* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7.2 and 7.3 Quadratic Formula and Discriminant Printable
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Two-body Dirac equations wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
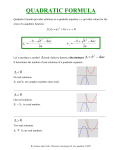
7.2/7.3 The Discriminant & Quadratic Formula Learning goal Solve quadratic equations by inspection (e.g., for x² = 49), taking square roots, completing the square, the quadratic formula and factoring, as appropriate to the initial form of the equation. Recognize when the quadratic formula gives complex solutions and write them as a ± bi for real numbers a and b. If a quadratic equation is written in standard form ax2 bx c 0 then it can be solved with the Quadratic Formula b b 4ac x 2a 2 discriminant : value beneath the radical determines # and type of solutions 2 b 4 ac Value of Discriminant >0 and a perfect square >0 and NOT a perfect square Number of Solutions Type of Solutions Graph Intercepts ___ x-intercepts ___ x-intercepts =0 ___ x-intercept <0 ___ x-intercepts Graph Ex 1 Determine the type & number of solutions. x 5 x 10 0 2 x 6x 9 0 2 Ex 2 Determine the type & number of solutions. x 5x 5 0 2 5x 5x 1 0 2 Ex 3 Solve using the QF 3 x 23 x 40 0 2 Ex 4 Solve using the QF 3 x 2 x 4 2 Ex 5 A swimming pool 6 m wide and 10 m long is to be surrounded by a walk of uniform width. The area of the walk happens to be equal to the area of the pool. What is the width of the walk? (Hint: Draw a diagram 1st)