Physical Properties
... Dobereiner’s research made chemists look at groups of elements with similar chemical and physical properties. ...
... Dobereiner’s research made chemists look at groups of elements with similar chemical and physical properties. ...
Chapter 2: Atoms Molecules and Ions
... reactant molecules into a mass ratio for a chemical reaction to be useful. 2) Mass ratios are determined by using atomic masses for the elements. i) Atomic masses (atomic weights) are found in periodic table beneath the chemical symbol, and represent the average of all the naturally occurring isotop ...
... reactant molecules into a mass ratio for a chemical reaction to be useful. 2) Mass ratios are determined by using atomic masses for the elements. i) Atomic masses (atomic weights) are found in periodic table beneath the chemical symbol, and represent the average of all the naturally occurring isotop ...
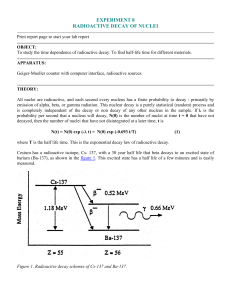
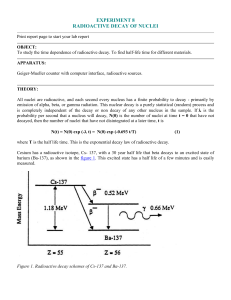
experiment 8 radioactive decay of nuclei
... Indium metal (49In, atomic number of 49) as found on the surface of the earth is 95.72 % mass 115 and 4.28% mass 113. (Using the nuclear masses of 114.9041 and 112.9043 instead of the number of nucleons, 115 and 113, the chemical weight of 114.82 can be calculated.) If the indium is placed where th ...
... Indium metal (49In, atomic number of 49) as found on the surface of the earth is 95.72 % mass 115 and 4.28% mass 113. (Using the nuclear masses of 114.9041 and 112.9043 instead of the number of nucleons, 115 and 113, the chemical weight of 114.82 can be calculated.) If the indium is placed where th ...
Phys 282 EXP 8
... Indium metal (49In, atomic number of 49) as found on the surface of the earth is 95.72 % mass 115 and 4.28% mass 113. (Using the nuclear masses of 114.9041 and 112.9043 instead of the number of nucleons, 115 and 113, the chemical weight of 114.82 can be calculated.) If the indium is placed where th ...
... Indium metal (49In, atomic number of 49) as found on the surface of the earth is 95.72 % mass 115 and 4.28% mass 113. (Using the nuclear masses of 114.9041 and 112.9043 instead of the number of nucleons, 115 and 113, the chemical weight of 114.82 can be calculated.) If the indium is placed where th ...
Atom - U of L Class Index
... discovered canal rays in 1886using a “reverse cathode ray” tube Those that pass through the hole (“canal”) can be analyzed for charge-mass ratio, which are much smaller than electron, but largest for hydrogen ...
... discovered canal rays in 1886using a “reverse cathode ray” tube Those that pass through the hole (“canal”) can be analyzed for charge-mass ratio, which are much smaller than electron, but largest for hydrogen ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
... to answer these questions, Rutherford proposed that there was another particle in the nucleus – it is called a neutron neutrons have no charge and a mass of 1 amu ◦ mass = 1.67493 x 10-24 g slightly heavier than a proton ...
... to answer these questions, Rutherford proposed that there was another particle in the nucleus – it is called a neutron neutrons have no charge and a mass of 1 amu ◦ mass = 1.67493 x 10-24 g slightly heavier than a proton ...
Atomic Structure - Renton School District
... 0 If the relative mass of a protons and neutrons is 1, why is the atomic mass = 12.01? 0 Different kinds of carbon exist! 0 Average atomic mass is the average of all types of carbon ...
... 0 If the relative mass of a protons and neutrons is 1, why is the atomic mass = 12.01? 0 Different kinds of carbon exist! 0 Average atomic mass is the average of all types of carbon ...
Physics, Chapter 44: Stable Nuclei
... esses. Here the molecular weight of large organic molecules is an important factor in the suitability of a fuel for a particular use, and this may be determined most easily with a mass spectrometer. ...
... esses. Here the molecular weight of large organic molecules is an important factor in the suitability of a fuel for a particular use, and this may be determined most easily with a mass spectrometer. ...
Lecture Notes Chapter 4-The Structure of the Atom
... Formed with an unblanced between p+ and eCharged form of an atom brought about by the gain of e- (-) or loss of e- (+) Ions are formed: 1. response to another atom 2. metals form (+) ions 3. non-metal form (-) ions 4. unlike charges attract; like charges repel. ...
... Formed with an unblanced between p+ and eCharged form of an atom brought about by the gain of e- (-) or loss of e- (+) Ions are formed: 1. response to another atom 2. metals form (+) ions 3. non-metal form (-) ions 4. unlike charges attract; like charges repel. ...
Name
... Essential Standard 9f: Apply simple mathematical relationships to determine one quantity given the other two (including speed= distance x time, density = mass/volume, force = pressure x area, volume = area x height). ...
... Essential Standard 9f: Apply simple mathematical relationships to determine one quantity given the other two (including speed= distance x time, density = mass/volume, force = pressure x area, volume = area x height). ...
atomic number
... The Atomic Number = # of protons in the nucleus. The Atomic Mass = # of Protons + Neutrons The number of Protons = Number of Electrons. Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels or electron shells. ...
... The Atomic Number = # of protons in the nucleus. The Atomic Mass = # of Protons + Neutrons The number of Protons = Number of Electrons. Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels or electron shells. ...
File
... meaning indivisible: the Greek philosopher Demokritos (460370 BCE) maintained that all matter could be divided and sub-divided into smaller and smaller units, and eventually there would be a tiny particle that could not be divided any further - an atom Understanding of atoms didn’t progress much b ...
... meaning indivisible: the Greek philosopher Demokritos (460370 BCE) maintained that all matter could be divided and sub-divided into smaller and smaller units, and eventually there would be a tiny particle that could not be divided any further - an atom Understanding of atoms didn’t progress much b ...
Education TI - Texas Instruments
... nucleus comprised of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons. In this model, electrons orbit the nucleus in circular paths at different distances called electron shells. This model became popular because it fit the experimental results for Hydrogen. Later, the application of the model to heavie ...
... nucleus comprised of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons. In this model, electrons orbit the nucleus in circular paths at different distances called electron shells. This model became popular because it fit the experimental results for Hydrogen. Later, the application of the model to heavie ...
Summary of lesson
... nucleus comprised of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons. In this model, electrons orbit the nucleus in circular paths at different distances called electron shells. This model became popular because it fit the experimental results for Hydrogen. Later, the application of the model to heavie ...
... nucleus comprised of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons. In this model, electrons orbit the nucleus in circular paths at different distances called electron shells. This model became popular because it fit the experimental results for Hydrogen. Later, the application of the model to heavie ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY
... **A Brief Note on the Antineutrino: As beta decay was studied over the years following 1899, it was found that the same exact beta decay produced an electron with variable energies. For example, let us study Li-8 becoming Be-8. Each atom of Li-8 produces an electron and the theory says all the elect ...
... **A Brief Note on the Antineutrino: As beta decay was studied over the years following 1899, it was found that the same exact beta decay produced an electron with variable energies. For example, let us study Li-8 becoming Be-8. Each atom of Li-8 produces an electron and the theory says all the elect ...
Chemistry I Accelerated StudyGuideline
... small, indivisible particles, each of which was called a(n) _____________. The theory that such particles existed was supported much later, by _____________ who proposed, in his law of _______________ _____ __________, that matter could not be created or destroyed. Then ___________ proposed, in his ...
... small, indivisible particles, each of which was called a(n) _____________. The theory that such particles existed was supported much later, by _____________ who proposed, in his law of _______________ _____ __________, that matter could not be created or destroyed. Then ___________ proposed, in his ...
Chapter39
... break up (fission). For lighter nuclei, energy is released when they fuse together (fusion). ...
... break up (fission). For lighter nuclei, energy is released when they fuse together (fusion). ...
Notes: Nuclear Chemistry
... a. These reactions are not affected by change in temperature or pressure. a. In these reactions atoms of one element are usually converted into atoms of different elements. a. In nuclear reactions matter and energy are inter-converted (E = mc2). a. One gram of matter produces 9.00 x1010 kJ of energy ...
... a. These reactions are not affected by change in temperature or pressure. a. In these reactions atoms of one element are usually converted into atoms of different elements. a. In nuclear reactions matter and energy are inter-converted (E = mc2). a. One gram of matter produces 9.00 x1010 kJ of energy ...
Atomic mass - Cloudfront.net
... So, atoms of different elements are different. Every carbon atom is identical to every other carbon atom. ...
... So, atoms of different elements are different. Every carbon atom is identical to every other carbon atom. ...
Atomic Structure - Miami East Local Schools
... 1. Matter is composed of tiny indivisible atoms 2. All atoms of a given element are exactly the same 3. Different elements are made of different atoms 4. Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds 5. Chemical reactions involve separating, combining, or re ...
... 1. Matter is composed of tiny indivisible atoms 2. All atoms of a given element are exactly the same 3. Different elements are made of different atoms 4. Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds 5. Chemical reactions involve separating, combining, or re ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.