* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra Review Toolkit part 1- 2 2013
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Exact solutions in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
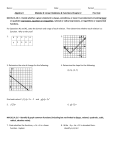
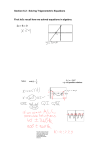
Geometry Name ____________________________________ Period _____ These are expected Algebra 1 skills needed for success in Geometry. Show all work. ALGEBRA 1 REVIEW TOOLKIT 1. Expressions. Simplify. a. 4 6( x 2) x 2 part 1 b. when x 3 c. when x 3 3x 2 x 8 3x 2 2 x 8 2 2. Equations. Solve for the variable. Check your solution. 6 z 3 8z 7 a. b. 3(m 2) 2m 14 3. Proportions. Solve for the variable. a. 5 x 8 100 b. 4 r r 9 c. 3 6 y y2 4. Simplifying radicals (square roots). Leave in exact form means you should have no decimals. 9 a. b. 18 d. 5 32 c. 2 49 5. Rationalizing the denominator. Leave in exact form. a. 10 2 b. 2 3 e. 4 20 6. Write the equation of the line below. 7. Identify the slope and y-intercept. y a. 5 4 x 2 y 10 b. 3 y 2 x 12 4 3 2 1 x -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 8. Parallel lines have the same slope (m1 = m2) and a different y-intercept. They never intersect. y1 1 x4 3 y2 1 x 2 3 9. Perpendicular lines have opposite reciprocal slopes. Multiplying the slopes equals -1. y1 3 x4 2 2 y2 x 2 3 m1 = m2 = m1 = m2 = b1 = b2 = b1 = b2 = y rise x run Geometry Name ____________________________________ Period _____ Algebra 1 skills that will be seen in review/preview practice. Show all work. ALGEBRA 1 REVIEW TOOLKIT PART 2 SYSTEMS: a graph that may or may not have a point of intersection of two equations (x,y). Sometimes two lines have no points (parallel lines) or an infinite number of points (lines lie on top of each.) Equal Values Method (Substitution Method) y 3x 5 y 4x 8 Substitution Method x 3 y 1 4 x 3 y 11 Elimination Method a. x y 4 x 2 y 13 b. x 5y 1 x 4y 2 c. 4x 3y 7 2 x 9 y 35 QUADRATICS: A graphed parabola that may have one or two solutions, called roots. If the discriminant is negative like 49 then it has no real roots (imaginary number). Multiplying polynomials. Simplify each expression. a. y 7 y 2 b. 2 x 5 c. 2 x x 2 3x 2 2 Factor the trinomials completely. Do not solve. a. x 2 13x 42 b. x 2 18 x 81 Graph the following quadratic without a table. y x 2 4x 3 c. 2 x 2 9 x 9 Review of how to graph a quadratic equation: 1. First factor and find the roots by using the Zero Product Property. 2. Find the line of symmetry by using the vertex formula x b . 2a 3. Substitute the x into the equation to find the y coordinate of the vertex. 3. Plot the y-intercept. Quadratic Formula. x 2 8x 6 0 Solve and leave in exact form. b b 2 4ac x 2a