radiation!!! - Mr Schmitt
... When these nuclei lose energy and break apart, decay occurs ▪ Radioactive decay releases energy from the nucleus as radiation ▪ Radioactive atoms release energy until they become stable, often ending up as different atoms ▪ For example: uranium-238 (parent nucleus) decays in several stages until i ...
... When these nuclei lose energy and break apart, decay occurs ▪ Radioactive decay releases energy from the nucleus as radiation ▪ Radioactive atoms release energy until they become stable, often ending up as different atoms ▪ For example: uranium-238 (parent nucleus) decays in several stages until i ...
Hein and Arena - faculty at Chemeketa
... • They always have the same number of protons, but they can have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. • The difference in the number of neutrons accounts for the difference in mass. • These are isotopes of the same element. ...
... • They always have the same number of protons, but they can have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. • The difference in the number of neutrons accounts for the difference in mass. • These are isotopes of the same element. ...
Matter and Measurement
... occur in simple proportions by volume. Moreover, the ratio of the volume of each product gas to the volume of either reacting gas is a ratio of small integers. For example, if the pressure and temperature are kept constant, two volumes of H2 gas reacts with one volume of O2 gas, producing two volume ...
... occur in simple proportions by volume. Moreover, the ratio of the volume of each product gas to the volume of either reacting gas is a ratio of small integers. For example, if the pressure and temperature are kept constant, two volumes of H2 gas reacts with one volume of O2 gas, producing two volume ...
atomic number.
... • Two electrons orbiting a nucleus with: 2 protons = Z = atomic number 2 neutrons = N • Total mass = A = Z+N ...
... • Two electrons orbiting a nucleus with: 2 protons = Z = atomic number 2 neutrons = N • Total mass = A = Z+N ...
Atomic Structure notes
... Late 1700’s - John Dalton- England Teacher- summarized results of his experiments and those of other’s ...
... Late 1700’s - John Dalton- England Teacher- summarized results of his experiments and those of other’s ...
Chapter 4 What are Atoms?
... as Dalton had implied, but that they contained charged particles. The most important individual discovery was that of Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937). Rutherford, who did much of his early research at McGill University in Montreal, showed that most of the atom was empty space. His research indicated t ...
... as Dalton had implied, but that they contained charged particles. The most important individual discovery was that of Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937). Rutherford, who did much of his early research at McGill University in Montreal, showed that most of the atom was empty space. His research indicated t ...
Chapter 3
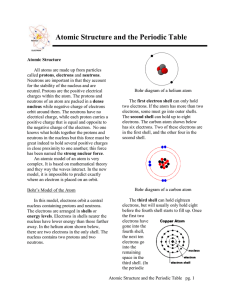
... ▶An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of the element. ▶ Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons have a negative charge. ▶ Protons and neutrons are present in a dense, positively cha ...
... ▶An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of the element. ▶ Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons have a negative charge. ▶ Protons and neutrons are present in a dense, positively cha ...
Chemistry Unit 2 - Finding Patterns
... configuration in the atoms of their elements? How does average atomic mass reflect the relative abundance of the isotopes of an element? How is molar mass related to atomic mass? In what ways does the periodic table organize what we know about the elements? What trends in chemical and physical prope ...
... configuration in the atoms of their elements? How does average atomic mass reflect the relative abundance of the isotopes of an element? How is molar mass related to atomic mass? In what ways does the periodic table organize what we know about the elements? What trends in chemical and physical prope ...
06_Medical equipment based on ionizing radiation principle
... Since we cannot see, smell or taste radiation, we are dependent on instruments to indicate the presence of ionizing radiation. The most common type of instrument is a gas filled radiation detector. This instrument works on the principle that as radiation passes through air or a specific gas, ionizat ...
... Since we cannot see, smell or taste radiation, we are dependent on instruments to indicate the presence of ionizing radiation. The most common type of instrument is a gas filled radiation detector. This instrument works on the principle that as radiation passes through air or a specific gas, ionizat ...
the Atom Regents Review Worksheets with answers.
... 28. A 100.00-gram sample of naturall y occurring boron contains 19.78 grams of boron-10 (atomic mass = 10.01 atomic mass units) an d 80.22 grams of boron- 11 (at omic mass = 11.01 atomic mass units). Which numerical setup can be used to determine t he atomic mass of naturall y occurring boron? A. (0 ...
... 28. A 100.00-gram sample of naturall y occurring boron contains 19.78 grams of boron-10 (atomic mass = 10.01 atomic mass units) an d 80.22 grams of boron- 11 (at omic mass = 11.01 atomic mass units). Which numerical setup can be used to determine t he atomic mass of naturall y occurring boron? A. (0 ...
File
... A) Daltons Theory Of Atomic Mass B) Law of Chemistry C) Symbols of an Element D) Average Mass of an Isotope ...
... A) Daltons Theory Of Atomic Mass B) Law of Chemistry C) Symbols of an Element D) Average Mass of an Isotope ...
1b Atomic Structure
... is the symbol for tungsten). In thinking about the atoms of a particular element, it is useful to have a sense of the atomic mass of a natural sample of this element taken from the earth. A natural sample is a mixture of all the different isotopes of that element. The weighted average, based on abun ...
... is the symbol for tungsten). In thinking about the atoms of a particular element, it is useful to have a sense of the atomic mass of a natural sample of this element taken from the earth. A natural sample is a mixture of all the different isotopes of that element. The weighted average, based on abun ...
Unit 2 - The Atom 1-3.key
... 2. The number of neutrons determines which isotope of a given element you have. ...
... 2. The number of neutrons determines which isotope of a given element you have. ...
Quantitative periodic table – dominoes
... How many times heavier is an arsenic atom compared to a hydrogen atom? ...
... How many times heavier is an arsenic atom compared to a hydrogen atom? ...
Assignment # 6 Atomic Structure Drill
... A CRT is similar to your TV. It has an anode (A Negative electrODE) and a cathode (A positive electrode). These are enclosed in an evacuated (air removed) glass container and when a charge is applied, the electrons flow from anode to cathode through the open space of the glass container. Thomson obs ...
... A CRT is similar to your TV. It has an anode (A Negative electrODE) and a cathode (A positive electrode). These are enclosed in an evacuated (air removed) glass container and when a charge is applied, the electrons flow from anode to cathode through the open space of the glass container. Thomson obs ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.