Week 1 Notes History of the Brain
... Are our mind and body two separate entities, or are they parts of the one whole? Ancient Greek philosophers debated this problem for many years, with most agreeing that the mind and body were separate. The mind could control the body, but the body could not influence the mind. René Descartes (1596-1 ...
... Are our mind and body two separate entities, or are they parts of the one whole? Ancient Greek philosophers debated this problem for many years, with most agreeing that the mind and body were separate. The mind could control the body, but the body could not influence the mind. René Descartes (1596-1 ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Between Diencephalon & Spinal Cord Three parts: - Midbrain * Colliculi – visual & auditory nuclei - Pons – Below midbrain; joins cerebellum to brainstem - Medulla Oblongata – Below Pons, Regulates heartbeat & breathing; has role in consciousness; joins brain & spinal cord ...
... Between Diencephalon & Spinal Cord Three parts: - Midbrain * Colliculi – visual & auditory nuclei - Pons – Below midbrain; joins cerebellum to brainstem - Medulla Oblongata – Below Pons, Regulates heartbeat & breathing; has role in consciousness; joins brain & spinal cord ...
This Week at Elida - Elida Local Schools
... In addition, greater inter connectedness among various regions of the brain allows for better communication between parts associated with different functions. For example, connections between regions of the brain responsible for logical reasoning become better connected with those responsible for ex ...
... In addition, greater inter connectedness among various regions of the brain allows for better communication between parts associated with different functions. For example, connections between regions of the brain responsible for logical reasoning become better connected with those responsible for ex ...
8 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
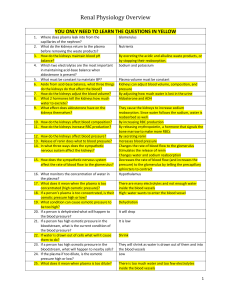
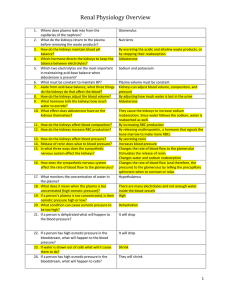
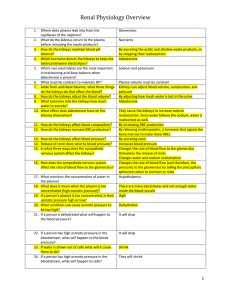
... 19. What condition can cause osmotic pressure to be too high? 20. If a person is dehydrated what will happen to the blood pressure? 21. If a person has high osmotic pressure in the bloodstream, what is the current condition of the blood pressure? 22. If water is drawn out of cells what will it cause ...
... 19. What condition can cause osmotic pressure to be too high? 20. If a person is dehydrated what will happen to the blood pressure? 21. If a person has high osmotic pressure in the bloodstream, what is the current condition of the blood pressure? 22. If water is drawn out of cells what will it cause ...
Nervous System Educator`s Guide
... Nerve fibers: The slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell Nerve impulse: A wave of physical and chemical excitation along a nerve fiber in response to a stimulus, accompanied by a transient change in electric potential in the membr ...
... Nerve fibers: The slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell Nerve impulse: A wave of physical and chemical excitation along a nerve fiber in response to a stimulus, accompanied by a transient change in electric potential in the membr ...
Circulatory system I: Blood Circulatory system I: Blood
... – Lub = closing of AV valves during isovolumetric contraction – Dub = closing of SLV ...
... – Lub = closing of AV valves during isovolumetric contraction – Dub = closing of SLV ...
Articles about the Brain Works
... swinging the arms. This means that the movement is smooth and controlled and you don't fall over when you turn around. The outside layer of the cerebrum has special areas, which receive messages about sight, touch, hearing and taste. Other areas control movement, speech, learning, intelligence and p ...
... swinging the arms. This means that the movement is smooth and controlled and you don't fall over when you turn around. The outside layer of the cerebrum has special areas, which receive messages about sight, touch, hearing and taste. Other areas control movement, speech, learning, intelligence and p ...
2. Physiology_Respiratory_System
... ♦ Increased venous pressure (heart failure, incompetent valves, venous obstruction, increased total ECF volume, effect of gravity, etc.,) Decreased osmotic pressure gradient across capillary ♦ Decreased plasma protein level ♦ Accumulation of osmotically active substances in interstitial space ...
... ♦ Increased venous pressure (heart failure, incompetent valves, venous obstruction, increased total ECF volume, effect of gravity, etc.,) Decreased osmotic pressure gradient across capillary ♦ Decreased plasma protein level ♦ Accumulation of osmotically active substances in interstitial space ...
lecture CNS
... comprised of an outer endosteal layer and and inner meningeal layer – large spaces for the circulation of blood can be found between these two layers = sinuses e.g. superior sagittal sinus 2. middle arachnoid mater – the dura mater forms sheets 3. inner, thin pia mater (falx cerebri) that separate t ...
... comprised of an outer endosteal layer and and inner meningeal layer – large spaces for the circulation of blood can be found between these two layers = sinuses e.g. superior sagittal sinus 2. middle arachnoid mater – the dura mater forms sheets 3. inner, thin pia mater (falx cerebri) that separate t ...
EEG - Wayne State University
... c. Subarachnoid: base of brain, due to rupture Berry aneurysm, arterial vasospasm, thunderclap HA ii. Causes 1. Hypertensive vascular disease (most common) Berry aneurysm (which can also be congenital!) 2. Amyloid angiopathy (think elderly w/ Alz) weakening of vessel walls that predisposes to he ...
... c. Subarachnoid: base of brain, due to rupture Berry aneurysm, arterial vasospasm, thunderclap HA ii. Causes 1. Hypertensive vascular disease (most common) Berry aneurysm (which can also be congenital!) 2. Amyloid angiopathy (think elderly w/ Alz) weakening of vessel walls that predisposes to he ...
16 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... ADH will only raise the water levels in the bloodstream (needed during dehydration from not drinking enough water). Aldosterone will raise the water and salt levels in the bloodstream (needed if there is excessive sweating, which causes loss of water and salt) Both may be released if blood pressure ...
... ADH will only raise the water levels in the bloodstream (needed during dehydration from not drinking enough water). Aldosterone will raise the water and salt levels in the bloodstream (needed if there is excessive sweating, which causes loss of water and salt) Both may be released if blood pressure ...
RESPIRATION
... Both these bodies receive their own special blood supply through minute arteries, directly from the trunk. Their blood flow is roughly 20 times their own weight. They are all the time exposed only to arterial blood. PO2 stimulates these chemoreceptors strongly. ...
... Both these bodies receive their own special blood supply through minute arteries, directly from the trunk. Their blood flow is roughly 20 times their own weight. They are all the time exposed only to arterial blood. PO2 stimulates these chemoreceptors strongly. ...
13a Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... 35. What affect does ADH have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood pressure? 36. When osmotic pressure is too high, what other endocrine gland secretes a hormone, and what is the name of the hormone? 37. What affect does aldosterone have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood press ...
... 35. What affect does ADH have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood pressure? 36. When osmotic pressure is too high, what other endocrine gland secretes a hormone, and what is the name of the hormone? 37. What affect does aldosterone have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood press ...
The Central Nervous System
... • Bathes skull, brain and spinal cord • Serves as a shock absorber for the brain and spinal cord • Provides nutrients and waste removal for brain tissue • 400-500 mL produced daily, only 140 mL is circulating at any time • Circulates through the ventricles and into the central canal and subarachnoid ...
... • Bathes skull, brain and spinal cord • Serves as a shock absorber for the brain and spinal cord • Provides nutrients and waste removal for brain tissue • 400-500 mL produced daily, only 140 mL is circulating at any time • Circulates through the ventricles and into the central canal and subarachnoid ...
ppt
... = end diastolic volume (EDV) minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
... = end diastolic volume (EDV) minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
slide_6
... = end diastolic volume (EDV) minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
... = end diastolic volume (EDV) minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
2 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... = end diastolic volume (EDV) minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
... = end diastolic volume (EDV) minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
Cardiovascular Reflex Stimulation of ADH Release by Decreased
... There are still other pathways controlling thirst. For example, dryness of the mouth and throat causes profound thirst, which is relieved by merely moistening them. The analog of thirst for sodium, salt appetite, is an important part of sodium homeostasis in most mammals. Salt appetite consists of t ...
... There are still other pathways controlling thirst. For example, dryness of the mouth and throat causes profound thirst, which is relieved by merely moistening them. The analog of thirst for sodium, salt appetite, is an important part of sodium homeostasis in most mammals. Salt appetite consists of t ...
Relation of the Lungs to the Thoracic (Chest) Wall
... its elastic recoil) “try” to move ever so slightly away from each other, there occurs an infinitesimal enlargement of the fluid-filled intrapleural space between them. But fluid cannot expand the way air can, and so even this tiny enlargement of the intrapleural space—so small that the pleural surfa ...
... its elastic recoil) “try” to move ever so slightly away from each other, there occurs an infinitesimal enlargement of the fluid-filled intrapleural space between them. But fluid cannot expand the way air can, and so even this tiny enlargement of the intrapleural space—so small that the pleural surfa ...
Respiratory Physiology - e-safe
... • As it falls the distribution of ventilation within the lungs changes leading to mismatching with pulmonary blood flow. • If it falls below a certain volume (the closing capacity), airway closure occurs leading to shunt. Resistance and compliance In the absence of respiratory effort, the lung ...
... • As it falls the distribution of ventilation within the lungs changes leading to mismatching with pulmonary blood flow. • If it falls below a certain volume (the closing capacity), airway closure occurs leading to shunt. Resistance and compliance In the absence of respiratory effort, the lung ...
Physiology – spinal anesthesia MGMC
... higher than motor ( may be 6 also ?) Sensory level of T3 – complete sympathetic block ...
... higher than motor ( may be 6 also ?) Sensory level of T3 – complete sympathetic block ...
HBTRC Tour - Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center
... The brain is composed of neurons that generate electrical activity that is transmitted from one neuron to another. These so-called neural circuits give rise to what we perceive as behavior affecting virtually every aspect of our daily activities, including those involving thought, movement and emoti ...
... The brain is composed of neurons that generate electrical activity that is transmitted from one neuron to another. These so-called neural circuits give rise to what we perceive as behavior affecting virtually every aspect of our daily activities, including those involving thought, movement and emoti ...
The anatomy and physiology of personality The brain
... Parts of brain are “lesioned” or damaged by being cut off from other brain structures or completely removed Most of the this research has been done with animals ...
... Parts of brain are “lesioned” or damaged by being cut off from other brain structures or completely removed Most of the this research has been done with animals ...
Mouth Esophagus Stomach Pyloric Valve Small Intestine
... Decreased response time Get more infections Increased risk for STD’s/HIV ...
... Decreased response time Get more infections Increased risk for STD’s/HIV ...
Intracranial pressure

Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF. CSF pressure has been shown to be influenced by abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure during coughing (intraabdominal pressure), valsalva maneuver, and communication with the vasculature (venous and arterial systems). ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and, at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. Changes in ICP are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained in the cranium. Intracranial hypertension, commonly abbreviated IH, IICP or raised ICP, is elevation of the pressure in the cranium. ICP is normally 7–15 mm Hg; at 20–25 mm Hg, the upper limit of normal, treatment to reduce ICP may be needed.