radioactivity: types of radiation
... What is Beta radiation? (b) A fast moving (high energy) electron. It is negatively charged. When a neutron in the nucleus disintegrates, it forms an electron (which is emitted as a beta particle) and a proton which remains in the nucleus. ...
... What is Beta radiation? (b) A fast moving (high energy) electron. It is negatively charged. When a neutron in the nucleus disintegrates, it forms an electron (which is emitted as a beta particle) and a proton which remains in the nucleus. ...
electromagnetic spectrum
... • Electric charges are the source of electric fields. • Moving charges generate magnetic fields. • Waves are the propagation of a disturbance. • They transport energy and momentum but do not transport matter. ...
... • Electric charges are the source of electric fields. • Moving charges generate magnetic fields. • Waves are the propagation of a disturbance. • They transport energy and momentum but do not transport matter. ...
Electromagnetic radiation
... This speed turns out to be = the speed of light! Conclusion and prediction: light is just a form of electromagnetic radiation there should be other forms of electromagnetic radiation (different frequencies) which can be produced by making charges “wiggle”; This was experimentally verified by H ...
... This speed turns out to be = the speed of light! Conclusion and prediction: light is just a form of electromagnetic radiation there should be other forms of electromagnetic radiation (different frequencies) which can be produced by making charges “wiggle”; This was experimentally verified by H ...
Electromagnetic Radiation Magnetism, and Electrostatics
... b. a decrease c. no change 22. Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy? a. as energy increases, both wavelength and frequency increase b. as energy increases, both wavelength and frequency decrease c. as energy increases, wavelength ...
... b. a decrease c. no change 22. Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy? a. as energy increases, both wavelength and frequency increase b. as energy increases, both wavelength and frequency decrease c. as energy increases, wavelength ...
â« â«
... • The orientation of the electric and magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves is • A) perpendicular to the direction of waves and parallel to each other. • B) parallel to the direction of the waves and parallel to each other. • C) parallel to the direction of the waves and perpendicular to each ...
... • The orientation of the electric and magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves is • A) perpendicular to the direction of waves and parallel to each other. • B) parallel to the direction of the waves and parallel to each other. • C) parallel to the direction of the waves and perpendicular to each ...
What is wave? How are EM waves different from mechanical waves?
... I can recognize the Sun’s energy reaches Earth as Electromagnetic wave energy. ...
... I can recognize the Sun’s energy reaches Earth as Electromagnetic wave energy. ...
Lecture 20
... Because em waves travel at a speed that is precisely the speed of light, light is an electromagnetic wave ...
... Because em waves travel at a speed that is precisely the speed of light, light is an electromagnetic wave ...
Atmosphere Test Review Practice
... f. a form of energy with wavelengths that are shorter than those of violet light ...
... f. a form of energy with wavelengths that are shorter than those of violet light ...
Electromagnetic Radiation and Computers
... What is electromagnetic radiation? Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) are invisible lines of force that occur whenever electricity is being conducted. These forces occur from both natural sources such as the sun or atmospheric and solar disturbances, and from man-made sources including electric lighting, ...
... What is electromagnetic radiation? Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) are invisible lines of force that occur whenever electricity is being conducted. These forces occur from both natural sources such as the sun or atmospheric and solar disturbances, and from man-made sources including electric lighting, ...
Chemistry 1A – Chapter 11 Objectives Name Hour Indiana State
... C.2.6 Use the periodic table and electron configuration to determine an element's number of valence electrons and its chemical and physical properties. Chapter 11 Objectives 11.2 Electromagnetic Radiation Do p.353 #5,6 ...
... C.2.6 Use the periodic table and electron configuration to determine an element's number of valence electrons and its chemical and physical properties. Chapter 11 Objectives 11.2 Electromagnetic Radiation Do p.353 #5,6 ...
Physics Final Review Sheet Name
... 63. An ambulance siren sounds different as it approaches you than when it moves away from you. What scientific term would you use to explain how this happens? ...
... 63. An ambulance siren sounds different as it approaches you than when it moves away from you. What scientific term would you use to explain how this happens? ...
Electromagnetic Radiation
... • Energy is “the ability to do work” • Energy transfer: – Conduction: transfer of kinetic energy by contact between atoms or molecules – Convection: transfer of kinetic energy by physically moving the mass that contains the energy – Radiation: propagation via waves/particles through a vacuum (or thr ...
... • Energy is “the ability to do work” • Energy transfer: – Conduction: transfer of kinetic energy by contact between atoms or molecules – Convection: transfer of kinetic energy by physically moving the mass that contains the energy – Radiation: propagation via waves/particles through a vacuum (or thr ...
Worksheet 6 - KFUPM Faculty List
... 1) (a) Photosynthesis uses 660-nm light to convert CO2 and H2O into glucose and O2. Calculate the frequency of this light. (b) An FM radio station broadcasts at 99.5 MHz. Calculate the wavelength of the corresponding radio waves. ...
... 1) (a) Photosynthesis uses 660-nm light to convert CO2 and H2O into glucose and O2. Calculate the frequency of this light. (b) An FM radio station broadcasts at 99.5 MHz. Calculate the wavelength of the corresponding radio waves. ...
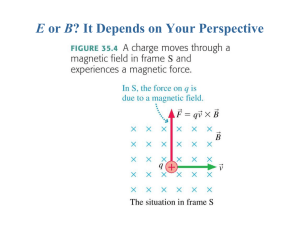
E or B? It Depends on Your Perspective
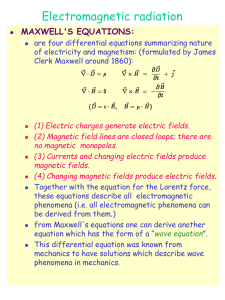
... Maxwell, using his equations of the electromagnetic field, was the first to understand that light is an oscillation of the electromagnetic field. Maxwell was able to predict that • Electromagnetic waves can exist at any frequency, not just at the frequencies of visible light. This prediction was the ...
... Maxwell, using his equations of the electromagnetic field, was the first to understand that light is an oscillation of the electromagnetic field. Maxwell was able to predict that • Electromagnetic waves can exist at any frequency, not just at the frequencies of visible light. This prediction was the ...
What Are Electromagnetic Waves?
... Electromagnetic wave is by measuring its frequency. Frequency refers to the number of waves a vibration creates during a period of time – like counting how frequently cars pass through an intersection in a given time. In general, the higher the frequency, or number of waves, the greater the energy o ...
... Electromagnetic wave is by measuring its frequency. Frequency refers to the number of waves a vibration creates during a period of time – like counting how frequently cars pass through an intersection in a given time. In general, the higher the frequency, or number of waves, the greater the energy o ...
Electromagnetic Waves
... perpendicular to each other and to the travel direction. EM waves are transverse waves. EM waves travel with the speed of light (c). EM waves carry both energy and momentum. For an EM wave: ...
... perpendicular to each other and to the travel direction. EM waves are transverse waves. EM waves travel with the speed of light (c). EM waves carry both energy and momentum. For an EM wave: ...
Chapter 17, Section 1: Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
... • All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in a vacuum, but they have different wavelengths and different frequencies. • Remember speed = wavelength x frequency • The electromagnetic spectrum is the complete range of electromagnetic waves placed in order of increasing frequency. ...
... • All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in a vacuum, but they have different wavelengths and different frequencies. • Remember speed = wavelength x frequency • The electromagnetic spectrum is the complete range of electromagnetic waves placed in order of increasing frequency. ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES.notes
... • Beyond the UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum lies the X-ray region. • W Roentgen discovered x-rays • One common way to generate X-rays is to bombard a metal target by high energy ...
... • Beyond the UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum lies the X-ray region. • W Roentgen discovered x-rays • One common way to generate X-rays is to bombard a metal target by high energy ...
Jan. 27 - Feb. 5
... Speed = 300,000 km/sec and constant in a vacuum (Einstein) c = λf so frequency and wavelength are related Varies in transparent media (prism) with blue slowest Prism splits light into colors Refraction Bending due to different velocities Faster = farther from normal Slower = closer to normal Red is ...
... Speed = 300,000 km/sec and constant in a vacuum (Einstein) c = λf so frequency and wavelength are related Varies in transparent media (prism) with blue slowest Prism splits light into colors Refraction Bending due to different velocities Faster = farther from normal Slower = closer to normal Red is ...
Chemistry Quiz Ch. 5 Electron Configuration and Quantum Theory
... 20. A specific (just right) amount of energy that can be absorbed or emitted is called: a. quantum b. photon c. particle ...
... 20. A specific (just right) amount of energy that can be absorbed or emitted is called: a. quantum b. photon c. particle ...
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The ""electromagnetic spectrum"" of an object has a different meaning, and is instead the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object.The electromagnetic spectrum extends from below the low frequencies used for modern radio communication to gamma radiation at the short-wavelength (high-frequency) end, thereby covering wavelengths from thousands of kilometers down to a fraction of the size of an atom. The limit for long wavelengths is the size of the universe itself, while it is thought that the short wavelength limit is in the vicinity of the Planck length. Until the middle of last century it was believed by most physicists that this spectrum was infinite and continuous.Most parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are used in science for spectroscopic and other probing interactions, as ways to study and characterize matter. In addition, radiation from various parts of the spectrum has found many other uses for communications and manufacturing (see electromagnetic radiation for more applications).