday, February 3, or give it to me in Marteena 312 by 8:00 AM that day. Use one different equation from the Block 3 objectives for each problem. 1. A ...
Mathematics 414 2003–04 Exercises 5 [Due Monday February 16th, 2004.]
... points where f is analytic in G (Hf = G \ {poles of f }), Hg the set where g is analytic. Show that in each of the following cases, there is a unique meromorphic function h on G such that: (a) h(z) = f (z) + g(z) for z ∈ Hf ∩ Hg . [We use this as a definition of f + g.] (b) h(z) = f (z)g(z) for z ∈ ...
... points where f is analytic in G (Hf = G \ {poles of f }), Hg the set where g is analytic. Show that in each of the following cases, there is a unique meromorphic function h on G such that: (a) h(z) = f (z) + g(z) for z ∈ Hf ∩ Hg . [We use this as a definition of f + g.] (b) h(z) = f (z)g(z) for z ∈ ...
Equation for the Bohr Model
... The equation given at the bottom of page 221 would be a useful form for spectroscopists (people who study spectroscopy or how light is emitted and absorbed by matter). The experimentalist will be measuring the wavelength of light emitted or absorbed in their experiment, and to them inverse wavenumbe ...
... The equation given at the bottom of page 221 would be a useful form for spectroscopists (people who study spectroscopy or how light is emitted and absorbed by matter). The experimentalist will be measuring the wavelength of light emitted or absorbed in their experiment, and to them inverse wavenumbe ...













![Mathematics 414 2003–04 Exercises 5 [Due Monday February 16th, 2004.]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000084574_1-c1027704d816dc0676e3e61ce7dab3b7-300x300.png)







