
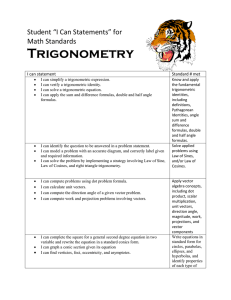
TAP 130- 2: Exponential changes
... the sign of the constant on the right-hand side, which is negative for decay with distance or time, and positive for growth. Each of equations (1), (2), (3) and (4) can be expressed in calculus notation, allowing the intervals to become arbitrarily small. Integration then leads to another form of eq ...
... the sign of the constant on the right-hand side, which is negative for decay with distance or time, and positive for growth. Each of equations (1), (2), (3) and (4) can be expressed in calculus notation, allowing the intervals to become arbitrarily small. Integration then leads to another form of eq ...
Key Concepts for Day 54 Quiz 1 on System of Linear Equations
... the graphing method, the substitution method, and the addition or subtraction method. 1. point or ordered pair - the lines cross 2. no solution – the lines are parallel 3. infinite solutions – the same line (equation) 1. Solve each equation for y to get y = mx +b form. 2. Find b, the y-intercept, on ...
... the graphing method, the substitution method, and the addition or subtraction method. 1. point or ordered pair - the lines cross 2. no solution – the lines are parallel 3. infinite solutions – the same line (equation) 1. Solve each equation for y to get y = mx +b form. 2. Find b, the y-intercept, on ...
Math 1320, Section 10 Quiz IV Solutions 20 Points Please answer
... The nice thing about completing the square is that, if done properly, the left side will always factor. Factoring the left side we have (x + 3)2 = 5. Now take the square root on both sides (i.e. extract the root) in the last equation to get ...
... The nice thing about completing the square is that, if done properly, the left side will always factor. Factoring the left side we have (x + 3)2 = 5. Now take the square root on both sides (i.e. extract the root) in the last equation to get ...
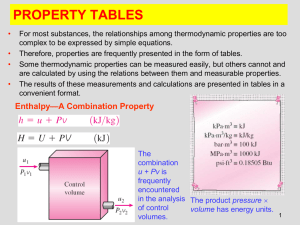
Joule-Thomson Expansion
... The porous plate will allow a gas to go through it, but only slowly. It acts as a throttle. On each side of the plate there is a piston that fits the tube tightly. Each piston can (in principle) be pushed up against the porous plate. The tube itself is insulated so that no heat can enter or leave th ...
... The porous plate will allow a gas to go through it, but only slowly. It acts as a throttle. On each side of the plate there is a piston that fits the tube tightly. Each piston can (in principle) be pushed up against the porous plate. The tube itself is insulated so that no heat can enter or leave th ...



















![[2013 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881813_1-433cb609ef4aa3f6141509bf2df16e48-300x300.png)
