AGING PRESENTATION
... technology, Terry et al. found out that there is not much age related neural loss in cortex. The small decrease has been explained as the cortical thinning or as the structural changes in neurons as they lose their dendritic trees and spines with age. ...
... technology, Terry et al. found out that there is not much age related neural loss in cortex. The small decrease has been explained as the cortical thinning or as the structural changes in neurons as they lose their dendritic trees and spines with age. ...
chapter 19 the vessel lecture notes
... • Vasoconstriction is due to sympathetic stimulation and endothelins Myogenic Controls • Myogenic responses of vascular smooth muscle keep tissue perfusion constant despite most fluctuations in systemic pressure • Passive stretch (increased intravascular pressure) promotes increased tone and vasocon ...
... • Vasoconstriction is due to sympathetic stimulation and endothelins Myogenic Controls • Myogenic responses of vascular smooth muscle keep tissue perfusion constant despite most fluctuations in systemic pressure • Passive stretch (increased intravascular pressure) promotes increased tone and vasocon ...
AACBIS - Brain Injury Alliance of Oregon
... Post concussion symptoms of cognitive and psychiatric nature that may or may not persist include: headache dizziness vomiting sleep disturbance irritability ...
... Post concussion symptoms of cognitive and psychiatric nature that may or may not persist include: headache dizziness vomiting sleep disturbance irritability ...
Hormonal Control
... when blood sugar levels are too high. Glucagon promotes the conversion of glycogen into glucose and adds glucose to the blood; it is produced when blood sugar levels are too low. Each of these hormones has a negative feedback mechanism; a return of blood glucose levels to normal causes the productio ...
... when blood sugar levels are too high. Glucagon promotes the conversion of glycogen into glucose and adds glucose to the blood; it is produced when blood sugar levels are too low. Each of these hormones has a negative feedback mechanism; a return of blood glucose levels to normal causes the productio ...
Blood Pressure and Pulse BIOL 204, Section 550 Lab Report By
... al, 2012). By looking at cardiac output (CO), “the product of the heart rate and stroke volume”, one can further understand the differences in arterial pressure and pulse for the experiments (Marieb & Hoehn, 2010). First, it is important to note that both heart rate and stroke volume are directly re ...
... al, 2012). By looking at cardiac output (CO), “the product of the heart rate and stroke volume”, one can further understand the differences in arterial pressure and pulse for the experiments (Marieb & Hoehn, 2010). First, it is important to note that both heart rate and stroke volume are directly re ...
Cardiac Qs
... Sympathetic nerves act as part of the reaction to the ‘fight, fright or flight’ scenario. The nerves are distributed not only to the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes but also to the cardiac muscle of both ventricles and atria. The effects of sympathetic innervation can be broken down into incre ...
... Sympathetic nerves act as part of the reaction to the ‘fight, fright or flight’ scenario. The nerves are distributed not only to the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes but also to the cardiac muscle of both ventricles and atria. The effects of sympathetic innervation can be broken down into incre ...
Participation of γ-Aminobutyric Acid Mechanism in the Nucleus
... In recent years, electroacupuncture (EA) has gained recognition as a safe and effective technique for treating several cardiovascular complications, and studies have validated its ability in manipulating blood pressure and heart rate. EA application at P5-6 acupoints stimulates the median nerves and ...
... In recent years, electroacupuncture (EA) has gained recognition as a safe and effective technique for treating several cardiovascular complications, and studies have validated its ability in manipulating blood pressure and heart rate. EA application at P5-6 acupoints stimulates the median nerves and ...
Document
... • anterior and posterior lobes – has a superficial layer of gray matter called the cerebellar cortex - like the brain – deep to this gray matter are tracts of white matter and gray matter nuclei – like the cerebrum – evaluates and coordinates involuntary and voluntary motor activities initiated by t ...
... • anterior and posterior lobes – has a superficial layer of gray matter called the cerebellar cortex - like the brain – deep to this gray matter are tracts of white matter and gray matter nuclei – like the cerebrum – evaluates and coordinates involuntary and voluntary motor activities initiated by t ...
Lecture
... • anterior and posterior lobes – has a superficial layer of gray matter called the cerebellar cortex - like the brain – deep to this gray matter are tracts of white matter and gray matter nuclei – like the cerebrum – evaluates and coordinates involuntary and voluntary motor activities initiated by t ...
... • anterior and posterior lobes – has a superficial layer of gray matter called the cerebellar cortex - like the brain – deep to this gray matter are tracts of white matter and gray matter nuclei – like the cerebrum – evaluates and coordinates involuntary and voluntary motor activities initiated by t ...
Renal Blood Flow and Glomerular Filtration Rate
... during volume depletion, hydrostatic pressure along the renal vasculature is decreased, leading to an initial decrease in renal blood flow and GFR (secondary to reduction of glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure). The reduced pressure decreases the stretch of the afferent arteriole, causing the ...
... during volume depletion, hydrostatic pressure along the renal vasculature is decreased, leading to an initial decrease in renal blood flow and GFR (secondary to reduction of glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure). The reduced pressure decreases the stretch of the afferent arteriole, causing the ...
Cardiovascular Physiology
... Endothelial cells move it to the interstitial space between the two layers of the artery Macrophages consume it and become lipid filled foam cells – In response they release cytokines which causes smooth muscle growth in the area & forms a lesion on the arterial wall ...
... Endothelial cells move it to the interstitial space between the two layers of the artery Macrophages consume it and become lipid filled foam cells – In response they release cytokines which causes smooth muscle growth in the area & forms a lesion on the arterial wall ...
Nervous System and Mental Health
... – Unresponsive; arouses only briefly despite repeated attempts ...
... – Unresponsive; arouses only briefly despite repeated attempts ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Diencephalon: Thalamus “Relay station” for all sensory impulses to cerebral cortex Consists of 2 lobes (may be joined by “Intermediate Mass” (a bridge of gray matter) Third ventricle is superior & medial to thalamus ...
... Diencephalon: Thalamus “Relay station” for all sensory impulses to cerebral cortex Consists of 2 lobes (may be joined by “Intermediate Mass” (a bridge of gray matter) Third ventricle is superior & medial to thalamus ...
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions
... less ADH is released in response to changes in blood pressure or blood volume than to a change in plasma osmolarity.) ADH causes vasoconstriction in the systemic circulation, raising peripheral resistance and thus raising blood pressure. ADH also acts on the kidney to increase water retention. Retai ...
... less ADH is released in response to changes in blood pressure or blood volume than to a change in plasma osmolarity.) ADH causes vasoconstriction in the systemic circulation, raising peripheral resistance and thus raising blood pressure. ADH also acts on the kidney to increase water retention. Retai ...
Physiology of Circulation
... pressure at which sounds first occur corresponds to the pressure when the artery is just barely able to open for a moment , which equals to systolic pressure (the 1st korotkoff sound). Continue releasing pressure until the sound muffle ; this equals to diastolic pressure (the 2nd korotkoff sound). T ...
... pressure at which sounds first occur corresponds to the pressure when the artery is just barely able to open for a moment , which equals to systolic pressure (the 1st korotkoff sound). Continue releasing pressure until the sound muffle ; this equals to diastolic pressure (the 2nd korotkoff sound). T ...
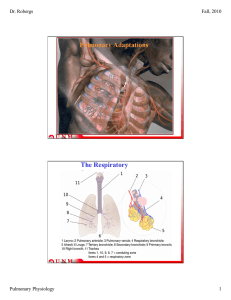
CHAPTER 2 - PULMONARY FUNCTION, TRANSPORT OF BLOOD
... b) During the hockey match, the player must increase the volume of gas exchanged in the lungs and muscles. Explain the ...
... b) During the hockey match, the player must increase the volume of gas exchanged in the lungs and muscles. Explain the ...
Chapter Questions Answer Key - Brain Injury Alliance of Oregon
... False. The rehab process often involves complex techniques, procedures or approaches by a diverse group of people. ...
... False. The rehab process often involves complex techniques, procedures or approaches by a diverse group of people. ...
The Central Nervous System
... – Subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhage—may force brain stem through foramen magnum, resulting in death ...
... – Subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhage—may force brain stem through foramen magnum, resulting in death ...
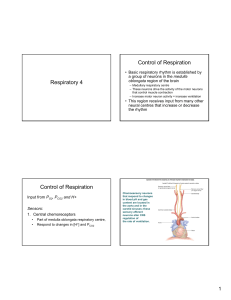
Respiratory 4 Control of Respiration Control of Respiration
... water? How does the kidney handle sodium and water? 1. How does the system respond to: 1. Increased (decreased) water volume? 2. Increased (decreased) sodium concentration ...
... water? How does the kidney handle sodium and water? 1. How does the system respond to: 1. Increased (decreased) water volume? 2. Increased (decreased) sodium concentration ...
18 The Heart new
... – 80% of ventricular filling is passive – Atrial contraction occurs at the end of diastole • Atrial kick moves the remaining 20% of blood in atria into ventricles ...
... – 80% of ventricular filling is passive – Atrial contraction occurs at the end of diastole • Atrial kick moves the remaining 20% of blood in atria into ventricles ...
v = F/A - VCOMcc
... The outermost concentric layer of flowing blood is in contact with the wall and thus has a flow velocity of 0 Moving inward, each successive layer flows more rapidly – Moving inward within the blood vessel, the area of contact between each successive layer decreases thus increasing the flow velocity ...
... The outermost concentric layer of flowing blood is in contact with the wall and thus has a flow velocity of 0 Moving inward, each successive layer flows more rapidly – Moving inward within the blood vessel, the area of contact between each successive layer decreases thus increasing the flow velocity ...
Lecture 16: The Nephron
... 5. Based on your results, which treatment do you think elicited the greatest ADH production? The least production? Explain. 6. What was the relationship between specific gravity of a urine sample and the rate at which urine was excreted? 7. For each of the five treatments, what is the relationshi ...
... 5. Based on your results, which treatment do you think elicited the greatest ADH production? The least production? Explain. 6. What was the relationship between specific gravity of a urine sample and the rate at which urine was excreted? 7. For each of the five treatments, what is the relationshi ...
Cerebellum
... • Capillary BP is reduced because of the total crosssectional area. • 3 most important variables are HR, SV, and TPR. • Increase in each of these will result in an increase in BP. ...
... • Capillary BP is reduced because of the total crosssectional area. • 3 most important variables are HR, SV, and TPR. • Increase in each of these will result in an increase in BP. ...
neural and chemical regulation of respiration
... They respond when PO2 decreases to less than 60mmHg DECREASE IN ARTERIAL PO2 If arterial PO2 is b/w 100 and 60mmhg, the breathing rate is relatively constant. However, if arterial po2 is less than 60mmhg, the breathing rate increases in a very steep and linear fashion. In this range of po2 pc are ve ...
... They respond when PO2 decreases to less than 60mmHg DECREASE IN ARTERIAL PO2 If arterial PO2 is b/w 100 and 60mmhg, the breathing rate is relatively constant. However, if arterial po2 is less than 60mmhg, the breathing rate increases in a very steep and linear fashion. In this range of po2 pc are ve ...
Intracranial pressure

Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF. CSF pressure has been shown to be influenced by abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure during coughing (intraabdominal pressure), valsalva maneuver, and communication with the vasculature (venous and arterial systems). ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and, at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. Changes in ICP are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained in the cranium. Intracranial hypertension, commonly abbreviated IH, IICP or raised ICP, is elevation of the pressure in the cranium. ICP is normally 7–15 mm Hg; at 20–25 mm Hg, the upper limit of normal, treatment to reduce ICP may be needed.