Did an 8th century gamma ray burst irradiate the Earth
... When this happens, some energy is released in the form of gamma rays, the most energetic part of the electromagnetic spectrum that includes visible light. ...
... When this happens, some energy is released in the form of gamma rays, the most energetic part of the electromagnetic spectrum that includes visible light. ...
Waves and Modern Physics
... gases, Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert Bunsen observed that when gases were heated to a high enough temperature, light of different frequencies was given ...
... gases, Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert Bunsen observed that when gases were heated to a high enough temperature, light of different frequencies was given ...
Lecture 13: Electromagnetic waves
... from radioactive decay. Their high energy makes these rays very dangerous. Gamma rays can also be seen coming in from outer space with energies of 1019 eV or wavelengths as small as 10−25 m!! These are called cosmic rays. Typical atomic spacings in a solid are of order 1 Angstrom = 10−10 m. This is ...
... from radioactive decay. Their high energy makes these rays very dangerous. Gamma rays can also be seen coming in from outer space with energies of 1019 eV or wavelengths as small as 10−25 m!! These are called cosmic rays. Typical atomic spacings in a solid are of order 1 Angstrom = 10−10 m. This is ...
Slide 1
... The term electromagnetic pulse (EMP) has the following meanings: The electromagnetic radiation from an explosion (especially a nuclear explosion) or an intensely fluctuating magnetic field caused by Compton-recoil electrons and photoelectrons from photons scattered in the materials of the electro ...
... The term electromagnetic pulse (EMP) has the following meanings: The electromagnetic radiation from an explosion (especially a nuclear explosion) or an intensely fluctuating magnetic field caused by Compton-recoil electrons and photoelectrons from photons scattered in the materials of the electro ...
Midterm Exam 1
... something is done to the system from the outside. • Be able to use the concept to reason your way through what will happen in simple situations such as those described in class. – Escape velocity & orbits ...
... something is done to the system from the outside. • Be able to use the concept to reason your way through what will happen in simple situations such as those described in class. – Escape velocity & orbits ...
Flame tests and Spectroscopy - Chemie
... Flame tests and Spectroscopy The photoelectric effect Usually the electrons surround the nucleus of an atom on certain orbits. By stimulation with light or heat these electrons can be removed temporarily from their original orbits. If they fall back on their original position they emit energy which ...
... Flame tests and Spectroscopy The photoelectric effect Usually the electrons surround the nucleus of an atom on certain orbits. By stimulation with light or heat these electrons can be removed temporarily from their original orbits. If they fall back on their original position they emit energy which ...
Physics 3323 Intermediate Electricity and Magnetism
... Homework and Quizzes: One problem set each week, available from blackboard each Wednesday, due at start of class the Friday following. Working together on the homework is encouraged, but the submitted work ...
... Homework and Quizzes: One problem set each week, available from blackboard each Wednesday, due at start of class the Friday following. Working together on the homework is encouraged, but the submitted work ...
λ - Chemistry 7
... A cook uses a microwave oven to heat a meal. The wavelength of the radiation is 1.20 cm. What is the energy of one photon of this microwave radiation? ...
... A cook uses a microwave oven to heat a meal. The wavelength of the radiation is 1.20 cm. What is the energy of one photon of this microwave radiation? ...
1 Introduction
... A changing magnetic field will induce a changing electric field and vice-versa. These changing fields form electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic (EM) waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate through. This means that electromagnetic waves can travel not on ...
... A changing magnetic field will induce a changing electric field and vice-versa. These changing fields form electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic (EM) waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a medium to propagate through. This means that electromagnetic waves can travel not on ...
Slide 1
... abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. ...
... abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. ...
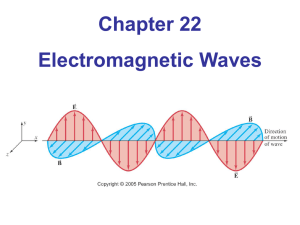
Ch22electromagneticwaves
... At the receiving end, the wave is received, demodulated, amplified, and sent to a loudspeaker: ...
... At the receiving end, the wave is received, demodulated, amplified, and sent to a loudspeaker: ...
electromagnetic waves
... (c) is similar to the radiations emitted during decay of radioactive nuclei. (d) has its wavelength range between 390 nm and 770 nm. (e) is absorbed from sunlight by ozone layer. (f) produces intense heating effect. Business ...
... (c) is similar to the radiations emitted during decay of radioactive nuclei. (d) has its wavelength range between 390 nm and 770 nm. (e) is absorbed from sunlight by ozone layer. (f) produces intense heating effect. Business ...
Syllabus, Introduction, and Review on Physical Laws ()
... properties of electricity and magnetism in four equations • This mathematical achievement demonstrated that electric and magnetic forces are really two aspects of the same phenomenon, which we now call electromagnetism ...
... properties of electricity and magnetism in four equations • This mathematical achievement demonstrated that electric and magnetic forces are really two aspects of the same phenomenon, which we now call electromagnetism ...
2 - Mineola ISD
... ¢A body contains internal KE due to the motion of its atoms ( they are constantly wiggling and jiggling) ¢Thermal Energy is the total internal KE of a body ¢Temperature is the average KE of a ...
... ¢A body contains internal KE due to the motion of its atoms ( they are constantly wiggling and jiggling) ¢Thermal Energy is the total internal KE of a body ¢Temperature is the average KE of a ...
Chapter 25 Electromagnetic Waves
... observed when the charges accelerate along the line of sight. These observations apply to electromagnetic waves of all frequencies. ...
... observed when the charges accelerate along the line of sight. These observations apply to electromagnetic waves of all frequencies. ...
notes - Purdue Physics
... electromagnetism demonstrates that electricity, magnetism and light are all manifestations of the same phenomenon, namely the electromagnetic field. Maxwell's achievements concerning electromagnetism have been called the "second great unification in physics” after the first one realized by Isaac New ...
... electromagnetism demonstrates that electricity, magnetism and light are all manifestations of the same phenomenon, namely the electromagnetic field. Maxwell's achievements concerning electromagnetism have been called the "second great unification in physics” after the first one realized by Isaac New ...
Electromagnetic Waves Webquest
... List 2 different places radio waves are used. Why do we often think of infrared waves as heat? Other than microwave ovens, where are microwaves used? What type of wave is the part of the spectrum that we see? What type of waves does the Sun emit? What type of waves do doctors use to take pictures of ...
... List 2 different places radio waves are used. Why do we often think of infrared waves as heat? Other than microwave ovens, where are microwaves used? What type of wave is the part of the spectrum that we see? What type of waves does the Sun emit? What type of waves do doctors use to take pictures of ...
• Maxwell`s equations and electromagnetic waves • sinusoidal
... • A point charge can generate electromagnetic wave if is being accelerated. • The point charge below is oscillating in simple harmonic motion (what does it mean for acceleration?) • How would the magnetic field lines look like? (Imagine the moving charge as current) ...
... • A point charge can generate electromagnetic wave if is being accelerated. • The point charge below is oscillating in simple harmonic motion (what does it mean for acceleration?) • How would the magnetic field lines look like? (Imagine the moving charge as current) ...
(Electromagnetic Wave).
... electric fields changing in time would create magnetic fields and vice-versa. – Maxwell further predicted that either accelerating charges (changing current) or changing magnetic fields would produce electric and magnetic fields that would move through space (Electromagnetic ...
... electric fields changing in time would create magnetic fields and vice-versa. – Maxwell further predicted that either accelerating charges (changing current) or changing magnetic fields would produce electric and magnetic fields that would move through space (Electromagnetic ...
Some Q - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... of the red light is 660 nm. What is the speed of the red light? What is the frequency of the red light? What is the energy of one red light photon? What is the energy of one mole of red light photons? A student obtains a blue laser pointer. What is the speed of the blue light? Which has a longer wav ...
... of the red light is 660 nm. What is the speed of the red light? What is the frequency of the red light? What is the energy of one red light photon? What is the energy of one mole of red light photons? A student obtains a blue laser pointer. What is the speed of the blue light? Which has a longer wav ...
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The ""electromagnetic spectrum"" of an object has a different meaning, and is instead the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object.The electromagnetic spectrum extends from below the low frequencies used for modern radio communication to gamma radiation at the short-wavelength (high-frequency) end, thereby covering wavelengths from thousands of kilometers down to a fraction of the size of an atom. The limit for long wavelengths is the size of the universe itself, while it is thought that the short wavelength limit is in the vicinity of the Planck length. Until the middle of last century it was believed by most physicists that this spectrum was infinite and continuous.Most parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are used in science for spectroscopic and other probing interactions, as ways to study and characterize matter. In addition, radiation from various parts of the spectrum has found many other uses for communications and manufacturing (see electromagnetic radiation for more applications).