Burns Pulm Lect 1 Physiol 2017
... • Amount of gas dissolved in blood can be limited by pulmonary blood flow (perfusion limited) • It takes 0.75 seconds for blood to flow through a pulmonary capillary, and only 0.25 seconds for alveolar O2 to equilibrate with blood O2; for the remaining 0.5 seconds, the blood will not take on more O2 ...
... • Amount of gas dissolved in blood can be limited by pulmonary blood flow (perfusion limited) • It takes 0.75 seconds for blood to flow through a pulmonary capillary, and only 0.25 seconds for alveolar O2 to equilibrate with blood O2; for the remaining 0.5 seconds, the blood will not take on more O2 ...
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
... parts: (1) cerebrum; (2) brainstem, which consist of midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata; (3) diencephalon, which consists of the thalamus and hypothalamus; and (4) cerebellum. Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the underside of the brain: 2 pairs arise from the cerebrum and 10 pairs of cra ...
... parts: (1) cerebrum; (2) brainstem, which consist of midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata; (3) diencephalon, which consists of the thalamus and hypothalamus; and (4) cerebellum. Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the underside of the brain: 2 pairs arise from the cerebrum and 10 pairs of cra ...
6. Brain Lateralization
... by the left hemisphere. The left and right hemispheres thus became known as dominant hemisphere and minor hemisphere respectively. The researchers found the evidence of language laterality when they compared the effects of left and right unilateral lesions due to the strokes to the brain. In present ...
... by the left hemisphere. The left and right hemispheres thus became known as dominant hemisphere and minor hemisphere respectively. The researchers found the evidence of language laterality when they compared the effects of left and right unilateral lesions due to the strokes to the brain. In present ...
Smoking can cost an arm and a leg KEY
... Your doctor also may check the pulses in your leg arteries for an abnormal whooshing sound called a bruit. He or she can hear this sound with a stethoscope. A bruit may be a warning sign of a narrowed or blocked artery. Your doctor may compare blood pressure between your limbs to see whether the pre ...
... Your doctor also may check the pulses in your leg arteries for an abnormal whooshing sound called a bruit. He or she can hear this sound with a stethoscope. A bruit may be a warning sign of a narrowed or blocked artery. Your doctor may compare blood pressure between your limbs to see whether the pre ...
Dear Notetaker:
... Know how O2 and CO2 are transported in the blood Dorsal respiratory group of neurons - Primary regulator of ventilation - During normal breathing, consists primarily of inspiratory neurons which are either on/off, stimulating phrenic nerve, stimulates diaphragm, contraction (inspiration), relaxation ...
... Know how O2 and CO2 are transported in the blood Dorsal respiratory group of neurons - Primary regulator of ventilation - During normal breathing, consists primarily of inspiratory neurons which are either on/off, stimulating phrenic nerve, stimulates diaphragm, contraction (inspiration), relaxation ...
CASE 14
... causes a change in blood flow. If MAP is increased, flow initially increases and local concentrations of metabolites (CO2, K+, H+, adenosine) decrease as a result of washout; local concentrations of substrates (O2) increase because supply is greater than demand. Opposite changes in metabolite and su ...
... causes a change in blood flow. If MAP is increased, flow initially increases and local concentrations of metabolites (CO2, K+, H+, adenosine) decrease as a result of washout; local concentrations of substrates (O2) increase because supply is greater than demand. Opposite changes in metabolite and su ...
Revised Lesson Plan 1 - The Brain
... The cerebellum is the second largest region of the brain. It receives information about muscle and joint position and coordinates the actions of these muscles. The brain stem connects the brain and spinal cord. It regulates the flow of information between the brain and the rest of the body. It is co ...
... The cerebellum is the second largest region of the brain. It receives information about muscle and joint position and coordinates the actions of these muscles. The brain stem connects the brain and spinal cord. It regulates the flow of information between the brain and the rest of the body. It is co ...
CASE STUDY - Atlas Orthogonal Chiropractic
... circularly polarized head coil was used to provide threedimensional fast low angle images at the pontomedullary junction to evaluate the relationships between the upper ventrolateral medulla and the branches associated with the vertebral artery on 32 patients. The results showed that 90.6% had neuro ...
... circularly polarized head coil was used to provide threedimensional fast low angle images at the pontomedullary junction to evaluate the relationships between the upper ventrolateral medulla and the branches associated with the vertebral artery on 32 patients. The results showed that 90.6% had neuro ...
Chapter 13 - Las Positas College
... 1. The limbic system is known as the “emotional brain”; a group of structures on the medial aspect of the cerebral hemispheres and the diencephalon. 2. The reticular formation has branching axons that project to the thalamus, cerebellum, and spinal cord, which make it ideal for governing the arousal ...
... 1. The limbic system is known as the “emotional brain”; a group of structures on the medial aspect of the cerebral hemispheres and the diencephalon. 2. The reticular formation has branching axons that project to the thalamus, cerebellum, and spinal cord, which make it ideal for governing the arousal ...
Slide 1
... vasopressin (AVP) and oxytocin (OT). The vascular organ of the lamina terminalis (OVLT) is especially sensitive to hyperosmolality. Hyperosmolality also activates other neurons in the anterior hypothalamus, such as those in the subfornical organ (SFO) and median preoptic nucleus (MnPO), and magnocel ...
... vasopressin (AVP) and oxytocin (OT). The vascular organ of the lamina terminalis (OVLT) is especially sensitive to hyperosmolality. Hyperosmolality also activates other neurons in the anterior hypothalamus, such as those in the subfornical organ (SFO) and median preoptic nucleus (MnPO), and magnocel ...
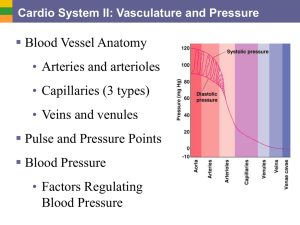
3b CardioII-Vasculature
... • Volume of blood forced into them at any time Blood pressure near the heart is pulsatile o Systolic pressure: pressure exerted during ventricular contraction o Diastolic pressure: lowest level of arterial pressure o Pulse pressure = difference between systolic and diastolic pressure ...
... • Volume of blood forced into them at any time Blood pressure near the heart is pulsatile o Systolic pressure: pressure exerted during ventricular contraction o Diastolic pressure: lowest level of arterial pressure o Pulse pressure = difference between systolic and diastolic pressure ...
The Urinary Physiology Chapter 17
... Metabolic acidosis/alkalosis includes all other situations than respiratory reasons. • Diuretics Diruretics are drugs that decrease Na+ reabsorption; increase the volume of urine passed out; decrease blood volume; decrease blood pressure. Homeostasis attains stability of total-body sodium mass and e ...
... Metabolic acidosis/alkalosis includes all other situations than respiratory reasons. • Diuretics Diruretics are drugs that decrease Na+ reabsorption; increase the volume of urine passed out; decrease blood volume; decrease blood pressure. Homeostasis attains stability of total-body sodium mass and e ...
THE PHYSIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLE OF MINIMUMI WORK. I. THE
... quantitative physiological inquiry, and, therefore, it is the most suitable subject for theoretical studies. The functions which must be performed by the oxygen transport system, if a steady state is to be maintained, are relatively clear-cut, the factors involved in the efficiency of transport are ...
... quantitative physiological inquiry, and, therefore, it is the most suitable subject for theoretical studies. The functions which must be performed by the oxygen transport system, if a steady state is to be maintained, are relatively clear-cut, the factors involved in the efficiency of transport are ...
Preview Sample 2
... production of CSF, and see the Supplemental Teaching Strategies and Tools section for demonstrations of the effects of daily CSF turnover and CSF buoyancy. Hydrocephalus is the condition resulting from a blockage of CSF flow through the central nervous system. The blockages usually occur at the narr ...
... production of CSF, and see the Supplemental Teaching Strategies and Tools section for demonstrations of the effects of daily CSF turnover and CSF buoyancy. Hydrocephalus is the condition resulting from a blockage of CSF flow through the central nervous system. The blockages usually occur at the narr ...
Periosteum - Maryville University
... • Nutrition. The CSF contains sugars and other elements that are used by central nervous system cells, specifically neurons and glial cells. • Waste disposal. The CSF removes waste products produced by the metabolism of the cells in the CNS. • Communication. The CSF also acts as a messaging medium. ...
... • Nutrition. The CSF contains sugars and other elements that are used by central nervous system cells, specifically neurons and glial cells. • Waste disposal. The CSF removes waste products produced by the metabolism of the cells in the CNS. • Communication. The CSF also acts as a messaging medium. ...
Michael Zundel, MD (MARC Presenter) Handout
... Upon standing, impaired vasoconstriction allows blood pooling in dependent extremities Venous pooling causes decreased venous return, leading to intrathoracic hypovolemia and compensatory reflex tachycardia Blood pressure usually normal but can be low Tx: Vasoconstrictors, mineralocorticoid analogs ...
... Upon standing, impaired vasoconstriction allows blood pooling in dependent extremities Venous pooling causes decreased venous return, leading to intrathoracic hypovolemia and compensatory reflex tachycardia Blood pressure usually normal but can be low Tx: Vasoconstrictors, mineralocorticoid analogs ...
Chapter 14
... Proportional firing rate to increased stretching Responding to pressures ranging from 60180 mmHg Receptors within the aortic arch are less sensitive than the carotid sinus receptors ...
... Proportional firing rate to increased stretching Responding to pressures ranging from 60180 mmHg Receptors within the aortic arch are less sensitive than the carotid sinus receptors ...
Medical Science/ Neuroscience
... appears to support, beyond several decades, our finding that somatostation controls brain A levels through modulating the activity of the major A-degrading enzyme, neprilysin. Taken together, now we propose a possible mechanism for the AD development as follows, down-regulation of somatostatin exp ...
... appears to support, beyond several decades, our finding that somatostation controls brain A levels through modulating the activity of the major A-degrading enzyme, neprilysin. Taken together, now we propose a possible mechanism for the AD development as follows, down-regulation of somatostatin exp ...
What is BLUE BRAIN - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... A very good example of utilization of blue brain is the case "short term memory". In some movies we might have noticed that a person might be having short term memories. ...
... A very good example of utilization of blue brain is the case "short term memory". In some movies we might have noticed that a person might be having short term memories. ...
Completed Notes
... Blunt force injury to brain and hemorrage and/or brain swelling Ex. Coup-Contrecoup brain injury: Blunt force blow to head causes brain to bounce within cranial cavity. Hitting hard cranial bone damages soft brain tissue and can also cause hemorrhaging and hematomas. ...
... Blunt force injury to brain and hemorrage and/or brain swelling Ex. Coup-Contrecoup brain injury: Blunt force blow to head causes brain to bounce within cranial cavity. Hitting hard cranial bone damages soft brain tissue and can also cause hemorrhaging and hematomas. ...
DOC
... Endorphins are brain chemicals released by the pituitary gland, the hypothalamus and many other neurons throughout the brain to help reduce pain and stress. Endorphins also activate your pleasure centers when you accomplish a goal, when you exercise and even when you eat chocolate! POP-UP_OCYTOCIN O ...
... Endorphins are brain chemicals released by the pituitary gland, the hypothalamus and many other neurons throughout the brain to help reduce pain and stress. Endorphins also activate your pleasure centers when you accomplish a goal, when you exercise and even when you eat chocolate! POP-UP_OCYTOCIN O ...
Flight Physiology
... Hemoglobin, which function as specialized oxygen transport system that allows far more oxygen to be carried by blood • At high altitude, we need to increase rate and depth of breathing in order to get enough oxygen into our lung. ...
... Hemoglobin, which function as specialized oxygen transport system that allows far more oxygen to be carried by blood • At high altitude, we need to increase rate and depth of breathing in order to get enough oxygen into our lung. ...
Intracranial pressure

Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF. CSF pressure has been shown to be influenced by abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure during coughing (intraabdominal pressure), valsalva maneuver, and communication with the vasculature (venous and arterial systems). ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and, at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. Changes in ICP are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained in the cranium. Intracranial hypertension, commonly abbreviated IH, IICP or raised ICP, is elevation of the pressure in the cranium. ICP is normally 7–15 mm Hg; at 20–25 mm Hg, the upper limit of normal, treatment to reduce ICP may be needed.