
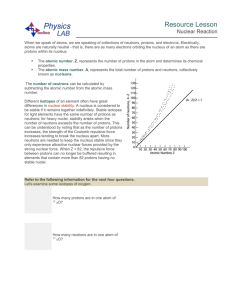
Resource Lesson Nuclear Reaction When we speak of atoms, we
... When we speak of atoms, we are speaking of collections of neutrons, protons, and electrons. Electrically, atoms are naturally neutral - that is, there are as many electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom as there are protons within its nucleus. ...
... When we speak of atoms, we are speaking of collections of neutrons, protons, and electrons. Electrically, atoms are naturally neutral - that is, there are as many electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom as there are protons within its nucleus. ...
p Atomic Structure notes packet 14_15
... In nuclear fission reactions (also called radioactive decay), a neutron is aimed at the nucleus of a large, unstable atom, like uranium, thorium, or other radioactive elements. The extra mass of the neutron causes the radioactive nucleus to split apart, forming lighter elements, free neutrons, and g ...
... In nuclear fission reactions (also called radioactive decay), a neutron is aimed at the nucleus of a large, unstable atom, like uranium, thorium, or other radioactive elements. The extra mass of the neutron causes the radioactive nucleus to split apart, forming lighter elements, free neutrons, and g ...
electrons and the structure of atoms
... element and the relative abundance of its isotopes. a. In nature, most elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes. b. Isotopes of an element do not have a specific natural percent abundance. c. The average atomic mass of an element is usually closest to that of the isotope with the highest ...
... element and the relative abundance of its isotopes. a. In nature, most elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes. b. Isotopes of an element do not have a specific natural percent abundance. c. The average atomic mass of an element is usually closest to that of the isotope with the highest ...
Adventures in Chemistry Julie T. Millard, Colby College
... Electrons in the highest occupied energy level are the greatest stable distance from the nucleus. These outermost electrons are known as valence electrons. Shell is a principal energy level defined by a given value of n, where n can be 1,2,3,4 etc… and is capable of holding 2n2 electrons. An orbital ...
... Electrons in the highest occupied energy level are the greatest stable distance from the nucleus. These outermost electrons are known as valence electrons. Shell is a principal energy level defined by a given value of n, where n can be 1,2,3,4 etc… and is capable of holding 2n2 electrons. An orbital ...
particle - Uplift North Hills
... numbers of protons and neutrons? However, as Z increases the `stability line' curves upwards. Heavier nuclei need more and more neutrons to be stable. Can we explain why? ● It is the strong nuclear force that holds the nucleons together, but this is a very short range force. ● The repulsive electric ...
... numbers of protons and neutrons? However, as Z increases the `stability line' curves upwards. Heavier nuclei need more and more neutrons to be stable. Can we explain why? ● It is the strong nuclear force that holds the nucleons together, but this is a very short range force. ● The repulsive electric ...
The Atom
... - atoms that have the same number of protons but have different numbers of neutrons. Some isotopes are radioactive. Otherwise they are mostly the same as the regular atom. ...
... - atoms that have the same number of protons but have different numbers of neutrons. Some isotopes are radioactive. Otherwise they are mostly the same as the regular atom. ...
Document
... ! identification of elements in the “atmosphere” of stars, discovery of helium. • The energies of K" x-rays can be calculated by replacing Z by Z–1 ! identification of some chemical elements for the first time. • Stimulated emission, the laser. Monday, April 5, 2010 ...
... ! identification of elements in the “atmosphere” of stars, discovery of helium. • The energies of K" x-rays can be calculated by replacing Z by Z–1 ! identification of some chemical elements for the first time. • Stimulated emission, the laser. Monday, April 5, 2010 ...
Alpha Decay Alpha decay can most simply be described like this: 1
... Gamma radiation ( ) is the emission of high energy photons in the range of 10-10 m, with no matter associated with it. Gamma rays are normally the by-products of other alpha or beta emissions. Gamma rays have no effect on either mass or charge, gamma rays only stabilize the nucleus by releasing some ...
... Gamma radiation ( ) is the emission of high energy photons in the range of 10-10 m, with no matter associated with it. Gamma rays are normally the by-products of other alpha or beta emissions. Gamma rays have no effect on either mass or charge, gamma rays only stabilize the nucleus by releasing some ...
chp. 7
... isolated about 10 mg of 226Ra from 8 tons of uranium ore. The half-life of Radium is 25 years. If this sample had been placed in a museum, how much of the radium would remain in the year 2100? ...
... isolated about 10 mg of 226Ra from 8 tons of uranium ore. The half-life of Radium is 25 years. If this sample had been placed in a museum, how much of the radium would remain in the year 2100? ...
Electrons
... charge, relative mass, and location 2. What does atomic number mean? 3. What atom has an atomic number of 32? 4. Determine the number of protons and electrons in a. Ne ...
... charge, relative mass, and location 2. What does atomic number mean? 3. What atom has an atomic number of 32? 4. Determine the number of protons and electrons in a. Ne ...
- Catalyst
... Question 7: Fill in the blanks of the statements below with the words in the box. Note, you will only use each word once. A. atom ...
... Question 7: Fill in the blanks of the statements below with the words in the box. Note, you will only use each word once. A. atom ...
Mass Number, A
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. Elements are made of very small indivisible particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical (all hydrogen atoms are identical). 3. The atoms of an element are different than the atoms of another element (hydrogen is different than helium). 4. Atom ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. Elements are made of very small indivisible particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical (all hydrogen atoms are identical). 3. The atoms of an element are different than the atoms of another element (hydrogen is different than helium). 4. Atom ...
Name
... 3. An isotope is an atom that has the ______________________ as other atoms of the same element do but that has a _______________________ a. example, hydrogen has three isotopes b. some isotopes are more common than others 4. If you know the atomic number and mass number of an atom, you can calculat ...
... 3. An isotope is an atom that has the ______________________ as other atoms of the same element do but that has a _______________________ a. example, hydrogen has three isotopes b. some isotopes are more common than others 4. If you know the atomic number and mass number of an atom, you can calculat ...
02 Atomic Structure [ppt 1MB]
... a substance that is made up of the same kind of atoms is an element I can describe the basic structure of an atom and state the location and charge of the proton, electron and neutron within the atom structure I can state the relative masses of the proton, neutron and electron. I can explain what is ...
... a substance that is made up of the same kind of atoms is an element I can describe the basic structure of an atom and state the location and charge of the proton, electron and neutron within the atom structure I can state the relative masses of the proton, neutron and electron. I can explain what is ...
The Development of Atomic Theory
... Isotopes of an element vary in mass because their numbers of neutrons differ INVESTIGATE: In your book under the heading of isotopes, please find the three most common isotopes of hydrogen and how often they occur in our universe. Describe a radioisotope and what happens to them. ...
... Isotopes of an element vary in mass because their numbers of neutrons differ INVESTIGATE: In your book under the heading of isotopes, please find the three most common isotopes of hydrogen and how often they occur in our universe. Describe a radioisotope and what happens to them. ...
Isotope

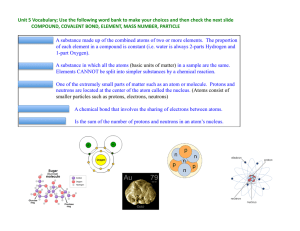
Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.
















![02 Atomic Structure [ppt 1MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000821172_1-5bf1afd152b32026d524139a10b8292f-300x300.png)


