Christopher Warner Title: Element Project Educational Filters: The
... particle found in atoms. Walter Bothe and James Chadwick, who repeated Bothe’s work, found high energy particles with no charge and a similar mass as the proton. This particle is now known as neutrons (Smoot, 1987). J.J. Thomson also noticed two kinds of neon atoms that were exactly alike chemically ...
... particle found in atoms. Walter Bothe and James Chadwick, who repeated Bothe’s work, found high energy particles with no charge and a similar mass as the proton. This particle is now known as neutrons (Smoot, 1987). J.J. Thomson also noticed two kinds of neon atoms that were exactly alike chemically ...
Chemistry Basics Review
... 2.The atomic number tells you the number of ______________________in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of _____________________in a neutral atom of that element. The atomic number gives the “identity “ of an element as well as its location on the Periodic Table. No two different e ...
... 2.The atomic number tells you the number of ______________________in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of _____________________in a neutral atom of that element. The atomic number gives the “identity “ of an element as well as its location on the Periodic Table. No two different e ...
nuclear test 2006
... Which one of the following best describes the relative speeds at which alpha, beta, and gamma particles travel after being emitted from radioisotopes? A Alpha is the slowest, beta and then gamma ...
... Which one of the following best describes the relative speeds at which alpha, beta, and gamma particles travel after being emitted from radioisotopes? A Alpha is the slowest, beta and then gamma ...
6.2 - Hockerill Students
... If you plot the neutron number N against the proton number Z for all the known nuclides, you get the diagram shown here Can you see that the stable nuclides of the lighter elements have approximately equal numbers of protons and neutrons? However, as Z increases the `stability line' curves upwards. ...
... If you plot the neutron number N against the proton number Z for all the known nuclides, you get the diagram shown here Can you see that the stable nuclides of the lighter elements have approximately equal numbers of protons and neutrons? However, as Z increases the `stability line' curves upwards. ...
Chapter 5
... accelerates spectrogram spectrogram, theions different positive ions. positive is recorded. isotopes occurs and their relative at amounts can be determined. magnetic field. ...
... accelerates spectrogram spectrogram, theions different positive ions. positive is recorded. isotopes occurs and their relative at amounts can be determined. magnetic field. ...
II. Masses of Atoms
... • WHEN TWO PROTONS ARE EXTREMELY CLOSE TO EACH OTHER, THERE IS A STRONG ATTRACTION BETWEEN THEM. • A SIMILAR ATTRACTION EXISTS WHEN NEUTRONS ARE VERY CLOSE TO EACH OTHER OR WHEN PROTONS AND NEUTRONS ARE VERY CLOSE TOGETHER. • THE SHORT-RANGE PROTON-NEUTRON, PROTON-PROTON, AND NEUTRON-NEUTRON FORCES ...
... • WHEN TWO PROTONS ARE EXTREMELY CLOSE TO EACH OTHER, THERE IS A STRONG ATTRACTION BETWEEN THEM. • A SIMILAR ATTRACTION EXISTS WHEN NEUTRONS ARE VERY CLOSE TO EACH OTHER OR WHEN PROTONS AND NEUTRONS ARE VERY CLOSE TOGETHER. • THE SHORT-RANGE PROTON-NEUTRON, PROTON-PROTON, AND NEUTRON-NEUTRON FORCES ...
File - CToThe3Chemistry
... 1. What is the atomic number? Where do you find the atomic number on your periodic table? The atomic number is the identifier for different elements’ atoms. It is found above the symbol for the element. 2. What is the relationship between the atomic number and the number of protons? The atomic numbe ...
... 1. What is the atomic number? Where do you find the atomic number on your periodic table? The atomic number is the identifier for different elements’ atoms. It is found above the symbol for the element. 2. What is the relationship between the atomic number and the number of protons? The atomic numbe ...
View PDF - Bridge City ISD
... word that means The first person who suggested that matter was made up of atoms was the Greek philosopher ____________ John Dalton’s atomic theory stated that atoms of the same ______ are exactly alike Most atoms have equal numbers of _____and ______ ...
... word that means The first person who suggested that matter was made up of atoms was the Greek philosopher ____________ John Dalton’s atomic theory stated that atoms of the same ______ are exactly alike Most atoms have equal numbers of _____and ______ ...
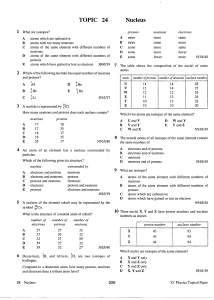
TOPIC 24 Nucleus - jmr physics website
... Compared to a deuterium atom, how many protons, neutrons and electrons does a tritium atom have? ...
... Compared to a deuterium atom, how many protons, neutrons and electrons does a tritium atom have? ...
In an atom
... Protons and neutrons are in the tiny positively charged nucleus accounting for most of the mass of the atom The negatively charged electrons are small and have a relatively small mass but occupy a large volume of space outside the nucleus ...
... Protons and neutrons are in the tiny positively charged nucleus accounting for most of the mass of the atom The negatively charged electrons are small and have a relatively small mass but occupy a large volume of space outside the nucleus ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _D__ 44) Which of the following is true about subatomic particles? a. Electrons have no charge and have almost no mass. b. Protons are negatively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. c. Neutrons have a negative charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. d. Electrons have almost no mass ...
... _D__ 44) Which of the following is true about subatomic particles? a. Electrons have no charge and have almost no mass. b. Protons are negatively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. c. Neutrons have a negative charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. d. Electrons have almost no mass ...
Electron - cloudfront.net
... have different numbers of electrons. • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of electrons are called ions. • When the number of protons and electrons is different, the atom becomes charged. ...
... have different numbers of electrons. • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of electrons are called ions. • When the number of protons and electrons is different, the atom becomes charged. ...
Chapter 4 Practice Test
... d. Cathode rays were found to be made of protons. All atoms are ____. a. positively charged, with the number of protons exceeding the number of electrons b. negatively charged, with the number of electrons exceeding the number of protons c. neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of ...
... d. Cathode rays were found to be made of protons. All atoms are ____. a. positively charged, with the number of protons exceeding the number of electrons b. negatively charged, with the number of electrons exceeding the number of protons c. neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of ...
Ch 6.7 - Explaining the Atom
... Evidence of Learning: Students can … - describe and relate atomic number, atomic mass, and mass number. - find the number of neutrons in an atom from its atomic number and atomic ...
... Evidence of Learning: Students can … - describe and relate atomic number, atomic mass, and mass number. - find the number of neutrons in an atom from its atomic number and atomic ...
Chapter 5
... A single atom is tiny (diameter of 0.1 to 0.5 nm). Because atoms are so small, determining the presence of subatomic particles was very difficult. New instruments in the early 1900s permitted detection of these particles. ...
... A single atom is tiny (diameter of 0.1 to 0.5 nm). Because atoms are so small, determining the presence of subatomic particles was very difficult. New instruments in the early 1900s permitted detection of these particles. ...
10/2/2013 1 5 Early Atomic Theory and Structure Chapter Outline
... positively charged nucleus to affect the path of an α particle (a positively charged He atom). © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... positively charged nucleus to affect the path of an α particle (a positively charged He atom). © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
atom - RCSD
... He placed charged metal plates on each side of the beam; beam deflected away from the negative plate Thompson found this occurred with any gas in the tube He deduced that atoms contained negative particles – we know them as electrons. Came up with the “Plum pudding” model of atom ...
... He placed charged metal plates on each side of the beam; beam deflected away from the negative plate Thompson found this occurred with any gas in the tube He deduced that atoms contained negative particles – we know them as electrons. Came up with the “Plum pudding” model of atom ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.