atomic mass - Cloudfront.net
... • Atoms are distinguished from each other by their number of protons • This determines the different types of elements. • Atoms are mainly empty space with a concentrated core in the center ...
... • Atoms are distinguished from each other by their number of protons • This determines the different types of elements. • Atoms are mainly empty space with a concentrated core in the center ...
Unit 2 * Symbols say WHAT?!
... Radioactivity- the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus emits charged particles and energy ...
... Radioactivity- the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus emits charged particles and energy ...
Big Science from the Small World of Atom
... electron occupation in the different shells (energy levels) so that the number of core electrons and the valence electrons can be counted. Students will learn how elements are arranged in the periodic table, how the number of valence electrons is correlated with group number in the periodic table. V ...
... electron occupation in the different shells (energy levels) so that the number of core electrons and the valence electrons can be counted. Students will learn how elements are arranged in the periodic table, how the number of valence electrons is correlated with group number in the periodic table. V ...
Chem102_ch03_atoms_and_the_periodic_table
... is called the electronic configuration and determines the chemistry of an atom. The different types of atoms are called elements, which are arranged systematically in the periodic table. Having eight valence electrons is particularly desirable (“the octet rule”). ...
... is called the electronic configuration and determines the chemistry of an atom. The different types of atoms are called elements, which are arranged systematically in the periodic table. Having eight valence electrons is particularly desirable (“the octet rule”). ...
Key Concept Summary - Bellingham High School
... fundamental units of positive charge and have essentially the same mass as He atoms. -particles are negatively charged particles produced by changes occurring within the nuclei of radioactive atoms and have the same properties as electrons. A third form of radiation, that is not affected by an elec ...
... fundamental units of positive charge and have essentially the same mass as He atoms. -particles are negatively charged particles produced by changes occurring within the nuclei of radioactive atoms and have the same properties as electrons. A third form of radiation, that is not affected by an elec ...
Fall 2015 Review-2
... ____ 14. The atomic mass of an element is the ____. a. total number of subatomic particles in its nucleus b. weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of the element c. total mass of the isotopes of the element d. average of the mass number and the atomic number for the element ____ 15. If thre ...
... ____ 14. The atomic mass of an element is the ____. a. total number of subatomic particles in its nucleus b. weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of the element c. total mass of the isotopes of the element d. average of the mass number and the atomic number for the element ____ 15. If thre ...
Atomic Structure Study Guide
... Thomson used an electric current to learn more about atoms. The Experiment: In his experiment, he used a sealed glass tube with most of the air removed from it. There was a metal disk at each end of the tube. Wires connected the metal disk at each end of the tube. Wires connect the metal disks to a ...
... Thomson used an electric current to learn more about atoms. The Experiment: In his experiment, he used a sealed glass tube with most of the air removed from it. There was a metal disk at each end of the tube. Wires connected the metal disk at each end of the tube. Wires connect the metal disks to a ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Molecules
... atoms on the periodic table to any other atom. All we have to do is to chose one to base everything on. At different times we have used different atoms as our key atom that we base the weights on, H one time, Oxygen another. Currently our mass system is based on carbon (more on this later) The term ...
... atoms on the periodic table to any other atom. All we have to do is to chose one to base everything on. At different times we have used different atoms as our key atom that we base the weights on, H one time, Oxygen another. Currently our mass system is based on carbon (more on this later) The term ...
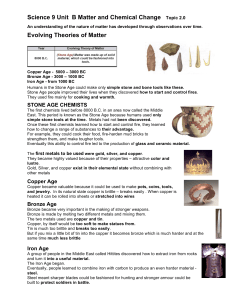
An understanding of the nature of matter has developed
... simple stone tools at the time. Metals had not been discovered. Once these first chemists learned how to start and control fire, they learned how to change a range of substances to their advantage. For example, they could cook their food, fire-harden mud bricks to strengthen them, and make tougher t ...
... simple stone tools at the time. Metals had not been discovered. Once these first chemists learned how to start and control fire, they learned how to change a range of substances to their advantage. For example, they could cook their food, fire-harden mud bricks to strengthen them, and make tougher t ...
CHAPTER 2 The nucleus and radioactive decay - Cin
... (α emission, β emission, or spontaneous fission) if its atomic mass is greater than the sum of the masses of the products formed by that decay mode. This means that nuclei above A>100 are unstable towards spontaneous fission into two nuclei of approximately the same mass and that nuclei above A>140 ...
... (α emission, β emission, or spontaneous fission) if its atomic mass is greater than the sum of the masses of the products formed by that decay mode. This means that nuclei above A>100 are unstable towards spontaneous fission into two nuclei of approximately the same mass and that nuclei above A>140 ...
Section 1A
... These positively charged ions are then acted upon by a 'velocity selector' (an electric field and magnetic field applied perpendicular to the pathway of the ions) which select those ions with the same velocity (though may differ in mass) to enter the circular chamber. ...
... These positively charged ions are then acted upon by a 'velocity selector' (an electric field and magnetic field applied perpendicular to the pathway of the ions) which select those ions with the same velocity (though may differ in mass) to enter the circular chamber. ...
Atomic Mass
... was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. The standard to which the masses of all other atoms are compared to was chosen to be the most abundant isotope of carbon, carbon-12. A mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) was assigned to the carbon12 atom. An amu is defined a ...
... was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. The standard to which the masses of all other atoms are compared to was chosen to be the most abundant isotope of carbon, carbon-12. A mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) was assigned to the carbon12 atom. An amu is defined a ...
IPS Unit 8 – Periodic Table Review Worksheet
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, eleme ...
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, eleme ...
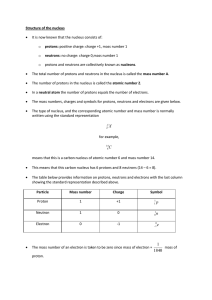
Unit 3 - Structure of the Atom
... Moseley (1913) – discovered each element has a unique positive charge in their nuclei. ...
... Moseley (1913) – discovered each element has a unique positive charge in their nuclei. ...
Chem - Humble ISD
... Atomic structure – protons, neutrons, electrons # protons identifies an atom Isotope – atom with a different number of neutrons Ion – atom that has lost or gained an electron(s) Nuclear reactions involve the nucleus and thus change the ID of an atom Indirect measurement of electrons, aka R ...
... Atomic structure – protons, neutrons, electrons # protons identifies an atom Isotope – atom with a different number of neutrons Ion – atom that has lost or gained an electron(s) Nuclear reactions involve the nucleus and thus change the ID of an atom Indirect measurement of electrons, aka R ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... * Light nuclides are stable when Z equals A-Z, that is, when the neutron/proton ratio is equal to 1. However, for heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. * Certain combinations of protons and neutrons seem to confer special stability. ...
... * Light nuclides are stable when Z equals A-Z, that is, when the neutron/proton ratio is equal to 1. However, for heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. * Certain combinations of protons and neutrons seem to confer special stability. ...
Structure of the Atom Today`s DCI
... The number located below the element’s symbol. No units listed in the periodic table…we must remember the units of the atomic mass are atomic mass units. The symbol for atomic mass units is u. For hydrogen the atomic mass is 1.00797 u. The mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.6736 x 10-24 g. ...
... The number located below the element’s symbol. No units listed in the periodic table…we must remember the units of the atomic mass are atomic mass units. The symbol for atomic mass units is u. For hydrogen the atomic mass is 1.00797 u. The mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.6736 x 10-24 g. ...
Chapter 7 - Bakersfield College
... 2. The atom's electrons, because of their small mass, have little effect on the alpha particles. 3. An atom is mostly empty space. 7-2. Nuclear Structure A. The nucleus of ordinary hydrogen is a single positively charged proton; other nuclei contain electrically neutral neutrons as well as protons. ...
... 2. The atom's electrons, because of their small mass, have little effect on the alpha particles. 3. An atom is mostly empty space. 7-2. Nuclear Structure A. The nucleus of ordinary hydrogen is a single positively charged proton; other nuclei contain electrically neutral neutrons as well as protons. ...
Introducing the Atom - Core Concepts: Periodic Table
... b. What are the odds of getting heads on any flip of a coin? 2. Explain that radioactive decay is measured by half-life. Explain that radioactive isotopes decay by losing half of their radioactive nuclei per each half-life. Ask students: If we begin with 60 radioactive nuclei, how many will remain ...
... b. What are the odds of getting heads on any flip of a coin? 2. Explain that radioactive decay is measured by half-life. Explain that radioactive isotopes decay by losing half of their radioactive nuclei per each half-life. Ask students: If we begin with 60 radioactive nuclei, how many will remain ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.