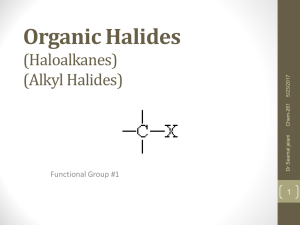Conjugate addition_Clayden
... The reason that α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds react differently is conjugation, the phenomenon we discussed in Chapter 7. There we introduced you to the idea that bringing two π systems (two C=C bonds, for example, or a C=C bond and a C=O bond) close together leads to a stabilizing interaction. ...
... The reason that α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds react differently is conjugation, the phenomenon we discussed in Chapter 7. There we introduced you to the idea that bringing two π systems (two C=C bonds, for example, or a C=C bond and a C=O bond) close together leads to a stabilizing interaction. ...
Chapter Seven - U of L Class Index
... The Sn 1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate in the ratedetermining step. 3°, benzylic and allylic substrates undergo Sn 1 reaction because they form relatively stable carbocations. 1° substrates undergo Sn2 reaction because they are sterically uncluttered. 2° substrates u ...
... The Sn 1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate in the ratedetermining step. 3°, benzylic and allylic substrates undergo Sn 1 reaction because they form relatively stable carbocations. 1° substrates undergo Sn2 reaction because they are sterically uncluttered. 2° substrates u ...
Module 5 Reactions with Miscellaneous Reagents
... bromination in the aromatic ring by substitution. In these reactions, the brominating agent could probably be the protonated NBS. Benzene when treated with NBS and a 1:1 mixture of conc. H2SO4 and water gives bromobenzene in 95% yield. Under these conditions, aromatic compounds having highly branche ...
... bromination in the aromatic ring by substitution. In these reactions, the brominating agent could probably be the protonated NBS. Benzene when treated with NBS and a 1:1 mixture of conc. H2SO4 and water gives bromobenzene in 95% yield. Under these conditions, aromatic compounds having highly branche ...
Reductive Deoxygenation of Ketones and Secondary Alcohols by
... The reductive deoxygenation of ketones and secondary alcohols to the corresponding methylene hydrocarbons has been achieved in good to excellent yield by the combined action of an aluminum hydride source and a strongly Lewis-acidic aluminum reagent. Such reductions were successful with diaryl ketone ...
... The reductive deoxygenation of ketones and secondary alcohols to the corresponding methylene hydrocarbons has been achieved in good to excellent yield by the combined action of an aluminum hydride source and a strongly Lewis-acidic aluminum reagent. Such reductions were successful with diaryl ketone ...
New Phenylglycine-Derived Primary Amine Organocatalysts for the
... the successful preparation of warfarin in CH2Cl2.[2a,2c] Especially the Cinchona derivatives 7 and 8 work remarkably well in this solvent,[2c] whereas the silyl ether 20 shows only very modest results in CH2Cl2 (Entry 20). We hypothesized that phase-transfer effects could be at play, but addition of ...
... the successful preparation of warfarin in CH2Cl2.[2a,2c] Especially the Cinchona derivatives 7 and 8 work remarkably well in this solvent,[2c] whereas the silyl ether 20 shows only very modest results in CH2Cl2 (Entry 20). We hypothesized that phase-transfer effects could be at play, but addition of ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 9 - Alkyl Halides I
... more EN, more stable afterwards RF fastest CH3I ...
... more EN, more stable afterwards RF fastest CH3I ...
Get PDF - Wiley Online Library
... with activated carbon[15] – solved this problem and resulted in the isolation of a stable product. Since a small allylic substituent is apparently sufficient to facilitate the ring-closing metathesis of dehydroamino acids and to prevent olefin isomerization, we decided to investigate whether the sco ...
... with activated carbon[15] – solved this problem and resulted in the isolation of a stable product. Since a small allylic substituent is apparently sufficient to facilitate the ring-closing metathesis of dehydroamino acids and to prevent olefin isomerization, we decided to investigate whether the sco ...
Organic Chemistry
... Addition of HOCl and HOBr • reaction is both regiospecific (OH adds to the more substituted carbon) and anti stereoselective • both selectivities are illustrated by the addition of HOBr to 1-methylcyclopentene Br2 / H2 O ...
... Addition of HOCl and HOBr • reaction is both regiospecific (OH adds to the more substituted carbon) and anti stereoselective • both selectivities are illustrated by the addition of HOBr to 1-methylcyclopentene Br2 / H2 O ...
Cl3CCN/PPh3 and CBr4/PPh3: two efficient reagent systems for the
... the case of 4-hydroxypyridine, the desired chloride was obtained in a 94% yield, whereas none of the expected bromide was obtained (entries 531 and 632). 3-Hydroxypyridine and 8-hydroxyquinoline gave no halo-product (entries 333, 434, 935 and 1036). The reaction also proceeded with hydroxyquinazolin ...
... the case of 4-hydroxypyridine, the desired chloride was obtained in a 94% yield, whereas none of the expected bromide was obtained (entries 531 and 632). 3-Hydroxypyridine and 8-hydroxyquinoline gave no halo-product (entries 333, 434, 935 and 1036). The reaction also proceeded with hydroxyquinazolin ...
Improved Synthesis of (3E,6Z,9Z)-1,3,6,9
... of the two species. Thus, a trapping method that is selective for winter moth would be desirable. A geometric isomer of the pheromone, (3E,6Z,9Z)-1,3,6,9-nonadecatetraene (2), can reportedly inhibit attraction of Bruce spanworm to traps without affecting winter moth catch, but use of the pheromone a ...
... of the two species. Thus, a trapping method that is selective for winter moth would be desirable. A geometric isomer of the pheromone, (3E,6Z,9Z)-1,3,6,9-nonadecatetraene (2), can reportedly inhibit attraction of Bruce spanworm to traps without affecting winter moth catch, but use of the pheromone a ...
FULL PAPER Observations on the Influence of Precursor
... With the rapid development of computational capability in the last two decades in mind we speculated that it might indeed be possible to generate a large number of possible conformations for the large and flexible cyclization precursors studied here. With the experimental data for the successful mac ...
... With the rapid development of computational capability in the last two decades in mind we speculated that it might indeed be possible to generate a large number of possible conformations for the large and flexible cyclization precursors studied here. With the experimental data for the successful mac ...
Changing counterion can switch the preference for selective 1,2
... Another example of a selectivity-controlled reaction of alkenes is hydroformylation via the use of scaffolding ligands. These bind covalently and reversibly to the substrate, leading to a temporarily intramolecular transformation that can lead to dramatically improved and reversed selectivity with s ...
... Another example of a selectivity-controlled reaction of alkenes is hydroformylation via the use of scaffolding ligands. These bind covalently and reversibly to the substrate, leading to a temporarily intramolecular transformation that can lead to dramatically improved and reversed selectivity with s ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... • PCB’s (polychlorinated biphenyls) – electrical transformers ...
... • PCB’s (polychlorinated biphenyls) – electrical transformers ...
Rutgers...Ch17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... Since the sigma complexes for ortho (and para) attack have resonance forms with tertiary carbons, they are more stable that the corresponding resonance forms for benzene's reaction with nitronium ion. Thus toluene reacts faster than benzene at the ortho and para positions. When reaction of toluene o ...
... Since the sigma complexes for ortho (and para) attack have resonance forms with tertiary carbons, they are more stable that the corresponding resonance forms for benzene's reaction with nitronium ion. Thus toluene reacts faster than benzene at the ortho and para positions. When reaction of toluene o ...
Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones – Nucleophilic Addition
... Ketones are less susceptible than aldehydes to attack by nucleophiles, so aldol additions occur more slowly with ketones. With ketones, the reaction proceeds well only if the product is removed from the basic solution or reacts further by dehydration. ...
... Ketones are less susceptible than aldehydes to attack by nucleophiles, so aldol additions occur more slowly with ketones. With ketones, the reaction proceeds well only if the product is removed from the basic solution or reacts further by dehydration. ...
Solvent and Temperature Effects on the Reduction and Amination
... The reaction of iPr-LAB (1 M in THF) with methyl iodide produces a mixture of aminoborane (BH2-N(iPr)2) and amineborane (BH3-NMe(iPr)2). At 0 °C, amination by SN2 mechanism is the major reaction and as the temperature increased to 65 °C, reduction reaction competed favorably with amination reaction ...
... The reaction of iPr-LAB (1 M in THF) with methyl iodide produces a mixture of aminoborane (BH2-N(iPr)2) and amineborane (BH3-NMe(iPr)2). At 0 °C, amination by SN2 mechanism is the major reaction and as the temperature increased to 65 °C, reduction reaction competed favorably with amination reaction ...
Manganese-Catalyzed Carbonylation of Alkyl Iodides
... Arynes are highly strained and reactive species that undergo a range of synthetically useful transformations when generated and used in situ, hence a number of methods for their formation have been developed. 1' 2 Although highly reactive in solution, arynes can be stabilized by electron rich metal ...
... Arynes are highly strained and reactive species that undergo a range of synthetically useful transformations when generated and used in situ, hence a number of methods for their formation have been developed. 1' 2 Although highly reactive in solution, arynes can be stabilized by electron rich metal ...
Development of Multi-Component Reactions using Catalytically Generated Allyl Metal Reagents
... In the past decades, the development of effective multi-component based synthesis has played an important role to achieve high atom economy and sustainable chemistry.1-7 The major challenges in this field are compatibility between the reagents and catalysts present to prevent catalyst inhibition and ...
... In the past decades, the development of effective multi-component based synthesis has played an important role to achieve high atom economy and sustainable chemistry.1-7 The major challenges in this field are compatibility between the reagents and catalysts present to prevent catalyst inhibition and ...
reactions of alcohols with alkenes over an aluminum
... temperatures di(alk-l-yl) ethers can be synthesized from n-alcohols using clay catalysts. The ethers produced were identified by GLC-MS cracking patterns. Generally the yield of the tertiary alcohol, 2-methyl pentan-2-ol, was between 0.8 and 1.2 mole, which is less than that which could have been pr ...
... temperatures di(alk-l-yl) ethers can be synthesized from n-alcohols using clay catalysts. The ethers produced were identified by GLC-MS cracking patterns. Generally the yield of the tertiary alcohol, 2-methyl pentan-2-ol, was between 0.8 and 1.2 mole, which is less than that which could have been pr ...
Some uses of mischmetall in organic synthesis
... The use of rare earth compounds in organic chemistry has grown considerably during the past twenty years. Mainly samarium, cerium, lanthanum, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, lutetium, scandium and yttrium metals and derivatives have been studied. These elements clearly differ in terms of reactivit ...
... The use of rare earth compounds in organic chemistry has grown considerably during the past twenty years. Mainly samarium, cerium, lanthanum, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, lutetium, scandium and yttrium metals and derivatives have been studied. These elements clearly differ in terms of reactivit ...
13_lecture_ppt
... Preparation of aldehydes and ketones • Principal means of preparation is oxidation of the corresponding alcohol – Primary alcohol produces an aldehyde – Secondary alcohol produces a ketone – Tertiary alcohol does not oxidize ...
... Preparation of aldehydes and ketones • Principal means of preparation is oxidation of the corresponding alcohol – Primary alcohol produces an aldehyde – Secondary alcohol produces a ketone – Tertiary alcohol does not oxidize ...
Ch. 09 Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides
... Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alcohols • Treatment of alcohols with a strong acid protonates the O converting the bad leaving group ¯OH into H2O, a good leaving group. • The pKa of (ROH2)+ is ~ -2, so protonation of alcohols only occurs with very strong acids. • This makes it possible t ...
... Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alcohols • Treatment of alcohols with a strong acid protonates the O converting the bad leaving group ¯OH into H2O, a good leaving group. • The pKa of (ROH2)+ is ~ -2, so protonation of alcohols only occurs with very strong acids. • This makes it possible t ...
Aromatic Compounds
... because of resonance but much less stable than the starting benzene ring Comparison of alkene addition and aromatic substitution ...
... because of resonance but much less stable than the starting benzene ring Comparison of alkene addition and aromatic substitution ...
Latest Publication (still not complete)
... observed reaction pathways and hence is crucial to the total understanding of the chemistry of chromium-pentacarbonyl carbene complexes. Fischer carbene complexes exhibit two characteristic features that are important in understanding their respective chemistry. The first of these features is the fa ...
... observed reaction pathways and hence is crucial to the total understanding of the chemistry of chromium-pentacarbonyl carbene complexes. Fischer carbene complexes exhibit two characteristic features that are important in understanding their respective chemistry. The first of these features is the fa ...
Diels–Alder reaction
.png?width=300)
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction (specifically, a [4+2] cycloaddition) between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. It was first described by Otto Paul Hermann Diels and Kurt Alder in 1928, for which work they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950. The Diels–Alder reaction is particularly useful in synthetic organic chemistry as a reliable method for forming 6-membered systems with good control over regio- and stereochemical properties. The underlying concept has also been applied to other π-systems, such as carbonyls and imines, to furnish the corresponding heterocycles, known as the hetero-Diels–Alder reaction. Diels–Alder reactions can be reversible under certain conditions; the reverse reaction is known as the retro-Diels–Alder reaction.